India takes up G20 presidency
Why in News? India will assume the Presidency of the G20 for one year from 01 December 2022 to 30 November 2023.
- Under its Presidency, India is expected to host over 200 G20 meetings across the country, beginning in December 2022.
- The G20 Leaders’ Summit at the Heads of State / Government level is scheduled to be held on 09 and 10 September 2023 in New Delhi.
- The 17th G20 Heads of State and Government Summit will happen in November 2022 in Indonesia, after which India will assume the presidency of G20 in December 2022.
What is the G20?
- About:
- The G20 was formed in 1999 in the backdrop of the financial crisis of the late 1990s that hit East Asia and Southeast Asia in particular.
- It aims to secure global financial stability by involving middle-income countries.
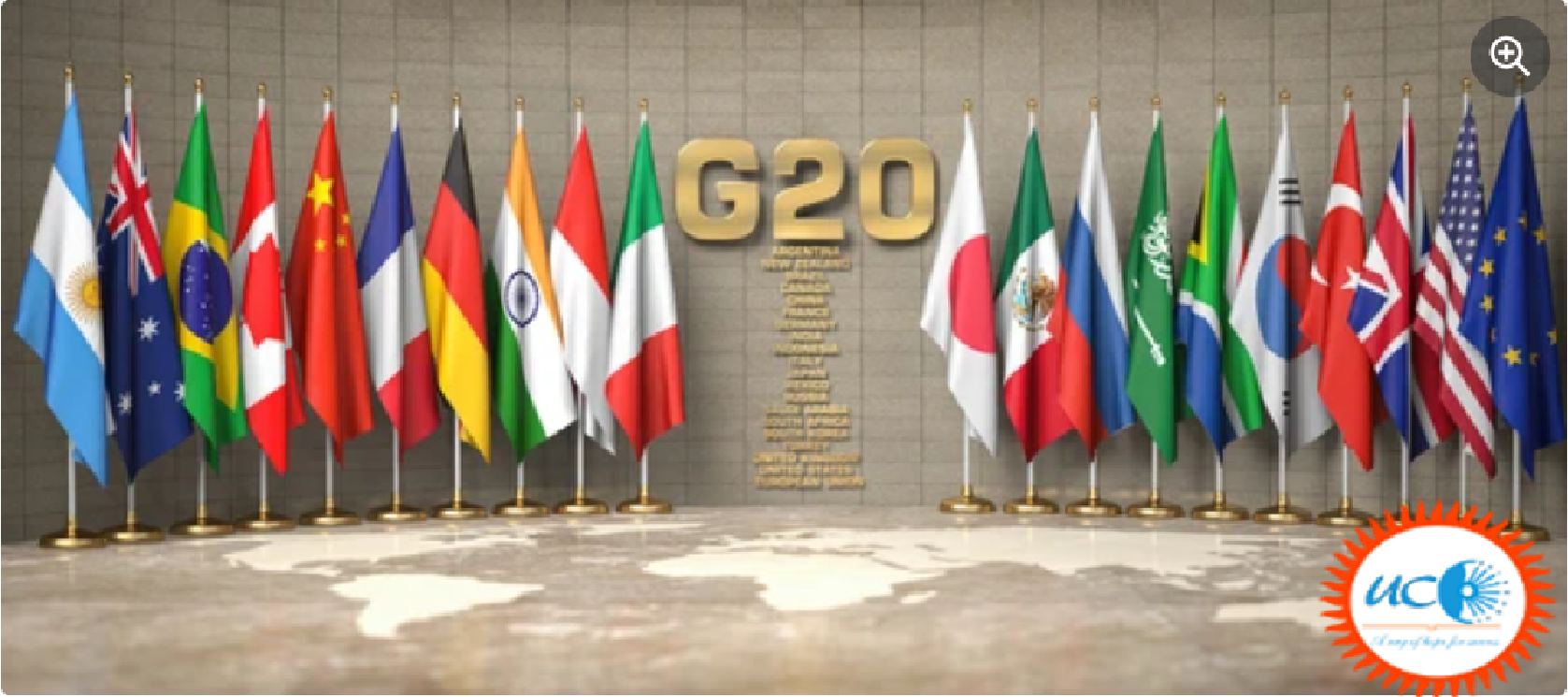
- Together, the G20 countries include 60 % of the world’s population, 80 % of the global GDP, and 75 % of global trade.
- Members:
- Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
- Spain is invited as a permanent guest.
- Guest Countries:
- India, as G20 Presidency, will be inviting Bangladesh, Egypt, Mauritius, Netherlands, Nigeria, Oman, Singapore, Spain and UAE as Guest countries.
- Troika:
- During the Presidency, India, Indonesia and Brazil would form the troika. This would be the first time when the troika would consist of three developing countries and emerging economies, providing them a greater voice.
- Troika refers to the top grouping within the G20 that consists of the current, previous and the upcoming presidencies (Indonesia, India and Brazil).
- Troika refers to the top grouping within the G20 that consists of the current, previous and the upcoming presidencies (Indonesia, India and Brazil).
- Key Priorities:
- Inclusive, Equitable and Sustainable Growth,
- LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment),
- Women’s Empowerment,
- Digital public infrastructure and tech-enabled development in areas ranging from health, agriculture and education to commerce,
- Skill-mapping, culture and tourism, climate financing, circular economy, global food security, energy security, green hydrogen, disaster risk reduction and resilience,
- Developmental cooperation, fight against economic crime, and multilateral reforms.
- During the Presidency, India, Indonesia and Brazil would form the troika. This would be the first time when the troika would consist of three developing countries and emerging economies, providing them a greater voice.
- Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
The G20 currently comprises:
(i) Finance Track, with 8 workstreams (Global Macroeconomic Policies, Infrastructure Financing, International Financial Architecture, Sustainable Finance, Financial Inclusion, Health Finance, International Taxation, and Financial Sector Reforms)
(ii) Sherpa Track, with 12 workstreams (Anti-corruption, Agriculture, Culture, Development, Digital Economy, Employment, Environment and Climate, Education, Energy Transition, Health, Trade and Investment, Tourism)
(iii) 10 Engagement Groups of private sector/civil society/independent bodies (Business 20, Civil 20, Labour 20, Parliament 20, Science 20, Supreme Audit Institutions 20, Think 20, Urban 20, Women 20, and Youth 20).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)