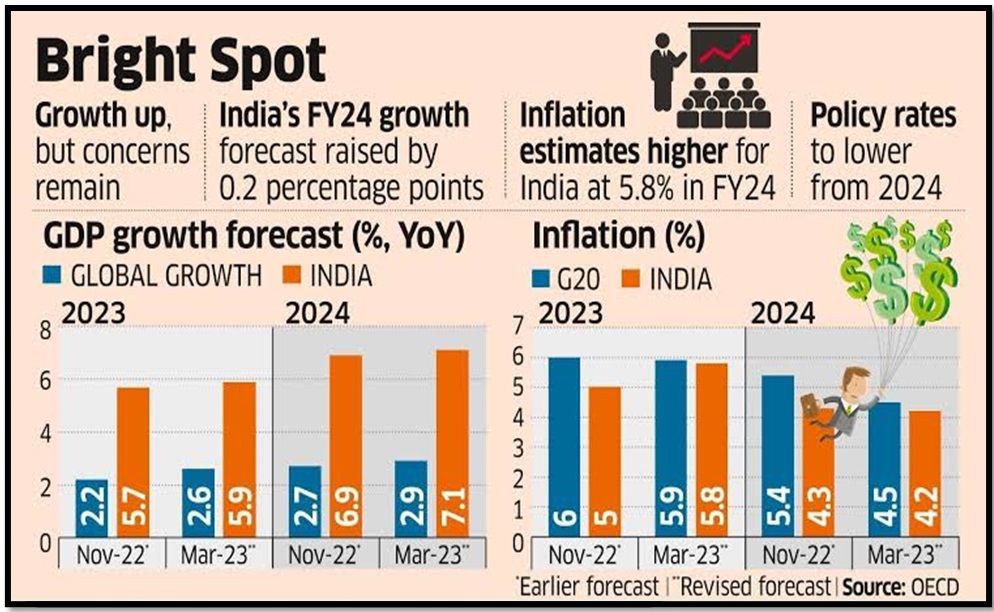
INDIAN ECONOMY: GROWTH AND CONSIDERATIONS
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
- Inclusive Growth and issues arising from it.
Focus:
- The article discusses the current state of the Indian economy, highlighting its
- robust growth, challenges, and the need for sustainable and inclusive development.
- With recent economic data releases showing promising figures, there’s a call for caution and targeted strategies to maintain momentum and address lingering concerns.
Source: IE
Positive Economic Indicators:
- Thrive Continues: Indian economy showcases robust growth, stable inflation, strong FDI inflows, and healthy bank and corporate balance sheets.
- Impressive Q3: The third quarter of 2023-24 witnesses a GDP growth of 8.4%, coupled with a PMI Manufacturing peak at 59.1 in March.
- Credit Health: Credit ratio stands robustly at 192 in H2 of 2023-24, exceeding the 10-year average of 157, signalling the resilience of the corporate and banking sectors.
- FDI Surge: Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows reach a notable $41 billion in 2023-24, elevating India’s forex reserves to around $643 billion.
- Optimistic Outlook: With strong economic indicators, GDP growth is projected to be around 7% in the ongoing financial year.
Growth Insights and Concerns:
- Growth Momentum: India records over 8% growth in the first three quarters of 2023-24, hinting at a potential full-year growth surpassing the estimated 7.6%.
- Investment Driven: The surge in GDP is predominantly led by investment, while consumption growth appears restrained.
- Subdued Consumption: Consumption GDP registers a modest 3% growth this year, compared to the pre-pandemic level of 7% in 2018-19.
- Spending Patterns: Despite spending spikes in sectors like automobiles and housing, lower price-point categories like FMCG and apparel witness cautious consumer spending.
- Rural Recovery: Rural demand displays a promising recovery, with FMCG volume growth improving from 2.2% to 6.2% in the latter half of 2023.
