HIDDEN HORMONE BOOSTS MATERNAL BONE HEALTH
Syllabus:
- GS 2: Issues Related to women Health
- GS 3: Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday Life.
Why in the News?
Scientists discovered a brain-derived hormone, CCN3, that boosts bone mass in lactating mothers, offering new treatment possibilities for osteoporosis and skeletal disorders.
Source: Nature Magazine
Introduction
- Scientists discovered a novel brain-derived hormone, CCN3, that strengthens maternal bones during lactation.
- This groundbreaking finding, published in Nature, unveils new treatment possibilities for osteoporosis and highlights the importance of funding female health research.
| National family health survey NFHS-5
Population Control and Fertility
Maternal and Child Health
Nutrition and Obesity
|
Osteoporosis and New Hormonal Insights
Osteoporosis: A Widespread Issue
- Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones, making them brittle.
- Each year, over 10 million people in India are affected, with aging women being more susceptible than men.
Role of Oestrogen
- The hormone oestrogen is vital for bone growth and formation.
- After menopause, decreased ovarian function reduces oestrogen levels, leading to bone mass loss.
Discovery of CCN3
- A recent study in Nature by researchers from the Universities of California, San Francisco, and Davis highlights a new brain-derived hormone, CCN3.
- This hormone is linked to increased bone mass in postpartum lactating mothers.
Impact of Oestrogen Drop During Breastfeeding
Role of Oestrogen
- Oestrogen stimulates bone growth, akin to a manager directing a construction crew.
- During breastfeeding, oestrogen production drops, theoretically weakening bones.
Unexpected Bone Strength
- Despite this drop, mothers’ bones strengthen to meet their babies’ calcium needs, indicating an alternative bone-strengthening mechanism.
CCN3 Hormone Discovery
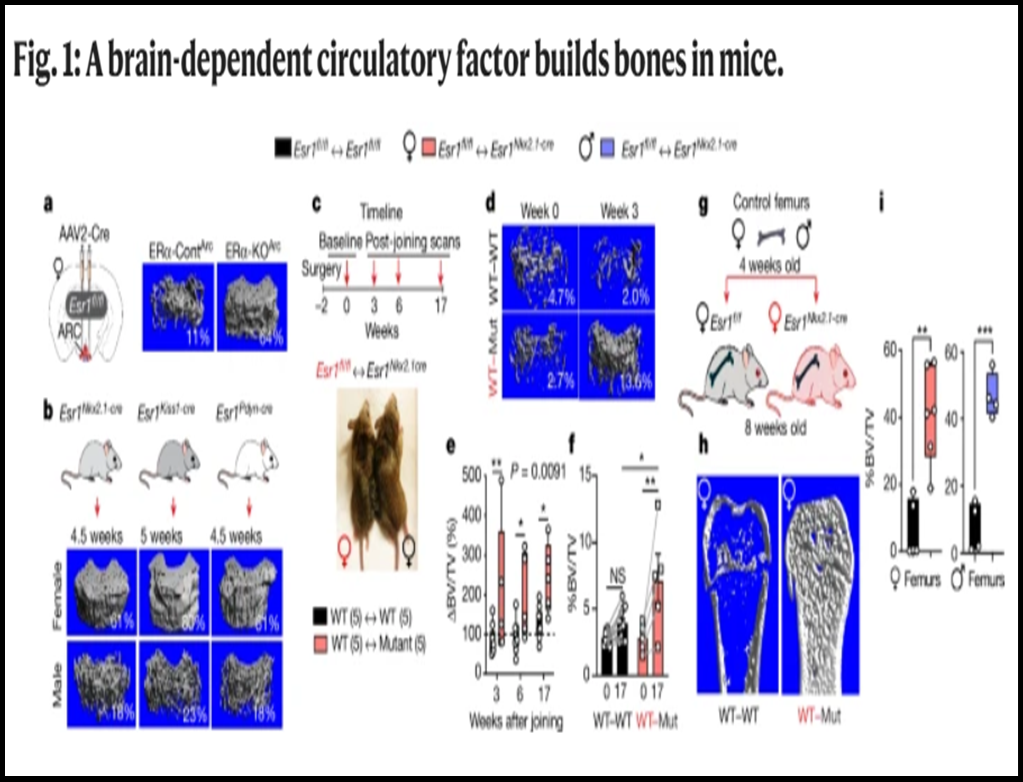
- Researchers at the Universities of California, San Francisco, and Davis found that KISS1 neurons in the hypothalamus use the CCN3 hormone to maintain bone mineralisation during lactation.
