Upcoming arrival of Joe-Biden for G20 summit-India-US Relationship.
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
- Tags: #IndiaUsrelations #IndiaUSPeopleToPeople #IndiaUSTrade.
Why in the News?
United States President Joe Biden will be visiting India to attend the G-20 Summit on September to attend G-20 summit. G-20 Summit is being held under India’s presidency.
The purpose of the G20 is to bring together the major economies of the world to tackle common challenges. “He (Biden) applauded India’s leadership in its ongoing G20 Presidency, which has brought renewed focus on strengthening multilateral institutions and international cooperation to tackle global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, fragility and conflict, along with work to accelerate achievement of the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and lay the foundation for strong, sustainable, balanced, and inclusive growth.”
India – US Relationships
Vibrant Bilateral Relations
- The flourishing Indian economy as a market, the increasing significance of the Indian diaspora in American politics and industry, as well as their shared belief that it is urgent to stop Chinese aggression, are just a few of the elements supporting India and the US’s bilateral relations.
- The alliance between these democratic powerhouses has the potential to redraw the geopolitical chessboard as the US extends its Indo-Pacific engagement and India strengthens its regional dominance.
Key milestones in India-US defense cooperation
- 2005: India and the US sign the New Framework for India-US Defense Cooperation.
- 2016: India is designated as a Major Defense Partner (MDP).
- 2018: India is moved into the Tier-1 of the US Department of Commerce’s Strategic Trade Authorization license exception.
Bilateral Dialogue
2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
- Provides guidance on political, military and strategic issues.
- 4th Dialogue held in April 2022 in Washington DC.
Defense Procurement
- Growing and amount to almost US$20 billion.
- Major US-origin platforms in use include C-130J, C17, Apache, Chinook, MH60R helicopters, P8I.
- Defense procurement activities are monitored through the Defense Production and Procurement Group (DPPG).
Military Exercises
- Malabar Exercise -Biennial naval exercise between India, US, and Japan
- Varuna Exercise – Biennial naval exercise between India and France
- Exercise Gagan Shakti – Annual air exercise between India and the US
Defense Agreements between India and the US
Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA)
- Signed in 2016
- Provides a framework for the two countries to share logistical support, such as fuel, spare parts, and airfields.
Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA)
- Signed in 2018
- Allows the two countries to share sensitive communications and security information.
Industrial Security Agreement (ISA)
- Signed in 2019
- Establishes a framework for the two countries to share sensitive defense-related information with each other’s industries.
Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA)
- Signed in 2020
- Allows the two countries to share geospatial intelligence, such as maps, charts, and satellite imagery.
Memorandum of Intent (MoU) on Defense Innovation Cooperation
- Signed in 2018
- Establishes a framework for the two countries to collaborate on defense innovation projects.
Counter-terrorism cooperation between India and the US
Pillars of cooperation
- Information exchange
- Capacity building
- Operational cooperation
- Regular dialogue
Joint Working Group on Counter-terrorism (JWG)
- Established in 2000
- Meets regularly to discuss ways to enhance counter-terrorism cooperation
- Held its 19th meeting in New Delhi on December 13, 2022
Dialogue on domestic and international terrorist designations listing proposals
- Initiated in 2017
- Aims to enhance cooperation in listing and delisting terrorists
Trade and Economic Relations between India and the US
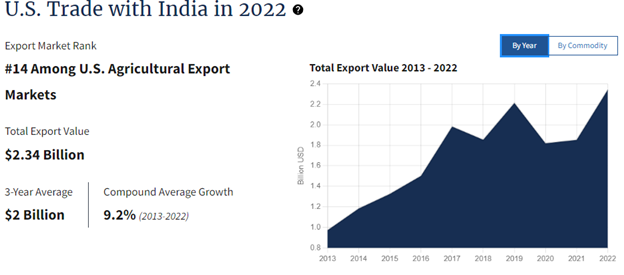
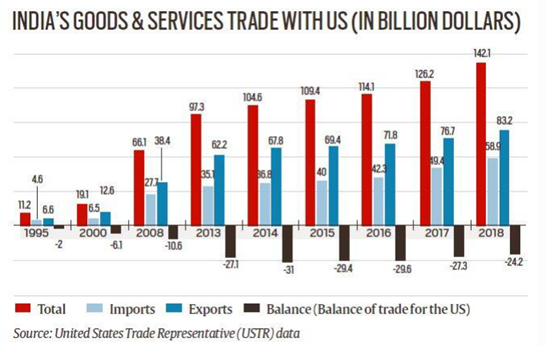
- The US is the largest trading partner of India.