Private Sector Investment and Economic Growth:
- Capital Expenditure: Government maintains its focus on capex, but a rise in private investment is pivotal for sustained growth momentum.
- Diverse Investments: Private sector demonstrates increased investment across sectors including steel, cement, petrochemicals, and renewable energy.
- Capacity Utilization: Manufacturing sector’s capacity utilization stands at 74%, suggesting an impending acceleration in private capex.
- Intent to Invest: CMIE data reveals a growing intent of private sector investment, promising future economic expansion.
- Order Book Surge: The order book of capital goods companies sees a sharp rise in the last fiscal year, further bolstering economic prospects.
Sectoral Performance and External Demand:
- Sectoral Growth: Manufacturing and services sectors predominantly drive India’s economic growth in 2023-24.
- Top Performers: Sectors like hotels, auto components, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals report commendable growth.
- Challenged Sectors: Chemicals, textiles, and polished diamonds face setbacks due to weak external demand.
- Exports Scenario: While merchandise exports grapple with global slowdowns, services exports remain resilient, especially in software and business consulting.
- Current Account Health: Estimated at a benign 0.6-0.7% of GDP for 2023-24, and around 1% for 2024-25, indicating economic stability.
Inflation, FDI Inflows, and Economic Stability:
- Moderating Inflation: CPI inflation is anticipated to moderate to around 4.8% in 2024-25 from an estimated 5.4% in 2023-24.
- FDI Momentum: Strong FDI inflows expected to persist in 2024-25, benefiting from Indian government bond inclusion in global indices.
- Inflation Concerns: Persistent high food inflation, particularly in vegetables (50%), pulses (19%), and spices (14%), remain a challenge.
- Central Bank Actions: RBI may consider a policy interest rate cut in H2 of the fiscal year, contingent on US Fed’s rate decisions.
- Retail Credit Surge: Despite rising interest rates, a substantial rise in retail credit is observed, reflecting changing consumption patterns and credit accessibility.
Retail Credit Growth and Banking Sector:
- Credit Surge: Retail credit growth remains high at around 18%, underscoring the changing consumption and savings patterns.
- Risk Management: RBI enhances banks’ risk weightage for unsecured personal loans to curb excessive personal loan growth.
- Banking Vigilance: Banks need to remain vigilant due to weak deposit growth, posing liquidity risks and pressuring net interest margins.
- Asset Quality: Despite robust credit growth, banks’ asset quality remains healthy, providing a cushion against potential risks.
- Liquidity Concerns: Strong credit growth juxtaposed with weak deposit growth highlights potential liquidity challenges for banks.
Way Forward for the Indian Economy:
Boost Consumer Confidence: Incentivize spending in key sectors to revive consumption-driven growth.
Enhance Rural Economy: Strengthen infrastructure and introduce targeted schemes to maintain rural demand growth.
Foster Private Investment: Simplify regulations and offer fiscal incentives to encourage private sector investments.
Diversify Export Strategy: Reduce dependency on specific sectors and countries to manage global economic fluctuations.
Address Liquidity Concerns: Promote savings, boost deposit growth, and implement effective liquidity management in the banking sector.
Prioritize Inclusive Growth: Adopt policies that reduce income disparities, promote sustainable development, and address environmental concerns.
Digital Push: Structural developments like digitalization and increased formalization have raised India’s potential growth trajectory.
Quality Focus: It’s pivotal for the government to emphasize quality growth and remain cautious of potential economic risks.
Fiscal Responsibility: With a new government soon to take charge, continued focus on fiscal consolidation and debt reduction is crucial.
Conclusion:
The Indian economy is comfortably placed, with an estimated GDP growth of around 7% in the current fiscal year. As a new administration is on the horizon, there should be an amplified focus on promoting inclusive and sustainable economic growth.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the recent economic performance of India, highlighting the growth drivers and challenges. Suggest measures for ensuring sustained and inclusive economic growth in the country.
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/download-types/indian-economy/