GENDER EQUALITY AS THE PLANK OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Relevance:
- GS 1 – Role of women and women’s organization
- GS 2 – Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes
- GS 3 – Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Why in the News?
- Women’s pivotal role in energy access, production, and consumption is hindered by barriers. These barriers restrict women’s participation and impact in the energy sector.
- Despite their significant contribution, women face obstacles that impede their full involvement in the energy industry.
- Addressing these barriers is crucial to enhance women’s participation and impact in the energy sector.
Gender Equality and Sustainable Energy Development
- The critical intersection between gender equality and sustainable energy development is often overlooked.
- Studies consistently highlight the fundamental importance of gender equality and women’s empowerment in achieving sustainable energy for all.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Gender equality and women’s empowerment are integral to achieving all Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- SDG5 on gender equality, SDG7 on clean, affordable energy, and SDG12 on climate action demonstrate strong interconnections.
- The achievement of SDGs is reliant on addressing gender equality as a core component.
- Significance of Gender Equality
- Gender equality serves as a prerequisite for sustainable development, beyond being a matter of social justice.
- Women’s pivotal role in energy access, production, and consumption underscores the importance of addressing gender disparities.
- Significant barriers often impede women’s participation and impact in the energy sector, affecting individual opportunities and hindering overall economic growth and environmental sustainability.
Women’s Role in Household Energy Management
- Women often bear primary responsibility for managing household energy, including cooking, heating, and lighting.
- However, energy infrastructure tends to reach women last, leading to disparities in access to modern energy sources.
- Lack of access to clean and reliable energy forces women to rely on traditional and harmful alternatives like biomass and kerosene.
Disproportionate Impact on Women and Children
- The lack of access to modern energy disproportionately affects women and children.
- World Health Organization (WHO) reports indicate that household air pollution is responsible for an alarming 3.2 million premature deaths annually, constituting nearly half of all air pollution-related deaths.
- Notably, 60% of these fatalities affect women and children.
- This perpetuates energy poverty and exposes families to health risks associated with household air pollution.
Gender Disparity in the Energy Sector
- The energy sector remains one of the least gender-diverse sectors globally.
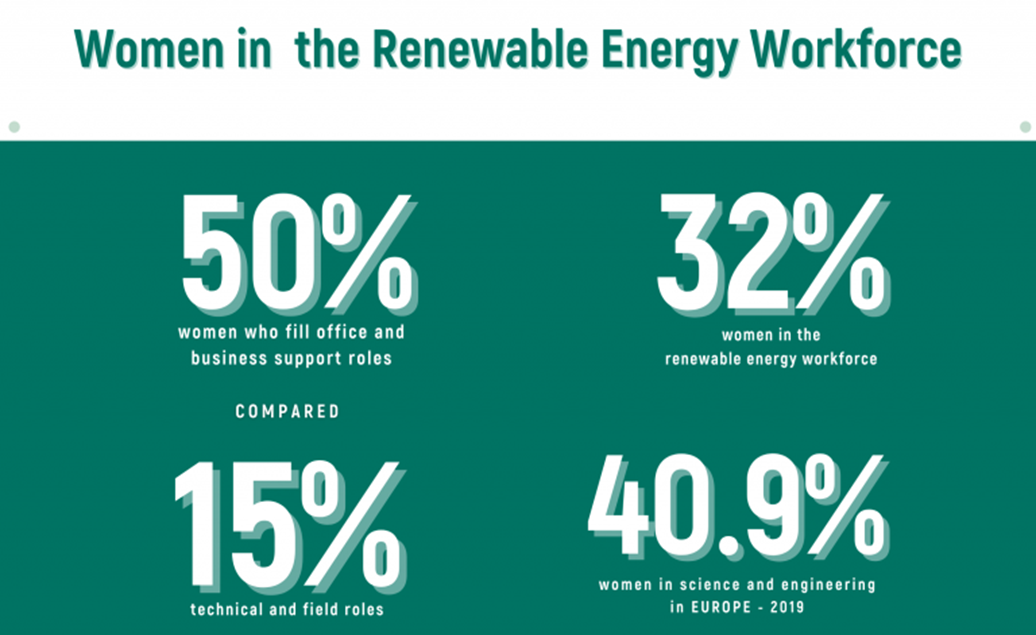
- Women represent only 32% of full-time employees in the renewable energy sector and 22% in the energy sector overall, compared to 48% in the global labor force.
