India – Tanzania Relations
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Bilateral, Regional, and Global Groupings and Agreement involving India and/or affecting India’s Interest.
Why in the News?
- India, and Tanzania to sign 15 agreements with an eye on $10 billion trade. Tanzania and India have shared a long history of strong, friendly, and cooperative relations.
- Their political ties, spanning from the 1960s to the 1980s, were largely influenced by their mutual commitment to anti-colonialism, anti-racism, various forms of socialism, and a shared desire for South-South Cooperation.
- Notably, former President Julius Nyerere held a revered status in India, receiving the Jawaharlal Nehru Award for International Understanding in 1974 and the International Gandhi Peace Prize in 1995.
Throughout this period, India and Tanzania collaborated closely in international forums. However, following the post-Cold War era’s policy adjustments, both nations embarked on economic reform initiatives nearly simultaneously. These reforms aimed at fostering broader engagement on the global political and economic stage, nurturing international business relationships, and encouraging foreign investment.
1st state visit after gap of 8 years
- India and Tanzania are expected to sign 15 agreements during the Tanzanian president’s visit to India.
- The two countries are expected to announce a strategic partnership and increased trade and investment.
- The Tanzanian president will also address a business forum in New Delhi.
- India and Tanzania have also been collaborating to enhance defence cooperation.
- The agreements are expected to cover a wide range of areas, including trade, investment, defence, and security.
- The two countries are also expected to discuss ways to boost maritime connectivity and cooperation in the pharmaceutical and energy sectors.
- The visit is seen as an opportunity to further strengthen the close ties between India and Tanzania.
- The visit is also seen as a way to promote economic growth and regional integration.
- The agreements are expected to benefit both countries and help to deepen their bilateral relations.
Tanzania – an important ally
- Tanzania’s Remarkable Growth: Tanzania stands out as one of the fastest-growing African nations in this decade, assuming a pivotal role in India-Africa relations.
- Strong Historical Ties: The historical backdrop showcases the enduring bond of close, friendly, and cooperative relations between Tanzania and India.
Diplomatic Presence
- Indian Diplomatic Presence: The High Commission of India in Dar es Salaam has been actively operating since November 1961, with the establishment of the Consulate General of India in Zanzibar following in October 1974.
Indian Navy Engagement
- Naval Diplomacy: In October 2019, India’s Navy showcased its global presence by deploying four indigenous ships to the ports at Dar es Salaam and Zanzibar, firmly anchoring relations in Tanzania.
Bilateral Treaties & Agreements
- Joint Trade Committee: In 2000, an agreement was forged to establish a Joint Trade Committee, fostering economic collaboration.
- Agricultural Cooperation: A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) in 2002 set the stage for cooperation in agriculture and allied sectors.
- Educational Exchange: The MOU on Education Cooperation in 2003 promoted educational ties.
- Defense Collaboration: Another significant MOU in 2003 focused on defense cooperation.
- Hydrography and Water Resources: In 2015, an MOU concerning hydrography and hydrographic data exchange was inked, followed by a MOU on water resource management and development in 2016.
- Financial Support: A substantial USD 500 million line of credit was extended in May 2018 by Exim Bank for vital water supply projects in 17 Tanzanian towns.
Commercial and Economic Relations
- Trade Partners: India stands as Tanzania’s largest trading partner, contributing 16% of the nation’s foreign trade.
- Investment Hub: India ranks among the top five sources of investment in Tanzania.
- Major Exports: India exports items such as petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, motor vehicles, electrical goods, iron and steel articles, sugar, and machinery to Tanzania.
- Tanzanian Exports: Notable Tanzanian exports to India include gold ore, cashew nuts, pulses, timber, spices (mainly cloves), ores, gemstones, and metal scrap.
Development Partnership
- Capacity Building: Tanzania benefits significantly from India’s capacity-building initiatives through programs like ITEC/SCAAP and the India Africa Forum Summit (IAFS).
- Project Execution: India has actively executed numerous projects in Tanzania under government grants and soft loans.
- Medical Support: India offered crucial medicines and vaccines to Tanzania as grant support in September 2018 and introduced a radiation therapy machine, ‘Bhabhatron-II,’ for cancer treatment.
- Financial Aid: India has also extended a Credit Line to Tanzania for various water supply projects in regions including Dar-es-Salaam, coastal Chalinze, Tabora, Igunga, and Nzega.
Cultural Engagement
- Cultural Hub: The Indian Cultural Centre (ICC) in Dar es Salaam, operating under the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), fosters cultural outreach since its inception in December 2010.
- Yoga Celebration: Tanzania actively celebrated the 5th International Day of Yoga on June 21, 2019, promoting India’s cultural and wellness heritage.
Indian Community
- Vibrant Diaspora: Tanzania proudly hosts a vibrant Indian-origin community of over 50,000 individuals.
- Economic Contributions: This community actively engages in trade, industry, and service sectors within Tanzania.
- Community Engagement: Initiatives like the Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Award and the ‘Bharat Ko Janiye’ quiz generate interest and participation among the Indian community.
Way Forward
- Historical Cooperation: From the 1960s to the 1980s, India and Tanzania shared a commitment to anti-colonialism, non-alignment, South-South Cooperation, and active collaboration in international forums.
- Modern Partnership: In recent years, India-Tanzania relations have matured into a contemporary and pragmatic partnership, characterized by robust political understanding, diversified economic engagement, people-to-people connections in education and healthcare, and a development partnership focusing on capacity building, concessional credit lines, and grant projects.
- Economic Diversification: Both nations will explore opportunities for expanding and diversifying economic engagement.
- Global Cooperation: India and Tanzania will collaborate on global issues and share common perspectives in international forums.
- Sustainable Growth: Both nations will work together to ensure sustainable economic growth and development.
- Innovation and Technology: Exploring opportunities for technological collaboration and innovation will be a key aspect of the future relationship.
|
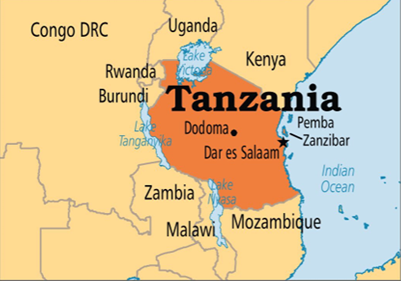
Tanzania 1. Tanzania is located in East Africa, situated within the African Great Lakes region. 2. It shares its borders with neighboring countries: Uganda to the north, Kenya to the northeast, the Comoro Islands, and the Indian Ocean to the east, Mozambique and Malawi to the south, Zambia to the southwest, and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. 3. Africa’s highest mountain, Mount Kilimanjaro, is found in northeastern Tanzania. 4. Tanzania is home to three of Africa’s Great Lakes: – Lake Victoria, Africa’s largest lake, lies to the north and west. – Lake Tanganyika, known for its unique fish species and being the continent’s deepest lake, is in the western part of Tanzania. – To the south, is Lake Malawi. |
Source: The Hindu, Indian Express, Business Standard.
Mains Question
India and Tanzania have a long history of close relations. In recent years, the two countries have signed a number of agreements to strengthen their ties in areas such as trade, investment, defence, and security. Discuss the major areas of cooperation between India and Tanzania, and the significance of these relations for both countries.