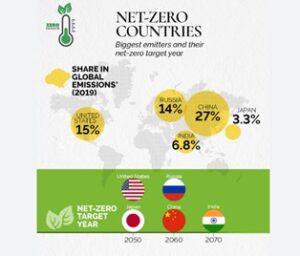
India among five major global economies in race to reach net-zero.
Relevance
- GS Paper 3 Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
- Tags: #netzero #suatainabledevelopment #co2 #India #Life #currentaffairs #upsc.
Why in the News?
The new report, ‘Competing in the new zero-carbon industrial era’ by think tank, Strategic Perspectives show that India is on the right track in the race to zero-carbon technologies.
India’s Advancements in Renewable Energy
- According to a recent report titled ‘Competing in the New Zero-Carbon Industrial Era,’ India has made significant strides in incorporating solar and wind energy into its electricity generation.
- The report highlights that India has nearly doubled its share of renewable energy from 5 percent in 2017 to 9 percent, demonstrating a positive trend towards sustainable energy sources.
India’s Unique Position in the Net-Zero Race
- While India’s initial fiscal capacity may not be on par with leading economies such as the United States, the European Union, China, and Japan, the report emphasizes India’s exceptional ability to position itself favorably in the emerging industrial era centered around achieving net-zero emissions.
- India’s approach to the transition to net-zero policies has bolstered its competitiveness, energy security, and long-term economic prosperity.
Positive Developments in India’s Net-Zero Journey
The report identifies several promising aspects of India’s commitment to net-zero carbon technologies:
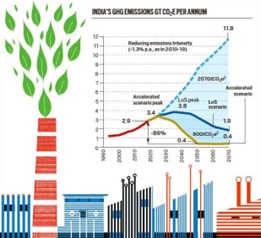
- Meeting Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): India is on track to meet its NDC targets. However, achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 will require substantial investments, estimated at USD 12.7 trillion. India’s robust economic growth, particularly in light of China’s slower post-pandemic recovery, has propelled it to become the world’s fifth-largest economy.
- Rapid Growth in the Electric Vehicle Industry: The electric vehicle industry in India is projected to experience a compound annual growth rate of 49 percent from 2022 to 2030. This growth is expected to create 50 million jobs by 2030.
- Pro-Transition Policies: Policies such as the Energy Conservation Act are incentivizing investors and industries to transition to sustainable practices.
Global Comparisons and Partnerships
- Regarding international financial support, India has been a leading recipient, with a focus on solar energy.
- The report underscores that the United States and India are closely trailing China and the European Union in wind sector manufacturing capacities, potentially gaining market shares through domestic policy implementation.
India’s Aspirations on the Global Stage
- As India assumes the G20 presidency, it aims to push for a global green development agreement encompassing climate finance, LIFE (Low-Income Food-deficit Countries), circular economy initiatives, progress on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), energy transitions, and energy security.
- With a rapidly growing economy, India is poised to maintain its position as the fifth-largest economy in the world, projected to reach USD 3.7 trillion in 2023.
Perspectives on India’s Green Goals
- India’s progress toward green goals is highlighting the scaling of renewable energy, state-level electric vehicle policies, and advancements in energy efficiency.
- There is importance of innovation, research and development, and creating an enabling environment to attract investments and reduce dependence on China.
- India’s need for extensive deployment of renewable energy to decarbonize various sectors, including transportation.
- India’s shift from fossil fuel imports to domestic manufacturing in the renewable energy sector and the importance of technology and financing to meet ambitious 2030 targets is remarkable.
The Global Race to Net-Zero
- There is emergence of a new industrial era driven by zero-carbon technologies. Major economies, including China, the European Union, and the United States, are vying for leadership in this era to secure domestic demand and global market shares.
- Targeted financial support and economic partnerships are crucial to facilitate a just energy transition worldwide.
- Countries falling behind in this transition risk continued dependence on costly fossil fuels.
- Europe, despite its renewable energy progress, should consider turning the European Green Deal into a reindustrialization plan to secure its net-zero transition and create quality jobs.
In conclusion, India’s journey toward net-zero emissions showcases its commitment to sustainable energy and economic growth, positioning it as a key player in the global transition to a zero-carbon future.
| Steps Taken by India to Achieve Net-Zero Emissions by 2070:
Renewable Energy Targets 1. India has progressively increased its renewable energy targets, from 175 GW by 2022 (Paris Agreement) to 450 GW by 2030 (UN Climate Summit), and most recently to 500 GW by 2030 (COP26). 2. The country aims to achieve 50% of its installed power generation capacity from non-fossil energy sources by 2030, up from the previous target of 40%. Goals of NDC (Nationally Determined Contributions) 3. Propagation of sustainable living through a mass movement for ‘LIFE’ (Lifestyle for Environment). 4. Adoption of a cleaner and climate-friendly development path. 5. A 45% reduction in the Emissions Intensity of GDP by 2030 from the 2005 level. 6. About 50% cumulative electric power capacity from non-fossil fuel-based sources by 2030, with support from technology transfer and international finance. 7. Creation of an additional carbon sink through increased forest and tree cover. 8. Enhanced climate change adaptation in vulnerable sectors, mobilization of funds, and technology diffusion. Other Initiatives 1. Extensive solar energy installation initiatives, irrespective of capacity achievement by 2022 or 2030. 2. India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) to reduce cooling demand. 3. Climate change combat efforts by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) and Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL). 4. Utilization of the Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) Fund for reforestation. 5. Launch of a Hydrogen Energy Mission for grey and green hydrogen. |
Sources: Business Standard, ForbesIndia.
Mains Question
“In the context of India’s progress towards net-zero emissions and its global positioning, discuss the key factors influencing India’s competitive edge in the new industrial era, and the challenges it faces in achieving its ambitious sustainability goals. (250 words)”