GLOSSING OVER UNEMPLOYMENT
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Inclusive Growth and issues arising from it.
- Effects of Liberalization on the Economy.
Focus:
India’s unemployment crisis and rising inequality, questioning the effectiveness of economic policies and highlighting the need for comprehensive reforms to address these critical issues.
Source: AlJazeera
The Current Unemployment Scenario
- Job generation: The Indian economy requires over 25 million jobs in the next five years to employ the currently unemployed.
- Growth claim: The Narendra Modi government claimed an 8.9% GDP growth last year, but job creation has not kept pace with this growth.
- Unemployment rate: Official statistics show a drop in unemployment from 4.2% in 2021 to 3.1% in 2023, which is not in line with the rapid GDP growth rate.
- Electoral impact: The 2024 general election results reflect the Bharatiya Janata Party’s (BJP) electoral setback due to unemployment issues, leading to a coalition government.
- Economic disparity: The coalition includes parties with contrary economic ideologies, highlighting the political cost of unemployment.
Inequality Gap is Widening
- Widening gap: The gap between the wealthy and the poor has widened significantly over the last two decades.
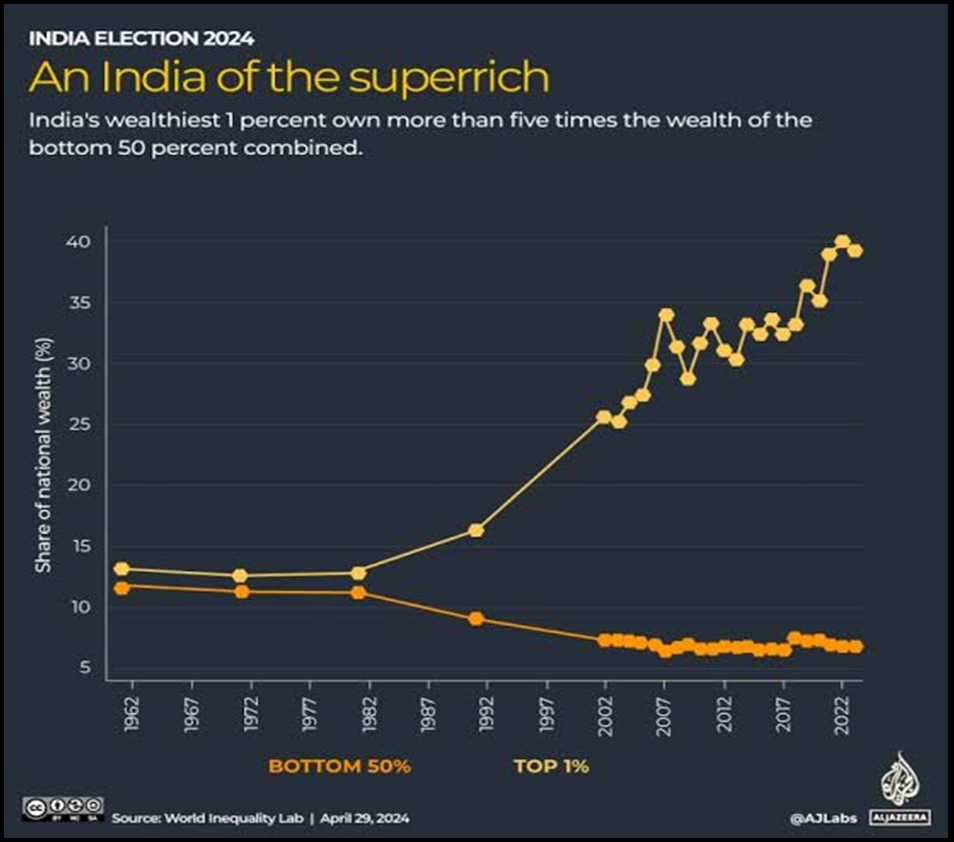
- Wealth inequality: Under BJP rule, official statistics show a sharp rise in wealth inequality, with 1% of India’s population owning 10% of the country’s wealth.
- K-shaped inequality: This K-shaped inequality indicates rising consumption/income for a few and decreasing for a large proportion of the less affluent population.
- Government claims: Prime Minister Modi claims that 25 crore people were lifted out of poverty due to GDP growth, but this remains to be seen in the next three years.
