India Invited to G7 Summit 2025: A Historic Engagement Amid Diplomatic Challenges
India Invited to G7 Summit 2025: A Historic Engagement Amid Diplomatic Challenges
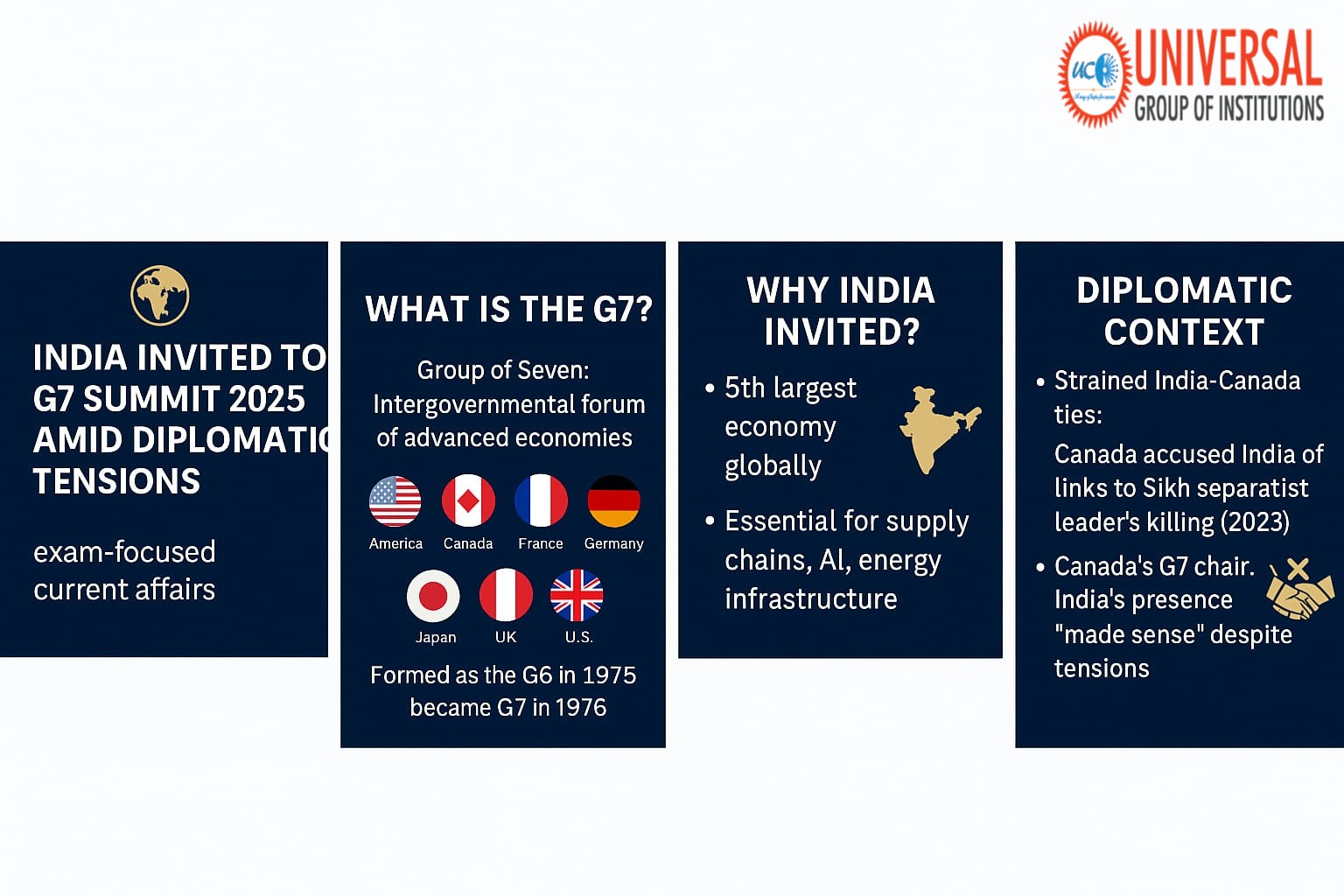
What is G7?
The Group of Seven (G7), the full form of G7, is a powerful intergovernmental forum of the world’s most advanced democracies and economies. It plays a crucial role in addressing global challenges, from climate change and water security to digital governance and peace and conflict resolution. The G7 also focuses on promoting clean and affordable energy solutions worldwide, emphasizing the importance of sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies. For those preparing for G7 UPSC topics, understanding the group’s composition and evolution is essential.
Members: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
The European Union participates as a non-enumerated member.
Evolution: From G6 to G8 and Back
- 1975: Formed as G6 to address global economic crises post the 1973 oil shock. Founding leaders included French President Valéry Giscard d’Estaing and German Chancellor Helmut Schmidt.
- 1976: Canada joined, making it G7.
- 1998: Russia joined, creating the G8.
- 2014: Russia was suspended after its annexation of Crimea, reverting the group to G7.
