General Provident Fund: Key Retirement Savings for Government Employees
Why in the news?
The General Provident Fund (GPF) highlights its benefits, flexibility, and role in ensuring financial security for government employees, as its features are being revisited for enhanced awareness.
About General Provident Fund (GPF):
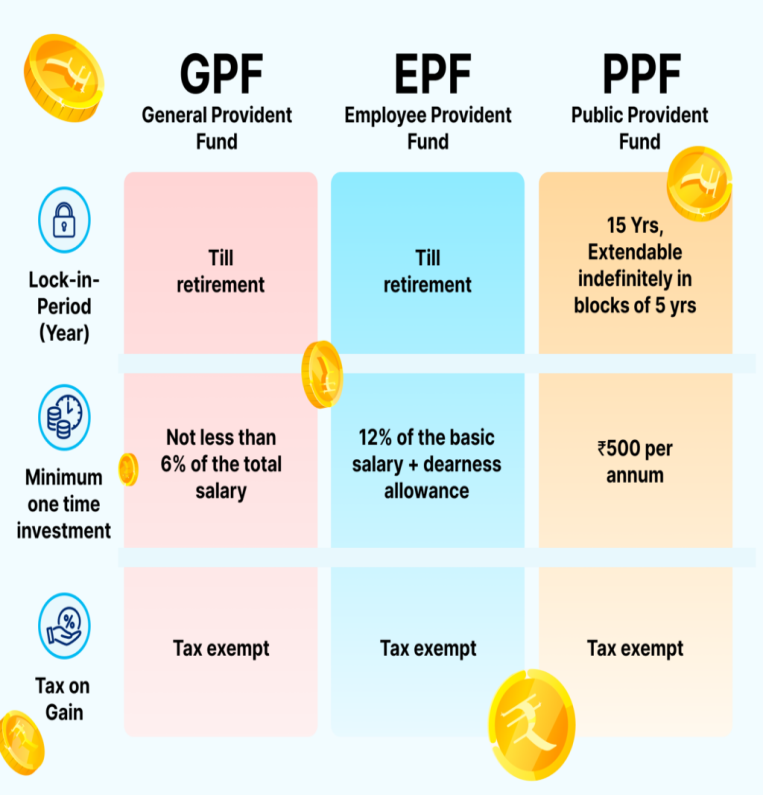
- The General Provident Fund (GPF) is a retirement savings scheme launched in 1960 exclusively for government employees in India.
- It facilitates savings by deducting a fixed percentage of the employee’s salary during their service period.
- Unlike the Employees Provident Fund (EPF), contributions to GPF are made solely by the employee.
Eligibility and Contribution Details:
- Eligibility:
- Permanent government employees.
- Temporary staff with at least one year of continuous service.
- Re-employed pensioners (excluding those under contributory provident funds).
- Contribution:
- Minimum: 6% of the employee’s salary.
- Maximum: 100% of the employee’s salary.
- Contributions are deducted monthly and earn interest, revised periodically by the government.
Features and Benefits
- Withdrawal Flexibility:
- Withdrawals allowed for specific purposes, such as marriage, education, or medical emergencies.
- Loan Facility:
- Employees can avail loans against their GPF balance under defined conditions.
- Settlement on Exit:
- Full balance, including accrued interest, is paid out upon retirement, resignation, or transfer to another department.
- Dependable Post-Retirement Income:
- Acts as a secure source of financial stability after retirement.
Employee Pension Scheme (EPS): Key Points
- Provides pension for organised sector employees post-retirement (from age 58).
- Requires a minimum of 10 years of continuous service.
- Under EPF, 8.33% of the employer’s 12% contribution is allocated to EPS.
- Employee’s entire 12% share goes to the EPF fund.
Different Pension Schemes in India:
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS)
- Applicable to government employees appointed before January 1, 2004.
- Offers 50% of last drawn salary + DA as assured pension.
- Entire pension amount borne by the government; fixed GPF returns guaranteed.
- National Pension System (NPS)
- Introduced in 2004; mandatory for post-2004 central government recruits.
- Defined contribution scheme; 10% employee contribution with matching government contribution.
- Pension depends on investment and contribution factors.
- Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)
- Applicable from April 2025 for post-2004 NPS retirees.
- Assured pension blending OPS and NPS benefits.
- Funded contributory scheme with voluntary state adoption option.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times