- Electoral skepticism: The recent election results challenge the government’s claims of being the fastest-growing large economy, as evidenced by the decline in BJP’s parliamentary strength.
Causes of Increasing Inequality Despite High Economic Growth in India
Concentration of Wealth: Wealth concentration in the hands of a few perpetuates inequality across generations, as advantages are passed down to descendants.
- Land Reform Failures: Inadequate land reforms leave a significant portion of the population landless or with insufficient land, increasing vulnerability to poverty.
- Crony Capitalism: Corruption and favoritism result in wealth accumulation among a select group, deepening economic inequality.
- Uneven Economic Gains: Economic growth often disproportionately benefits certain sectors or income groups, leading to uneven wealth distribution.
- Regressive Taxation: Tax systems that favor the wealthy or lack progressivity contribute to income inequality.
- Inadequate Social Safety Nets: Insufficient social safety nets and welfare programs leave vulnerable populations without necessary support, widening the wealth gap.
- Financialization Focus: Emphasis on financial markets and speculation over productive investments concentrates wealth in the financial sector.
- Wage Gaps: Significant wage disparities between skilled and unskilled workers, along with informal labor markets offering lower wages and fewer benefits, widen income inequality.
- Educational Inequality: Unequal access to quality education restricts upward mobility, reinforcing existing disparities.
- Automation Impact: Automation and technological advancements displace jobs and stagnate wages for certain groups, exacerbating income inequality.
- Skill Mismatch: Rapid technological changes create a mismatch between available skills and job requirements, widening the income gap.
- Digital Divide: Limited access to digital tools and resources prevents marginalized communities from benefiting from technological progress, deepening economic disparities.
The Need for Economic Overhaul
- Overhaul needed: The BJP government’s economic management needs significant changes to address unemployment and inequality.
- Cabinet appointments: Recent cabinet appointments do not inspire confidence in a potential economic overhaul.
- Growth claims: The government claims an 8.2% GDP growth in 2023-24, but the calculation methods have not been disclosed.
- Budget deficit: Growth in the last two years has been driven by a large budget deficit for capital expenditure, not structural investments.
- Sustainability doubts: The 8.2% growth in 2023-24 appears unsustainable, with expectations of further decline in 2024-25.
| Government Initiatives
Tackling Unemployment:
Addressing Income Inequality
|
Need for a New Strategy:
- Call for reforms: Government economists have called for next-generation reforms to accelerate national economic growth.
- Parliamentary challenge: With the BJP losing its majority in Parliament, implementing these reforms will be challenging.
- Agriculture sector: In agriculture, 92% of jobs are in the unorganized sector, highlighting the need for a strategic overhaul.
- Industry and services: In industry and services, 73% of jobs are in small- and medium-informal sectors, with only 27% in formal sectors.
- Long-term strategy: India needs a new long-term economic strategy, but the current political scenario and lack of cohesive majority make this difficult.
Moving Forward
- Electoral price: The high electoral price paid by the BJP underscores the urgency of addressing unemployment and inequality.
- Economic priorities: Future economic policies must prioritize job creation and reducing the inequality gap.
- Coalition dynamics: The coalition government must navigate differing economic ideologies to formulate effective policies.
- Public trust: Rebuilding public trust in economic management is crucial for political stability and electoral success.
- Sustainable growth: Ensuring sustainable economic growth requires structural reforms and inclusive policies that benefit all sections of society.
- Youth employment: Creating targeted programs for youth employment can harness the demographic dividend and reduce unemployment rates.
- Skill development: Investing in skill development and vocational training can equip the workforce for emerging industries and technological advancements.
- Inclusive policies: Implementing inclusive economic policies that address regional disparities and marginalized communities can promote balanced growth and social cohesion.
Conclusion:
India’s economic future hinges on addressing unemployment and inequality. The recent electoral results underscore the need for inclusive policies and structural reforms to ensure sustainable growth, public trust, and balanced development, positioning India as a resilient and equitable economy.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the current unemployment scenario in India and its socio-economic implications. Analyze the impact of rising inequality on political stability and suggest comprehensive strategies to address these issues in the context of the recent electoral outcomes.
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/analyzing-income-inequality-in-india/