G7’s Role Over 50 Years
2025 marks the 50th anniversary of the G7, which has played a key role in:
- Global economic coordination and recovery
- Tackling climate change and promoting clean and affordable energy initiatives
- Managing financial crises
- Leading pandemic responses and improving health infrastructure
- Promoting peace, diplomacy, and democratic norms
- Shaping policy on AI regulation, digital governance, and critical minerals
- Addressing energy security and the energy transition
- Fostering multilateralism and geopolitical peace
- Conducting global stocktake on climate action progress
- Addressing nature loss and promoting biodiversity conservation
- Enhancing environmental education and awareness
- Collaborating with the World Bank community on development issues
The G7 has also been instrumental in discussions on fossil fuel subsidies and their impact on climate goals, as well as promoting just transition strategies for affected communities. The forum has increasingly emphasized global solidarity initiatives to address shared challenges, including the impacts of climate change on agriculture and crop growth analysis.
2025 G7 Summit: Key Details
- Host: Canada (Chair: Mark Carney)
- Venue: Kananaskis, Alberta
- Dates: June 15–17, 2025
- Theme: “Navigating Global Transition: Peace, Prosperity, Planet”
This year’s summit is significant not only for its 50-year milestone but also due to changing geopolitical equations and the inclusion of key Global South nations like India. It builds upon discussions from the G7 summit 2024 and G7 summit 2023, focusing on pressing global issues including climate resilience, adaptation finance, and the promotion of clean and affordable energy technologies.
Why India Was Invited
- India is the 5th largest economy globally by nominal GDP, with a significant agricultural sector including important cash crops.
- It plays a vital role in energy security, AI development, digital infrastructure, and clean and affordable energy technology.
- G7 leaders believe India’s presence is essential for inclusive global dialogue and addressing challenges like climate change, water security, and the energy transition.
- India’s participation strengthens the G7’s commitment to multilateralism and global economic recovery.
- India’s environment minister is expected to contribute valuable insights on environmental challenges and solutions, including issues like cement industry land degradation.
India–Canada Tensions: The Diplomatic Backdrop
The India G7 summit invitation comes against the backdrop of India Canada tensions:
- Canada had accused Indian operatives of being linked to the 2023 killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a Canadian Sikh separatist leader.
- This led to strained diplomatic ties, tit-for-tat expulsions, and a pause in bilateral negotiations.
- Despite this, Canadian G7 Chair Mark Carney emphasized that India’s presence is logical and necessary, reinforcing diplomacy over disengagement and promoting peace and conflict resolution.
Domestic Opposition in Canada
- Sikh advocacy groups have condemned the invitation, calling it a betrayal of justice, especially as the summit coincides with the anniversary of Nijjar’s assassination.
- However, Carney clarified that law and diplomacy can co-exist, and invited nations must participate in peaceful global dialogue to address challenges like climate change and energy security.
India’s Strategic Value at G7
- Voice of the Global South on issues like vaccine equity, debt relief, and development finance
- Leader in climate action leadership, through initiatives like the International Solar Alliance and commitment to the Paris Agreement
- Model for digital transformation and digital public infrastructure (e.g., UPI, Aadhaar, ONDC)
- Balancing power in Indo-Pacific diplomacy and multipolar global governance
- Contributor to discussions on renewable energy, clean and affordable energy, and industrial decarbonization
- Participant in dialogues on fossil fuel subsidies and just transition strategies
- Key player in strengthening global supply chains and economic stability
- Advocate for climate resilience and adaptation finance in developing nations
- Promoter of global solidarity initiatives in various sectors
- Contributor to discussions on improving health infrastructure in developing countries
- Expertise in agricultural advancements, including crop growth analysis techniques
India’s role in the G7 discussions is particularly significant given its journey since India’s independence. The country’s experience in addressing challenges such as cement industry land degradation while pursuing economic growth offers valuable insights for other developing nations.
Summary Table for Prelims
Topic |
Details |
|
G7 Formation Year |
1975 (as G6) |
|
Current Members |
Canada, USA, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Japan |
|
G8 Phase |
1998–2014 (with Russia) |
|
2025 Host Country |
Canada |
|
Chairperson |
Mark Carney |
|
Summit Location |
Kananaskis, Alberta |
|
Dates |
June 15–17, 2025 |
|
India’s Global Rank |
5th largest economy (nominal GDP) |
|
Theme |
Peace, Prosperity, Planet (50th Anniversary) |
|
Diplomatic Context |
Nijjar case and India–Canada tensions |
|
Key Focus Areas |
Climate change, energy security, digital governance, AI regulation, water security, nature loss, clean and affordable energy, environmental education |
UPSC Mains Practice Question (GS Paper 2 – IR)
India’s invitation to the 2025 G7 Summit comes amid serious diplomatic tensions with Canada. Evaluate how informal global groupings like G7 can contribute to peace, dialogue, and inclusive global governance while addressing challenges such as climate change, energy transition, and digital transformation. Consider the role of such forums in promoting climate resilience, adaptation finance, and just transition strategies, especially in relation to fossil fuel subsidies and the development of clean and affordable energy sources.
Additional Context:
While the G7 Summit 2025 is a significant event, it’s worth noting that other global forums also play crucial roles in international diplomacy. For instance, the BRICS summit 2024 venue is yet to be announced, but it will likely address similar global challenges from the perspective of emerging economies. The interplay between these different international groupings highlights the complex nature of global governance and the importance of diverse voices in addressing worldwide issues, including those related to agriculture, such as cash crops and crop growth analysis, as well as environmental concerns like cement industry land degradation. This multilateral approach to global challenges has been a hallmark of India’s foreign policy since India’s independence, reflecting the country’s commitment to international cooperation and sustainable development.