Human-touch to India’s Mineral ecosystem
Syllabus
- GS 2: Government policies and interventions
Why in the News?
District Mineral Foundations has demonstrated significant community-based progress in mining-affected areas in India, completing its 10th year under the Prime Minister’s Mineral Sector Welfare Scheme.
Introduction
- District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) is an example of Cooperative Federalism, which transformed India’s mineral wealth into local development.
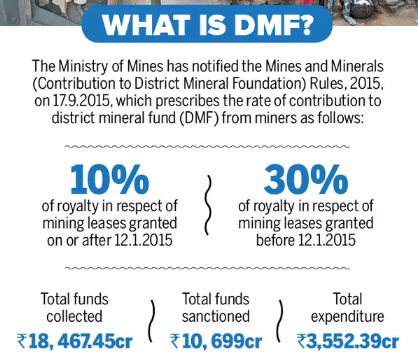
- Launched in 2015 under Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, the DMFs supports community-centric projects, providing the funds to support welfare projects in mine-affected areas.
- This framework balances national priorities with local needs and promotes socio-economic development in mining areas.
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana
- Launch: 2015
Objective
- welfare of people living in mining areas.
- Minimizing environmental health impacts of mining.
- To ensure sustainable livelihoods.
Strategy
- DMFs manage PMKKKKY on a fee basis.
- 30% royalty for leasing old buildings, 10% DMF amount for new leasing.
- Funding ₹6,000 crore annually.
Distribution of funds
- 70% in high priority areas: drinking water, health, education, environment, women’s welfare and so on.
- 30% in other Priority sectors: infrastructure, energy, irrigation and environmental sustainability.
Coal block allocation Exposed
- In 2014, SC exposed coal block allocation flaws, after Comptroller General (CAG) report of 2012.
- The CAG report of 2012 highlighted irregularities in Coal Block allocations between 2004 and 2009, insisting on urgent need for transparency.
Foundation of DMF in 2015
- Parliament amended the Mining and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act in 2015, making auctions mandatory.
- District Mineral Foundation (DMF) established by 2015 Act, to ensure the benefits of royalties reach local communities.
- DMF is supported by Licensees and leaseholders, contributing a part of royalty to DMF, encouraging community as are key player in natural resource-led development.
DMF: Journey so Far
- A decade after its inception, the District Mineral Foundation (DMF) has raised around ₹1 lakh crore.
- The money has been used to spur decentralized, community-focused development in counties affected by mining.
- What started with a huge Treasury loss has become a powerful way to elevate the community.
- Today, DMFs operate in 645 districts in 23 states, resulting in over 3 lakh sanctioned projects under the Prime Minister Mineral Sector Welfare Scheme (PMKKKY).
- These projects aim to reduce the hazardous impact of mining on communities to ensure long-term sustainable livelihoods.
Community Empowerment
- Central to the DMF approach is the belief that communities should be key stakeholders in the development process.
- At the recent DMF Gallery launch in New Delhi, success of Self-Help Groups (SHGs) was evident in Odisha, where women turned artists into entrepreneurs.
- In Katni in Madhya Pradesh, DMFs are empowering youth with drone technology knowledge, many are finding jobs and others preparing for new opportunities.
Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas
- In line with India’s evolving mining scenario, DMFs work with the National Mission on Essential Minerals.
- This initiative focuses on protecting India’s mineral resources and expanding the country’s global footprint, under the auspices of Minerals Abroad India Ltd. (KABIL)
- KABIL along with DMF supports this mission by enhancing the well-being of the communities affected by the minerals.
- ‘Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, Sabka Prayas’ idea is encouraged in partnerships between the state government and the local communities.
Local Administration
- DMF is maintained under the supervision of the District Collector, ensuring that the funds reach the most needed areas.
- The National DMF Portal has played a key role in digitizing the DMF industry, increasing transparency and efficiency.
- DMFs complement regional management efforts, bridging gaps in national priorities and local well-being.
Innovation and strategic planning
Innovation
- Each District Mineral Foundation (DMF) is adopting new strategies to maximize the impact of its projects. Highlights include:
- Inclusion: Some DMFs include elected representatives on their governing body, while others include non-elected gram sabha members.
- This approach ensures diverse representation in decision-making.
- Technical expertise: Many DMFs have developed dedicated technical departments to improve the execution of the project.
- Employees from the state Public Works Department have also been enlisted to ensure smooth implementation of the project.
Planning
- To ensure systematic development, DMFs are three-year programs.
- This shift from a distributed to a well-planned approach is expected to significantly improve the efficiency of projects.
- After studying successful examples, efforts are now focused on harmonizing best practices across DMFs, at the same time respecting local knowledge.
- To ensure continued interoperability, district authorities are encouraged to align DMF activities with existing central and state programs, especially in aspirational districts helping achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- DMFs also support forest dwellers by promoting activities related to the cultivation and processing of medicinal herbs.
Future Plans
- DMFs play a role in recognizing and training rural athletes through sports program development.
- These efforts are in line with the government’s ‘whole of government’ approach, ensuring extensive outreach to affected communities.
Aligning centre-state initiatives
- District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) are an example of Cooperative federalism, aligning national and local priorities.
- By integrating central and state policies, DMFs ensure that infrastructure meets local needs, maximizing the impact of initiatives at all levels of government.
Conclusion
DMFs have become powerful tools for inclusive governance, they are transforming underserved communities and empowering marginalized communities. DMF offers a global model of balancing economic growth and social welfare opportunities.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the impact of District Mineral Foundations to socio-economic development of mining community. Highlight the innovative measures adopted by DMF to encourage sustainable development.