- Bilateral trade in goods and services crossed US$191 billion in 2022.
- Merchandise trade reached US$133 billion and services trade reached around US$58 billion in 2022.
- India received the highest ever FDI of US$81.72 billion in FY2020-21.
- The US was the second largest source of FDI in India during FY2020-21, with inflows of US$13.82 billion.
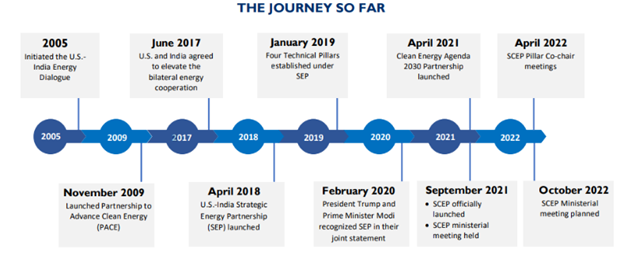
India-US Strategic Energy Partnership
- In April 2021, the two countries launched the “U.S.-India Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 Partnership”.
- The partnership has two tracks: the Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP) and the Climate Action and Finance Mobilization Dialogue (CAFMD).
Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP) Has five pillars
- Power and energy efficiency
- Renewable energy
- Responsible oil and gas
- Sustainable growth
- Emerging fuels and technologies (hydrogen, bio-fuels, and waste to energy)
An Energy Storage Task Force was launched to support large-scale integration of renewable energy needed to support the clean energy transition.
Climate Action and Finance Mobilization Dialogue (CAFMD)
The CAFMD has three pillars
- Climate
- Finance mobilization
- Adaptation and resilience
Bilateral hydrocarbons trade
- The bilateral hydrocarbons trade with the US started in 2017 and amounted to US$19 billion during 2022.
- The US has become India’s 4th largest crude oil and 2nd largest LNG supplier.
International Solar Alliance
- The US joined the International Solar Alliance in November 2021 and ratified the ISA Agreement in September 2022.
- India participates in the Major Economies Forum hosted annually by the US with focus on climate actions.
India-US Space Cooperation
- India and the US have a long history of cooperation in the civil space arena in Earth Observation, Satellite Navigation, Space Science and Exploration.
- ISRO has robust civilian space cooperation with NASA, NOAA, USGS and academic institutions.
- A Joint Working Group on Civil Space Cooperation has been set up, which meets biannually.
Specific projects
NISAR
- ISRO and NASA are developing a microwave remote sensing satellite for Earth observation, NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR).
- NASA/JPL will contribute L-band Radar, while ISRO will contribute S-band Radar.
- The satellite and launch vehicle are to be realized in early 2024.
Chandrayaan-1, MOM, Chandrayaan-2
- ISRO availed NASA/JPL’s Deep Space Network Antenna support for its Chandrayaan-1, Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), Chandrayaan-2 mission, and Chandrayaan-3 satellite.
Scientific Personnel Exchange Programme
- ISRO and NASA successfully implemented Scientific Personnel Exchange Programme in earth observation applications under the framework signed in April 2017.
Commercial front
- ISRO has launched more than 200 satellites from US, onboard Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), as co-passengers.
Initiative for Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET)
- The iCET was launched by the National Security Advisors of India and the US in January 2023.
- It seeks to facilitate strategic technology collaborations in critical and emerging technologies.
- The focus areas of iCET are: AI, quantum, telecom, space, biotech, semiconductors, emerging defence technologies, and biotech.
- The second round of iCET meeting was held in New Delhi in June 2023.
Health Cooperation
- There is a long-standing research collaboration in the health sector to develop new therapeutics and diagnostics.
- The Bilateral Vaccine Action Program (VAP) resulted in the development of ROTAVAC vaccine against rota virus which causes severe diarrhea in children.
- India supplies about 40% of generic formulations marketed in the US.
