GET A PPPIECE OF INNOVATION ACTION
Relevance: GS 3 – Growth & Development, Infrastructure, Investment Models, Mobilization of Resources
Why in the News?
- India maintains its 40th position out of 132 economies in the Global Innovation Index, as per the World Intellectual Property Organization’s report.
- Over the past few years, India has demonstrated a consistent upward trend in the Global Innovation Index rankings moving from 81st place in 2015 to its current ranking of 40 in 2023.
R&D EXPENDITURES
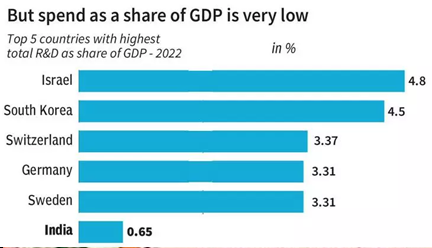
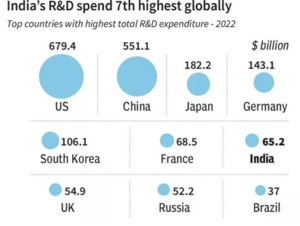
- R&D expenditures in India have plateaued at approximately 6% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), indicating a lack of significant growth in investment in this critical sector.
- There is a recognized need to boost public sector spending on R&D to stimulate innovation and technological advancement within the country.
- It is frequently argued that the private sector should play a more active role in R&D investment to complement public sector efforts and drive innovation further.
- MNCs Leveraging India Potential: Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are increasingly utilizing India as a hub for innovation, recognizing the country’s potential in fostering technological advancements and breakthroughs.
- Despite MNCs’ involvement, the overall output of India’s innovation ecosystem falls short of expectations, highlighting underlying challenges that hinder its full potential.
- Local enterprises express concerns over the limited availability of well-trained R&D professionals, underscoring the need for a skilled workforce to drive innovation within the country.
Experiments in Innovation Financing
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF): The modalities of the newly established ANRF, which commenced operations on Monday, lack clarity, creating uncertainty regarding its functioning and objectives.
- ₹1 Lakh Crore Corpus for Research and Innovation: The interim budget announced a significant corpus of ₹1 lakh crore for research and innovation;
- However, details regarding its allocation and utilization remain ambiguous, raising questions about its effectiveness in fostering innovation.
- Underutilization of Publicly Supported Industry Consortia: Despite the introduction of various initiatives, publicly supported industry consortia are reported to be underutilized, indicating a gap between policy intent and practical implementation in leveraging these consortia for innovation.
Advantages of Strategic PPPs
- Attracting Private Investments
- Strategic PPPs offer an avenue to attract private investments by leveraging the strengths of both sectors.
- Private entities are encouraged to invest in R&D projects through collaborative efforts with the government.
- Leapfrogging Local Capacity
- PPPs facilitate the leapfrogging of local capacity to innovate by pooling resources and expertise from both public and private sectors.
- Through strategic partnerships, India can tap into advanced technologies and practices that may not be readily available domestically.
Critical Elements for Efficacy
- Clarity of Strategic Intent
- The success of PPPs in India hinges on the clarity of strategic intent, ensuring alignment with national development goals and objectives.
- Clear delineation of roles, responsibilities, and objectives is essential for effective implementation and outcomes.
- Presence of Critical Elements
- Financing: Ensuring adequate financial resources are allocated and managed effectively to sustain PPP initiatives.
- Operational: Establishing robust operational frameworks to streamline processes and optimize resource utilization.
- Governance: Implementing transparent governance structures to facilitate decision-making and mitigate potential conflicts of interest.
- Evaluation: Incorporating robust evaluation mechanisms to assess the impact and effectiveness of PPP initiatives over time.
Functionality of PPPs in R&D
- Formal Relationship and Decision-Making: By co-investing scarce resources such as funding, personnel, infrastructure, and knowledge, PPPs strive to achieve specific science, technology and innovation (STI)
- Combining Complementary Capabilities: Leveraging each sector’s strengths enhances the overall effectiveness and efficiency of R&D endeavors.
- Addressing Market and Government Failures: PPPs serve as a mechanism to address market and government failures, particularly by reducing technological and regulatory uncertainties.
- Collaborative R&D activities under PPPs help mitigate risks and facilitate the development and adoption of innovative solutions.
- Diffusion of Best Practices and Spillovers: Joint R&D activities foster the diffusion of best practices and knowledge sharing between public and private partners.
- By encouraging spillovers, PPPs contribute to broader societal benefits and the advancement of science and technology.
TECHNIQUES OF PPPs IMPLEMENTATION
Consultative Process for Area Identification:
- Leveraging a consultative process to identify focus areas ensures stakeholder input and alignment with national priorities.
- Emphasizing pre-competitive projects with lower collaboration barriers enhances feasibility and encourages broader participation.
Trust Building and Transparent Structuring:
- Paramount importance is placed on building trust among partners through transparent structuring of PPPs.
- Transparent frameworks foster confidence and facilitate effective collaboration among stakeholders.
Financing Dynamics:
- Strategic STI PPPs are typically financed equally by government, academia, and industry.
- Initially, the Government of India may lead financing efforts to incentivize private participation, while ensuring long-term sustainability without crowding out private investments.
Tiered Membership Structure:
- Implementing a tiered membership structure with additional incentives for Indian firms promotes participation from both large and small enterprises.
- Such a structure encourages diversity in participation and fosters a conducive environment for innovation.
Duration and Agility:
- Recommending initial partnerships to operate for less than three years to ensure agility and trust-building.
- Success in short-term partnerships paves the way for longer-term collaborations to serve national missions effectively.
Operational Management:
- Operations of PPPs should be led by individuals possessing appropriate knowledge and expertise.
- Openness to international participation enhances competitiveness and facilitates the creation of a skilled workforce.
Inclusion of MNC R&D Centers:
- Advocating for the participation of MNC R&D centers based in India to capitalize on potential knowledge spillovers.
- Mitigating regulatory hurdles enables broader participation and enriches the innovation ecosystem.
WAY FORWARD FOR SUCCESS OF PPP PROJECTS
Determining PPP Nature:
- Nature of activities and infrastructure requirements dictate whether PPPs should operate virtually or otherwise.
- Flexible contractual arrangements and transparent mechanisms for sharing and transferring IP minimize potential disputes.
Critical Governance Framework:
- Strong governance framework is imperative to navigate the inherent tension between public goals and private interests in PPPs.
- Leadership must reconcile this tension and ensure well-defined distributional mechanisms to treat stakeholders’ interests fairly.
Autonomous Operation and Orchestration:
- GoI should focus on orchestrating PPPs and allow them to run autonomously.
- This approach ensures effective partnerships while maintaining government oversight.
Adaptability and Regular Evaluations:
- Leveraging adaptability of PPPs requires regular evaluations to facilitate necessary structural and operational changes.
- Continuous evolution ensures alignment with evolving goals and objectives.
Embracing Moonshots and Special Support:
- India should heed Vikram Sarabhai’s recommendation by providing special support for task-oriented development projects in areas with deficiencies.
- Prior political decision-making ensures strategic alignment and effective resource allocation.
Positioning Strategic PPPs:
- While not a panacea, strategic PPPs can significantly improve the competitiveness of the Indian innovation ecosystem.
- Leveraging these partnerships effectively can drive transformative change and foster innovation-led growth.
Mains question
Discuss the role of strategic Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) in enhancing India’s innovation ecosystem and governance adaptability. (250 marks)