IEA REPORT ON GLOBAL COAL DEMAND DECLINE (2026)
Why in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts a 2.3% decline in global coal demand by 2026, despite record production this year.
Source: Indian Express
India’s Role in Global Coal Demand:
India is expected to be the “driving force” for coal demand until 2026, while China and Europe anticipate a decline due to a shift toward renewable energy.
Regional Disparities in Coal Demand (2023):
- The IEA report forecasts a 1.4% global increase in coal demand in 2023, exceeding 8.5 billion tonnes.
- Notably, demand falls by 20% in the European Union and the United States but rises by 8% in India and 5% in China.
Source: Samjho Learning
Factors Influencing Demand:
- The IEA attributes the expected decline to changing global climate conditions, shifting from El Nino to La Nina, leading to better rainfall by 2024-2026.
- This favours increased hydroelectric power output.
- The expected decrease is attributed to a global shift towards renewable energy sources.
- Factors such as plateauing demand in China contribute to this trend.
Renewable and Nuclear Outlook:
- Increasing deployment of low-cost solar photovoltaics is expected to boost renewable power generation.
- Nuclear generation, especially in China, India, and the European Union, is predicted to experience moderate growth.
Coal’s Importance and Challenges:
- Despite projections of a decline, global coal consumption is expected to remain above 8 billion tonnes through 2026.
- Coal is crucial for electricity generation, steel-making, and cement production, but it is also a significant source of CO2 emissions.
Structural Shifts in Coal Demand:
- The IEA views the decline in coal demand as more structural, propelled by the sustained expansion of clean energy technologies.
- The report emphasizes the need for greater efforts to meet international climate targets and reduce unabated coal use.
Global Production Trends:
China, India, and Indonesia, the top three global coal producers, are expected to break output records in 2023, collectively contributing over 70% of the world’s coal production.

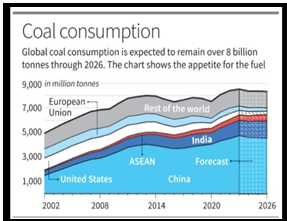 Source: Indian Express
Source: Indian Express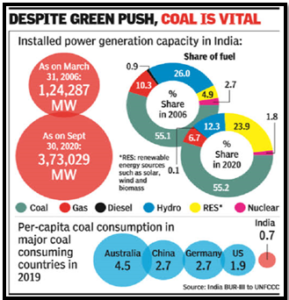 Source: Samjho Learning
Source: Samjho Learning

