INDIA AND U.S. STRENGTHEN DEFENSE TIES WITH NEW AGREEMENTS AND COLLABORATION
Why in the news?
India and the U.S. Have signed two new defence agreements, improving army cooperation and advancing co-production and generation-sharing initiatives.
source:medium
About the new Agreement:
- India and the U.S. Signed two new defence agreements: the Security of Supply Arrangement (SOSA) and a Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) concerning Liaison Officers.
- SOSA makes a speciality of reciprocal assist for defence items and offerings, while the MoA permits Indian officers to be stationed in U.S. Strategic commands.
- These agreements keep a series of bilateral pacts aimed toward deepening defence cooperation, which commenced with the 2002 General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA).
Strategic Initiatives:
- The agreements are part of a broader roadmap for defence commercial cooperation established in
- Priority regions include intelligence-sharing, surveillance, reconnaissance, and co-manufacturing of defence system like jet engines and unmanned aerial motors.
- The INDUS-X initiative, launched in June 2023, targets to construct a defence innovation bridge between the two international locations, fostering collaboration in crucial and rising technology.
About Security of Supply Arrangement (SOSA):
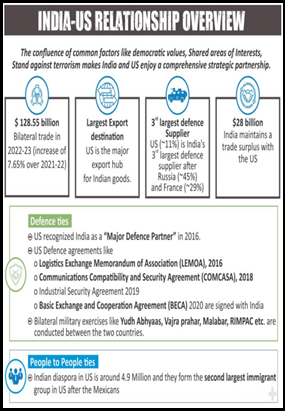
Overview of India-U.S. Bilateral Relations:
|