Importance of KISS1 Neurons
- Located in the arcuate nucleus (ARC), KISS1 neurons regulate metabolism, reproduction, and bone health, crucial for maintaining bone mass in females.
How Does the Body Balance Bone Formation and Resorption?
Bone Mass Regulation
- The body balances bone mass by coordinating skeletal stem cell-based bone formation with osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.
- Skeletal stem cells build bone tissue, while osteoclasts break it down.
Research Findings
- Researchers isolated skeletal stem cells from wild-type mice and transplanted them into mutant mice, leading to increased bone mineralization in the mutant females.
Brain-Derived Factors
- By delivering these stem cells near the arcuate nucleus (ARC) of mutant mice, mineralized bone-like structures formed in the hypothalamus.
- Such structures did not appear in wild-type mice, suggesting a brain-derived factor promotes bone formation in mutants.
What Drives Bone Changes in Mutant Mice?
Investigating the Factor
- To identify the factor influencing bone changes, researchers placed mutant mice on a high-fat diet, affecting KISS1 neurons and potentially the production of the factor in question.
- As anticipated, this diet caused the mutant mice to lose bone mass.
Gene Analysis
- RNA was extracted from the arcuate nucleus (ARC) of these mice and sequenced.
- Two genes, Ccn3 and Penk, showed earlier upregulation but lost their effects after the high-fat diet.
- Upregulation means a gene is expressed more, producing more of the protein it encodes.
Role of CCN3
- Among these genes, only the hormone CCN3, produced by the Ccn3 gene, was consistently found in all KISS1 neurons in mutant mice.
- CCN3 was notably upregulated in mutant female mice, which lacked oestrogen receptor alpha.
- This suggests a sex-specific regulatory mechanism for bone formation involving CCN3, as it was not found in wild-type females, males, or mutant males.
Impact of CCN3
- CCN3 increased both the frequency and the maturity of skeletal stem cells into bone and cartilage-forming cells.
- This hormone enhanced the ability of these stem cells to build stronger and healthier bones, leading to improved bone health in the mutant female mice.
How Does CCN3 Affect Bone Health and Maternal Well-being?
Contribution to Maternal Health
- Bone Health Maintenance: CCN3 plays a crucial role in maintaining maternal bone mass during lactation, counteracting bone loss due to decreased oestrogen levels.
- Increased Bone Strength: By enhancing bone mineralization, CCN3 ensures that mothers have stronger bones, which is essential for their overall health and recovery.
- Accelerated Repair: CCN3 treatment speeds up bone repair in cases of fractures, which is beneficial for postpartum recovery.
- Balanced Bone Formation: It supports the maturation of skeletal stem cells into bone-forming cells, ensuring continuous bone health.
Decreasing Maternal Mortality Rate in India
- Preventing Osteoporosis: By mitigating bone loss and maintaining bone strength, CCN3 reduces the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures, contributing to lower mortality.
- Healthier Postpartum Recovery: Ensures better overall health and recovery for new mothers, potentially lowering mortality rates.
- Support for Calcium Needs: Improves bone density during lactation, addressing nutritional deficiencies that can lead to severe health issues.
Reducing Child Mortality Rate in India
- Healthier Mothers: Stronger, healthier mothers can provide better care and nourishment, positively impacting infant health.
- Reduced Bone Density Impact: Preventing severe maternal bone loss ensures mothers can better manage their health, indirectly benefiting child health.
- Improved Maternal Health: Healthier mothers are less likely to suffer from complications that could impact infant care and survival.
Conclusion
The discovery of CCN3 highlights the importance of funding female health research and offers new potential for treating hereditary and chronic skeletal disorders, expanding treatment options for osteoporosis.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Analyse how hormonal changes during pregnancy and lactation impact maternal bone density and discuss CCN3’s potential in addressing postpartum osteoporosis in India.
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/study-investigates-heart-diseases-role-in-maternal-mortality/