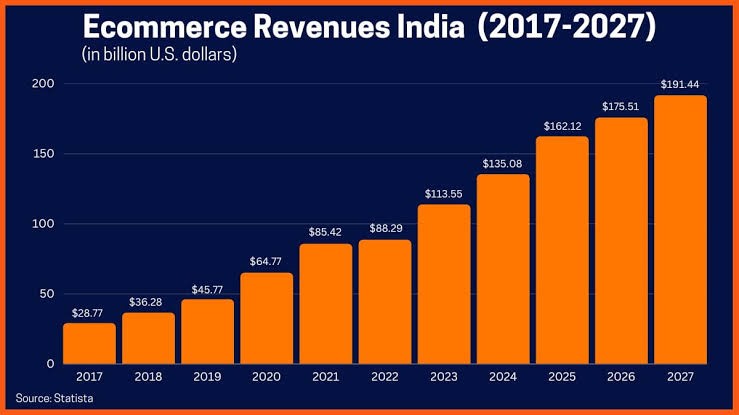
Growth of E-Commerce in India
Syllabus:
GS 3 :
- Effect of liberalization in economy
- E-Commerce and Transitions therein
Why in the News?
A report published by Pahle India Foundation (PIF) and People Research on India’s Consumer Economy (PRICE) has helped in identifying the changes brought by e-commerce in consumer benefits and employment besides affecting the traditional retail sector in India. The study highlights digital adoption issues as well as prospects for policy intervention to ensure inclusive benefits from e-commerce.
Overview and Context:
- Increased Online Engagement: As over 90% of the respondents stated that, they use over an hour a week on the internet and 40% of the surveyed spend over 10 hours.
- Weekly Online Shopping: According to the study 85% of the online users shop on a weekly basis showing yet another sign of the increase of the e-commerce market as a part of the people’s daily life.
- Dependence on E-commerce: An increasing move towards digital platforms revealed that 67% of consumer’s made a purchase in the last 30 days online.
- Diverse Product Range: Some of the needs that e-commerce platforms satisfy include electronics, food necessities, and many others, delivered to clients’ doorstep.
- Urban Adoption: The study highlights the dominance of e-commerce in urban India ,leading to the new era of retailing in India.
Consumer Payment Preferences
- Popularity of Cash on Delivery (COD): Among all the three options, COD remained to be the most popular choice of the respondents as 90% of them still opt for it.
- Rise of UPI Payments: UPI comes right after at 81% and its usage is gradually increasing in the minds of the consumers.
- Limited Use of Cards: Total credit and debit cards expenditures constitute below 10 percent showing that the citizens of the country prefer them very low.
- Trust Issues in Digital Payments: This is due to some of the insecurities people have with other forms of digital payments other than COD & UPI.
- Need for Confidence-Building: Thus, attempts are needed to tilt consumers’ behaviour and make them trust other forms of digital payments apart from UPI.
Consumer Welfare and E-commerce
- Convenience as a Key Driver: Convenience was perceived as the most effective factor improving the consumer welfare through e-commerce.
- Increased Competition: E-commerce offers more choices so there is more competition which inturn benefits consumers with better option.
- Boost in Consumer Confidence: Online platforms offer consumer confidence in finding products and services.
- Challenges in Cost-effectiveness: The criteria of cost-effectiveness ranked lower because the consumers still have problems with the identification of the best prices.
- Grievance Redressal Issues: Consumers still care about solving concerns on e-commerce platforms ,impacting overall satisfaction.
Challenges for Traditional Offline Retailers:
- Low Adoption of E-commerce Platforms: A major challenge to technological adoption is that only 10% of offline retailers list their products on e-commerce channels.
- Digital Literacy Barriers: The small retailers have similar problems or constraints in adopting digital tools, which makes them play a limited role in the e-commerce operations.
- Increased Costs and Competition: Some of the offline sellers noted some challenges such as high costs and competition as factors to pull out from e-commerce.
- Digital Payment Resistance: While 54 % of the offline sellers use digital payments, still 30% are threatened by the usage of technology.
- Need for Digital Access: Measures to help small businesses obtain necessary digital tools are vital to their survival in the context of the digital economy.
Employment and Digital Adoption in E-commerce.
- Job Growth in E-commerce: The sector has witnessed an increase in new management posts by 42% as a result of increase in the complexity of work.
- Expansion of Other Roles: Other positions including marketing, sales, and customer support have also been created , further boosting the competitiveness of e-commerce.
- Workforce Churn: Old school jobs are slowly disappearing and new age jobs more technology inclined are taking their place hence calling for up-skilling in the market.
- Adoption of Digital Tools: Digital marketing is being adopted by 58% of the online sellers use digital marketing while 54% adopt retail management software as a tool to improve operations.
- Positive Impact on Sales: The usage of digital tools causes improved sales by 50% and profit growth by 42%, according to the sellers.
Policy Recommendations and Challenges
- Need for Digital Training: Some initiatives still require policy intercessions by government in order to increase online literacy and in adoption among traditional retailers.
- Financial Incentives for Small Retailers: It’s also important to provide financial backup to these businesses as this can help them in listing their products at any e-commerce site.
- Improving Trust in Digital Payments: Consumer protection laws need to be made stringent and at the same time consumer awareness campaigns should be carried out to minimize the use of COD.
- Addressing the Skills Gap: Future job seekers should embrace education that encourages formation of vocational training particularly on new dimensions relating to e-commerce.
- Enhancing Logistics Infrastructure: To make e-commerce a sustainable business model in India a greater emphasis needs to be placed on delivery and logistics.
Key Initiatives related to E-commerce in India:
- BharatNet project:
- Connect local bodies in every Panchayat through internet which will expand the coverage of e- commerce in rural areas.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC):
- An open network that seeks to enable all Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) to have the necessary chance in digital commerce and e-commerce.
- Digital India initiative:
- The initiative of Digital India has offered some strong support to other government back launched schemes like Start up India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat which has a very good scope to changed into worldwide success.
Way Forward
- Promote Digital Literacy and Training: Provide government supported business training sessions in order to understand and acquire modern tools as well as platforms by the small retailers and traditional businesses.
- Strengthen Consumer Protection Laws: Strengten laws governing digital transactions and conduct advocacy programmes to increase customers’ trust in electronic transactions.
- Financial Incentives for Small Businesses: Financial or other incentives need to be given to small retailers so that they can list their products on e-commerce channels.
- Invest in Vocational Training: Shift attention towards reskilling the workforce with digital skills such as social media management, marketing and analysis among others.
- Enhance Logistics and Infrastructure: Upgrade the delivery and the logistics infrastructure to match the increasing e-commerce environment to afford and deliver improved and efficient services.
Conclusion
The online buying and selling is also increasingly becoming more popular across India and is in the process of transforming the retail sector and employment status in India overall but presents a very big challenge to conventional retailers. By adopting right policies on e-literacy, infrastructure, and consumer protection India can tap the e-commerce potential to empower all classes of people and enable growth.
Source:The Mint
Mains Practice Question
Analyze the influence of e-commerce to the traditional retailers and employment in India. What are the policy actions that are required to ensure that the benefits of e-commerce are fairly spread in the society?