GROWTH OBSESSION: ECONOMIC GROWTH AND INEQUALITY
Syllabus:
GS3 :
- Inclusive Growth and issues arising from it.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
Focus:
- Media outlets extensively cover the annual World Economic Forum, echoing the growth-centric narratives propagated by global leaders.
- Notably, Indian leaders set ambitious economic targets, envisioning the nation as a $10 trillion economy.
- Despite aspirations for economic prosperity, democratic principles advocate for a holistic approach that considers societal well-being beyond mere economic expansion.
Growth and Inequality
- Recent economic growth in India has coincided with a surge in inequality, a trend that dates back to the 1980s.
- The gap between the affluent elite and the marginalized sections of society has widened considerably, positioning India as one of the world’s most unequal societies.
- While economic growth has been robust, its benefits have disproportionately favored the affluent, exacerbating social disparities.
Source: The India Forum
Testaments of Inequality :
- Analysis of rural wage data reveals stark inequality in income distribution.
- Real wage rates for agricultural labour have seen a marginal increase of 4.6% from 2014 to 2022-23.
- Conversely, non-agricultural and construction workers have experienced a decline in real wage rates during the same period.
- A significant portion of the rural workforce continues to grapple with stagnant or declining real wages, highlighting the unequal distribution of economic gains.
Causes of Growth Inequality:
Unemployment-Underemployment:
- Low labour productivity due to unemployment and underemployment exacerbates poverty and inequality.
- Planned economic growth fails to create sufficient employment opportunities, leading to stagnant income levels.
Inflation Effects:
- Inflation disproportionately benefits profit earners while wage earners suffer.
- Real income declines during inflation, diminishing the purchasing power and standard of living of the poor.
Tax Evasion:
- High personal income tax rates incentivize tax evasion, contributing to income and wealth concentration.
- Rampant tax evasion fosters income distribution imbalances, reinforcing inequality.
Regressive Taxation:
- Indirect taxes, the primary revenue source for governments, are regressive in nature, exacerbating inequality over time.
- Dependence on indirect taxes increases income disparities.
New Agrarian Strategy:
- The Green Revolution primarily benefits wealthy farmers and landowners, widening income distribution gaps.
- Landless laborers and marginal farmers face worsening economic conditions despite increased agricultural productivity.
Education Disparity:
- Variations in educational opportunities contribute to income inequality.
- High demand for skilled personnel in certain fields results in higher earnings, while lack of access to education leads to lower incomes.
Gender, Race, and Cultural Factors:
- Gender, racial, and cultural disparities within communities exacerbate economic inequality.
- Ethnic minorities and specific racial groups face higher levels of poverty and economic exclusion.
Source: Business today
Consequences of Growth Inequality:
- Social Conflict:
- Inequality fuels social conflict among different social groups, leading to violent clashes and unrest.
- Ethnic movements and demands for reservations highlight disparities and provoke conflicts among various caste and ethnic groups.
- Marginalization of Minorities:
- Religious, ethnic, and gender disparities marginalize minority groups, hindering their engagement in mainstream society.
- Economic exclusion of religious minorities impacts overall GDP growth.
- Low Development Indices:
- Socioeconomic disparities contribute to low development indices, including infant mortality rate, maternal mortality rate, and poor educational outcomes.
- Public healthcare and education suffer due to economic disparities, affecting lower-income groups disproportionately.
- Constitutional Contravention:
- Growth inequality violates constitutional principles of equality, including status, opportunity, and wealth distribution.
- Regional Disparities:
- Regional imbalances jeopardize cooperative federalism by creating unequal development and opportunities across regions.
- Corporate Influence:
- Excessive corporate influence in policymaking and erosion of workers’ rights exacerbate income inequality.
- Cost-minimization pursuits by corporations widen income gaps, prioritizing shareholder returns over equitable wealth distribution.
- Social Maladies:
- Inequality fosters social maladies like violence and mental health disorders, deepening societal divisions.
- Disparities in income and opportunity hinder collective action for public goods provision, hindering progress in areas like sanitation and environmental conservation.
- Undermining Democracy:
- Economic inequality undermines democratic principles by perpetuating disparities and limiting socio-economic mobility.
- Limited opportunities for advancement diminish prospects for inclusive societal growth and development.
Way Forward:
- Skill Development:
- Invest in skill development to capitalize on the demographic dividend and reduce inequality.
- Transition to a skill-led economy to create more opportunities for youth.
- Progressive Taxation:
- Implement progressive taxation policies targeting the wealthy and luxury goods to reduce income disparities.
- Allocate tax revenue to fund public programs aimed at lessening inequality.
- Equal Opportunity:
- Establish mechanisms for equal opportunity in employment and entrepreneurship.
- Provide scholarships and stipends to enable access to education for economically disadvantaged individuals.
- Promote Labour-Intensive Manufacturing:
- Encourage labour-intensive industries such as construction, textiles, and footwear to absorb unemployed individuals.
- Boost manufacturing sectors to create employment opportunities and reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth:
- Promote and implement an inclusive growth agenda to address growing inequality.
- Focus on human development indicators like healthcare, education, and social safety nets to minimize disparities.
- Addressing Wealth Concentration:
- Consider introducing inheritance tax targeting the super-rich to mitigate wealth concentration and promote more equitable distribution of resources.
- Encouraging Private Sector Investment:
- Improve the business environment and enact pro-enterprise policies to attract private sector investment, stimulating economic growth and creating opportunities for all segments of society.
- Investment in Human Development:
- Invest in healthcare, education, and social safety nets to minimize inequality.
- Increase government investment in research and development (R&D) and innovation to spur economic growth and reduce disparities.
A more inclusive approach to development is essential for building a resilient and prosperous nation that upholds the values of democracy and social justice.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/growth-mania-can-be-injurious-to-society/article67790032.ece
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the relationship between economic growth and inequality in India.

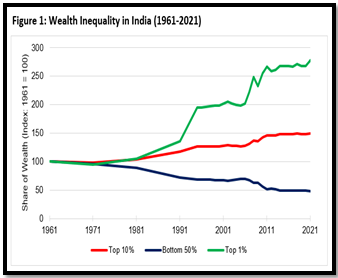 Source: The India Forum
Source: The India Forum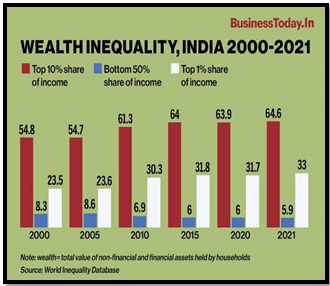 Source: Business today
Source: Business today

