IMPORTANCE OF BOTH QUAD AND BRICS
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
- Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in the News?
The recent Quad Foreign Ministers’ meeting in Japan, after a 10-month hiatus, highlights significant geopolitical shifts and underscores the importance of multilateral alliances amid global conflicts and rising Chinese influence.
Source: Visual Capitalist
Overview:
- Strategic Timing: The Quad Foreign Ministers’ meeting in Japan, after a 10-month gap, occurs amid UNSC paralysis, violations of international law, and increasing Chinese influence globally.
- Geopolitical Context: The rise of a Russia-China-North Korea-Iran axis and the U.S. seeking credible partners in its security architecture highlight the need for India’s engagement in diverse strategic groupings.
- ASEAN Vulnerability: ASEAN countries face increasing vulnerabilities, with the South China Sea remaining a critical flashpoint, necessitating strong alliances and strategic collaborations.
- S. Strategy: The U.S. realizes it needs both allies and credible partners, including non-ally countries like India, to strengthen its Indo-Pacific security framework.
- Security Objectives: The strategic objectives of the Quad extend beyond military security, focusing on the broader economic and technological architecture of the Indo-Pacific region.
- International Dynamics: The international landscape, marked by conflicts like the Ukraine war and tensions in Gaza, underscores the importance of multilateral groupings for maintaining global stability.
About QUAD
|
India’s Role in the Quad
- Broad Vision: India’s vision for the Quad goes beyond geopolitical security, aiming to redraw the security and techno-economic architecture of the Indo-Pacific region.
- Technological Focus: The Quad’s work on reorienting global supply chains of critical technologies, including digital, telecom, health, power, and semiconductors, aligns with India’s strategic interests.
- Enhanced Relations: India’s involvement in the Quad has strengthened its bilateral relations with partners, especially the U.S., fostering greater cooperation and mutual benefits.
- AUKUS Formation: The formation of AUKUS emphasizes military capabilities and deterrence against China, adding a new dimension to Indo-Pacific security dynamics.
- India’s Reluctance: Despite benefiting from Quad, India’s reluctance to fully embrace a purely security-focused vision highlights its unique strategic perspective and non-treaty ally status.
- Inclusive Approach: India’s independent policy and call for diplomatic solutions, such as in the Ukraine war, reflect its broader approach to international relations, beyond mere military alliances.
Significance of QUAD for India
- Strategic Importance: Provides a platform to address common challenges in the Indo-Pacific, especially the rise and assertiveness of China.
- Economic Benefits: Involves initiatives like the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor, Blue Dot Network, and Supply Chain Resilience Initiative, benefiting India through investments.
- Maritime Security: Enhances Indian maritime security through joint naval exercises and coordination on navigation freedom, piracy, and illegal fishing.
- Regional Stability: Promotes regional stability in the Indo-Pacific based on a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific and a rules-based international order.
- Post-COVID Opportunities: Presents opportunities for India to attract manufacturing shifted out of China by Japan and the US, addressing supply chain disruptions
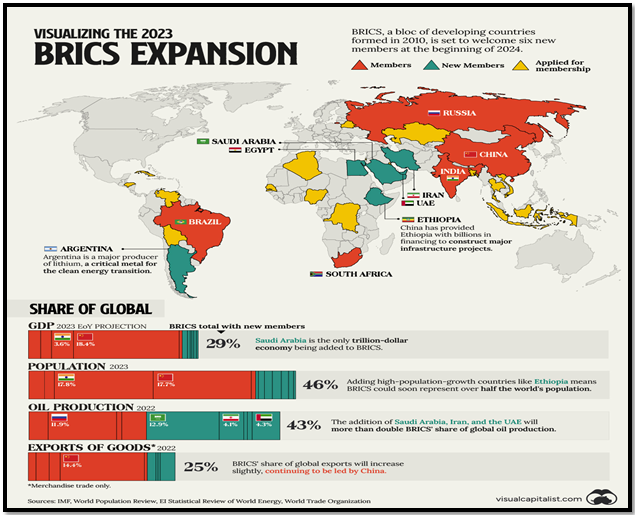
About BRICS
|
India’s Engagement with BRICS
- Founding Member: India was an enthusiastic founder of BRICS, aiming to reform the multilateral system and promoting “reformed multilateralism” at various summits.