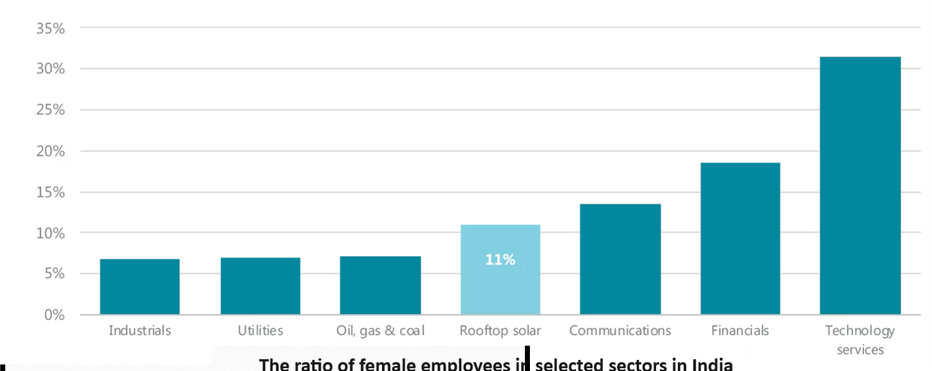
- As per the International Energy Agency (IEA), In India, a mere 10% of women hold technical posts in the energy sector, highlighting significant gender disparities.
Contributing Factors to Gender Disparity
- Disparities in educational access, limited opportunities for women to acquire technical skills and training, and inequitable company policies contribute to gender disparities in the energy sector.
- These factors hinder women’s participation and advancement within the industry, perpetuating gender inequality.
Perception Change and Gender Mainstreaming in Energy Policies
Addressing challenges in the energy sector requires a shift in perception regarding women’s roles. Efforts must focus on integrating gender considerations into energy policies at sub-national, national, and international levels.
Roles of Various Stakeholders:
- Governments, non-state actors, international institutions, and philanthropic organizations have pivotal roles.
- They should create enabling environments, offer innovative solutions, and establish transformative platforms to enhance women’s participation in the sustainable energy transition.
Opportunities in Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE)
- Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) presents an opportunity to quickly provide affordable energy access and alleviate women’s daily burdens.
- State governments in India, in collaboration with philanthropic organizations, are deploying DRE solutions to empower women and increase productivity.
Initiatives Promoting Women’s Participation
- Programs like the Women at the Forefront initiative and the Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge (ENTICE) provide platforms for individuals, particularly women, to engage in entrepreneurial ventures and drive collective action for sustainable energy practices.
- The Solar Mamas initiative by Barefoot College in India trains illiterate women to become solar engineers, bringing clean power and light to their communities and inspiring similar initiatives globally.
Empowering Women in the Energy Sector
- Empowering women in the energy sector is not just morally right but also a strategic investment in our collective future.
- Studies indicate that closing the gender gap in employment and entrepreneurship could significantly boost global GDP.
Benefits of Women’s Participation in Energy
- Increased participation of women in the energy sector leads to more innovative solutions, higher productivity, and improved social and environmental outcomes.
- A recent report by Powering Livelihoods reveals that over 71% of early adopters of clean technology livelihood appliances in India, totaling over 16,000, are women.
Changing Dialogue on Gender and Energy:
- The dialogue on gender and energy has shifted from viewing women as vulnerable groups to recognizing them as key agents of change.
- Women are acknowledged as consumers, producers, distributors, and decision-makers across the energy sector.
- Gender-responsive and women-led initiatives in the clean energy space have proven successful.
Harnessing the Power of Women and Energy:
- Now is the opportune moment to leverage the power of women and energy to build a more inclusive, prosperous, and sustainable world for current and future generations.
Mains question
Discuss the significance of empowering women in the energy sector for sustainable development and economic growth. Provide examples and analyze their impact. (250 words)