- The India-US Health Dialogue oversees collaboration in public health.
- India participated in the US-led Global Action Plan (GAP) framework to bridge policy gaps and end the COVID pandemic.
Education Cooperation
Education partnership is an important pillar of India-US ties.
- The USIEF has awarded around 20,000 Fulbright-Nehru and other grants to US and Indian scholars, professionals, and students.
Specific initiatives
21st Century Knowledge Initiative
- Funded university linkages and junior faculty development.
Global Initiative of Academic Networks (GIAN)
- Facilitates visits by 1000 U.S. teachers annually to teach in India.
India-U.S. Working Group on Education and Skill Development (WGESD)
- Focuses on skilling and vocational education, certification and recognition, matchmaking between higher educational institutions and engaging with private sector.
Impact
- Indian students in the US contribute $5.88 billion to the US economy.
Cultural Cooperation
Cultural cooperation between India and the U.S. is rich and manifests in diverse ways.
- Indian Embassy and Consulates organize cultural events to showcase Indian culture.
- Artists and technical experts from both countries undergo training in institutions in the U.S. and India.
- Programs highlighting Indian cultural heritage and initiatives, such as the International Day of Yoga, International Year of Millets, Mission LiFE, and Ayurveda day.
Diaspora/People-to-People Ties
- There are about 4 million Indian Americans/Indian origin people residing in the US.
- Indian Americans are one of the most successful communities and excel in diverse fields, including politics.
- The Indian diaspora has been a catalyst in cementing closer ties between India and the U.S.
Specific examples
- There are many Indian American community organizations and professional organizations of Indian Americans.
- Five persons of Indian origin are in the U.S. Congress.
- Indian Americans have made significant contributions to the US economy, academia, and culture.
India’s Multi-Aligned Foreign Policy
- India’s foreign policy is based on the principle of “multi-alignment”, which means seeking positive ties with as many countries as possible.
- This approach is rooted in the Indian concept of “vasudhaiva kutumbakam”, which means “the world is one family”.
- India has carefully managed its relationships with Saudi Arabia and Iran, Israel and the Palestinian Territories, and the US and Russia.
- India has also reserved the right to engage with countries that are not US allies, such as Russia, Iran, and China, if its national interests dictate such a need.
Benefits
- Multi-alignment allows India to maintain its independence and flexibility in international relations.
- It also helps India to avoid being drawn into conflicts between other countries.
- Multi-alignment has helped India to achieve its foreign policy goals, such as economic development and regional security.
Challenges and Roadblocks in India-US Relations
Economy-related Challenges
- High Trade Barriers: India’s increased import duties and complex customs processes causing friction.
- Mini Trade War: Trade tensions and tit-for-tat tariff hikes affecting several goods
- Data Localisation and E-commerce Policy: US concerns over India’s data localisation and e-commerce regulations impacting digital trade.
- GSP Withdrawal: US revoked preferential trade privileges granted to India, triggering retaliatory tariff hikes.
Political Concerns
- E-commerce and Data Policy: US criticism of India’s data localisation and e-commerce policy as trade-distortive.
- H-1B Visa Restrictions: Indian objection to US limits on H-1B work visas, hindering Indian professionals’ movement.
- Iranian Oil Waivers: US refusal to allow India’s oil imports from Iran, leading to diplomatic tensions.
Defence-related Issues
- Russian Defence Equipment Dependency: India’s purchase of Russian S-400 missiles under CAATSA sanctions causing friction.
Other Contentions
- IPR Enforcement: India’s presence on ‘Priority Watch List’ for Intellectual Property Rights issues.
- Huawei 5G Participation: Differences over India’s reluctance to ban Huawei for 5G trials.
- US Exit from Afghanistan: US withdrawal affecting regional dynamics and straining India-US relationship
As India and the U.S. strengthen their ties, working together on economic matters and democratic initiatives, they need strong cooperation on the global stage. It’s crucial for the partnership to evolve from focusing solely on people-to-people efforts to more practical and action-oriented strategies. Both countries should unite their efforts to tackle growing social, economic, and geopolitical challenges with a shared vision.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Question
Discuss the evolution of India-USA relations over the past few decades. Analyze the key factors that have contributed to the deepening of this strategic partnership?