- Initiatives and Challenges: While BRICS initiatives like the New Development Bank and the Contingent Reserve Arrangement have been pioneering, China’s dominance within BRICS poses challenges for India.
- Reluctant Expansion: India has been cautious about expanding BRICS, wary of China’s intentions to use the grouping to push its worldview and counter the West.
- Changing Dynamics: The Ukraine war and shifts in global politics have led Russia to align more with China within BRICS, altering the grouping’s dynamics and impacting India’s strategy.
- Balancing Act: India needs to engage more actively within BRICS to counter moves that could undermine its interests, ensuring support for its positions within the group.
- Strategic Importance: As the only country common to both Quad and BRICS, India must balance its engagements, ensuring neither grouping is downplayed in its strategic calculus.
Strategic Implications
- Complementary Engagements: India’s participation in both Quad and BRICS needs to complement each other, leveraging the strengths of both groupings to achieve a balanced strategic outcome.
- Geopolitical Balancing: The strategic dynamics of Quad and BRICS require India to balance its geopolitical approach, addressing challenges from major players like China and Russia while fostering stability.
- Economic and Security Linkages: India’s role in Quad emphasizes techno-economic cooperation, while BRICS focuses on broader geopolitical influence, necessitating a nuanced approach to global economic and security issues.
- Influence in Multilateral Forums: Active engagement in both groupings enhances India’s influence in multilateral forums, allowing it to shape global agendas and address international challenges effectively.
- Strategic Autonomy Maintenance: By participating in both groupings, India maintains its strategic autonomy, avoiding over-reliance on any single bloc and preserving its ability to act independently.
- Regional Stability: India’s involvement in Quad contributes to Indo-Pacific security, while BRICS offers a platform for addressing global South issues, impacting regional and global stability.
- Diplomatic Leverage: India’s dual role provides diplomatic leverage, allowing it to mediate between conflicting interests and advocate for its strategic priorities on the global stage.
- Economic Diversification: Engagement in Quad supports technological and economic diversification, while BRICS initiatives contribute to broader economic collaboration, enhancing India’s global economic positioning.
Way Forward / Recommendations:
- Enhanced Coordination: Strengthen coordination between India’s Quad and BRICS strategies to ensure that actions in one grouping do not undermine objectives in the other.
- Active Diplomacy: Increase diplomatic efforts to influence outcomes within both Quad and BRICS, ensuring that India’s positions are well-represented and supported.
- Strategic Investments: Invest in areas of mutual interest within both groupings, such as technology and infrastructure, to maximize benefits and foster deeper cooperation.
- Unified Messaging: Develop a unified messaging strategy that clearly articulates India’s positions and goals within both Quad and BRICS, avoiding contradictions and enhancing clarity.
- Balanced Engagement: Engage actively in both Quad and BRICS without allowing one to overshadow the other, maintaining a balanced approach to international relations.
- Leverage Economic Opportunities: Utilize opportunities within BRICS for economic collaboration and development, while using Quad to advance technological and strategic initiatives.
- Strengthen Bilateral Relations: Enhance bilateral relations with key members of both groupings to build stronger partnerships and support India’s strategic interests.
- Focus on Multilateral Goals: Emphasize India’s commitment to multilateralism and global cooperation in both groupings, advocating for reforms and initiatives that align with its broader international objectives.
Conclusion
India’s strategic engagements in both Quad and BRICS are crucial for enhancing its global influence. By balancing its roles in these groupings, India can effectively navigate complex geopolitical landscapes, promote stability, and foster economic and technological development.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the significance of India’s participation in both Quad and BRICS in the context of global geopolitical shifts. How can India balance its strategic objectives in these two multilateral groupings to enhance its international standing and influence?
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/india-welcomes-consensus-based-approach-to-expand-brics-pm/