India and the Northern Sea Route.
Relevance:
GS Paper- 2, International Relations.
Tags: #upsc #northsearoute #arcticregion #geo-economic #northpole #RussianEEZ.
Why in the news?
- Murmansk, popularly called the capital of the Arctic region and the beginning point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is witnessing the rising trend of Indian involvement in cargo traffic.
Significance of the Arctic region to India
- The vulnerability of the Arctic region, which is above the Arctic Circle and includes the Arctic Ocean with the North Pole at its center, to unprecedented changes in the climate may have an impact on India in terms of economic security, water security and sustainability.
- The region also constitutes the largest unexplored prospective area for hydrocarbons remaining on the Earth as it is estimated that the region may hold over 40 per cent of the current global reserves of oil and gas.
- There may also be significant reserves of coal, zinc and silver.
- However, the government’s Arctic Policy of 2022 mentions that the country’s approach to economic development of the region is guided by UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Advantages
Geo-economic benefits
- It can become a global energy superhighway for the transport of various natural resources like hydrocarbons, from the Arctic.
- It can help establish strong supply networks to the Arctic which will ensure the uninterrupted flow of cargo.
- As the NSR is entirely within the Russian EEZ, it can help Russia gain more influence on the global stage.
Economically profitable
- The reduced distance of the route leads to fuel savings and reduced costs for staff labor and chartering vessels.
- The Northern Sea Route does not charge payments for passage, unlike the Suez Canal.
- There are no queues in the NSR like in the Suez Canal. The NSR is also free from piracy which affects the Suez Canal.
Challenges
- The Arctic region is not a hospitable environment and is becoming progressively more unstable as global warming continues.
- The surface temperatures in the region are rising twice as fast as in other regions of the world.
- The stability of the polar vortex is reducing due to the frequent occurrences of extreme cold in Russia and Europe,
- The unusual jetstream patterns are also altering the paths of the northern storms in the region.
- The unpredictable weather conditions impact the working of ships and workers, search-and-rescue resources, and infrastructure.
- The shallow depth of the Laptev Strait restricts the size of ships that can pass through the route.
- The NSR is minimally policed leading to concerns over its use for the transport of illegal goods, weapons, etc.
- The region has become another site of geopolitical contest between Russia and NATO on account of the presence of what is believed to be one-fourth of the world’s untapped petroleum reserves.
History of India’s engagement with the Arctic
- India’s engagement with the Arctic can be traced to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920 in Paris and India is undertaking several scientific studies and research in the Arctic region. This encompasses atmospheric, biological, marine, hydrological and glaciological studies.
- Apart from setting up a research station, Himadri, at, Svalbard, in 2008, the country launched its inaugural multi-sensor moored observatory and northernmost atmospheric laboratory in 2014 and 2016 respectively.
- Till last year, thirteen expeditions to the Arctic were successfully conducted. In May 2013, India became an observer-State of the Arctic Council along with five others including China.
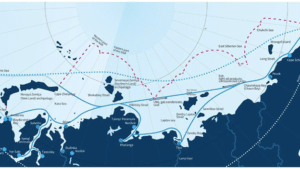
Northern Sea Route
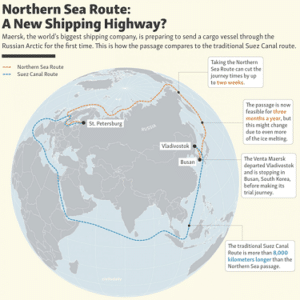
- The Northern Sea Route (NSR), the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles four seas of the Arctic Ocean.
- Running to 5,600 km, the route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
- A paper published states that in theory, distance savings along the NSR can be as high as 50% compared to the currently used shipping lanes via Suez or Panama.
- The 2021 blockage of the Suez Canal, which forms part of the widely-used maritime route involving Europe and Asia, has led to greater attention on the NSR.
How is Russia making the NSR navigable?
- Icebreaking assistance is necessary to ensure safe navigation through the Northern Sea Route, as the seas in the Arctic are ice-bound for most of the year.
- Russia is the only country that possesses a nuclear-powered icebreaker fleet, which is operated by FSUE Atomflot, a subsidiary of Rosatom State Nuclear Energy Corporation which is the NSR infrastructure operator.
- The fleet consists of seven nuclear-powered icebreakers and one nuclear container ship with three more to be commissioned between 2024 and 2027.
- Lenin, the first nuclear-powered icebreaker in the world was commissioned in 1959 and decommissioned in 1989.
What are the driving factors for India to participate in the NSR development?
Rising trade
- The growth in cargo traffic along the NSR was around 73% between 2018 and 2022 and is continuously rising.
- India’s imports of record amounts of oil and coal from Russia in recent years have been made possible by the reliable and safe NSR.
Geographical positioning
- The majority of India’s trade is via the sea route. Therefore, the NSR which is shorter, safer, and thus cheaper than routes such as the Suez Canal is a viable prospect for India.
- Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) project-The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor is directly linked to the organized shipping terminal through the NSR.
- The CVMC, which passes through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea, and the Malacca strait is around 10,500 km long as compared to the currently used Mumbai-St. Petersburg route which is 16,000 km long.
- The CVMC route will reduce the transit time from Russia to India by one-third to 12 days.
Chinese influence
- The strong partnership and alliance between Russia and China could extend to the Arctic region.
- This is a major concern for India due to its geopolitical tensions with China and its reliance on the NSR for cheap, safe, and efficient transport of its exports and imports.
Way forward
- The NSR development plan which was approved by the Russian government in 2022 set a cargo traffic target of 80 million tonnes and 150 million tonnes for 2024 and 2030 respectively.
- In March 2023, a Russian delegation held meetings with the Indian business community on the development of the NSR, and Indian partnerships in the NSR and promised to ensure the year-round operation of the route.
Mains Question:
Discuss the importance of the Northern Sea Route in India’s ambition to be global economic superpower?