“INDIA WAIVES LOCAL TRIALS FOR GLOBALLY APPROVED DRUGS”
Why in the news?
India’s government has waived local clinical trial requirements for drugs approved in the U.S., U.K., Japan, Australia, Canada, and the EU. This aims to enhance drug accessibility and affordability.
About Policy Change for Drug Approvals:
- Waiver of Clinical Trials: The Union government has decided to waive the requirement for clinical trials in India for drugs approved in the U.S., U.K., Japan, Australia, Canada, or the EU.
- Categories for Waiver: The waiver applies to five categories:
- Drugs for rare diseases
- Gene and cellular therapy products
- New drugs used in pandemic situations
- New drugs for special defence purposes
- Drugs with significant therapeutic advances over current treatments.
- Regulatory Framework: The order, issued by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation, modifies Rule 101 of the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules, 2019, allowing for the exemption of local clinical trials based on approvals from specified countries.
Impact on Drug Accessibility:
- Enhanced Access: The policy aims to make drugs manufactured abroad more accessible and affordable in India by streamlining the approval process.
- Pharma Industry Reaction: The Organisation of Pharmaceutical Producers of India (OPPI) has welcomed the move as progressive, highlighting its potential to expedite drug approvals and improve patient access to essential medications.
- Call for Broader Waivers: OPPI advocates for extending waivers to additional therapeutic categories to further enhance access to innovative treatments.
source:slideshare
World Drug Report 2024 Highlights:
Most Used Drugs:
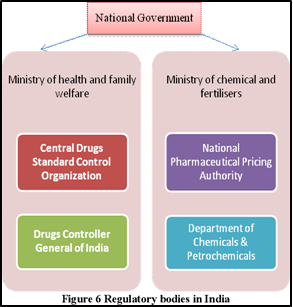
Key Regulation of Drugs in India: Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940:
Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO):
Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI):
Related Government Initiatives: Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Pharmaceuticals:
Promotion of Bulk Drug Parks Scheme:
Strengthening Pharmaceuticals Industry Scheme:
National Medical Devices Policy, 2023:
|