Gaza Strip: Complex Challenges Persist
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
- Tags: #GazaStrip #Israel #Hamas #Palestine #IndiaIsraelrelations #UPSCMains.
Why in the News?
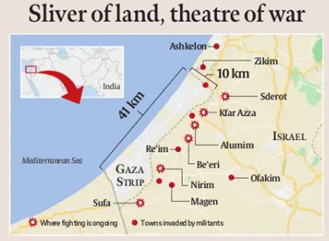
The Gaza Strip experienced its deadliest day in 15 years as a result of an unprecedented attack by Hamas into Israel, leading to nearly 300 Palestinian casualties in 24 hours, as reported by Palestinian officials.
What is the Gaza Strip?
- The Gaza Strip is a Palestinian territory situated along the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Israel and Egypt.
- It covers 363 square kilometers and is home to approximately 2.3 million people, making it one of the world’s most densely populated regions.
Significance of Gaza
- Gaza holds historical and cultural significance for both Palestinians and Israelis.
- It is part of the lands associated with the Jewish kingdom in the Hebrew Bible.
- Gaza and the West Bank together constitute the State of Palestine, with India being one of the first countries to recognize it in 1988.
Conditions in Gaza
Gaza faces challenges including rapid population growth, inadequate services, high unemployment, and Israeli sanctions.
- Economic Activities: Agriculture, light industry, and handicrafts are key economic activities. Many Palestinians work in Israel but cannot stay overnight.
- Unemployment: Gaza’s unemployment rate was 4% in the second quarter of 2023, primarily due to Israeli restrictions.
- Densely Populated Urban Areas: Gaza City is more densely populated than major global cities like Tel Aviv, London, and Shanghai.
- Limited access to basic necessities affects the overall quality of life for residents.
- Dependency on Israel: Gaza heavily relies on Israel for crucial resources, including water, electricity, and food.
- Most of Gaza’s imports, including food, consumer goods, and construction materials, come from Israel and Egypt, its primary trade partners.
- Electricity Dependency: Gaza receives the majority of its electricity from Israel, with one aging power plant in operation.
- Water Crisis: Gaza faces a water crisis, with groundwater sources contaminated by pollution and saltwater intrusion. Over 90% of the water in Gaza’s sole aquifer is no longer safe to drink.
History of Conflict in Gaza
Ottoman Era (1516-1917)
- Gaza was part of the Ottoman Empire for centuries.
- In World War I, British forces captured Gaza from the Ottomans in 1917.
British Mandate (1917-1948)
- Gaza fell under British rule as part of the League of Nations mandate for Palestine.
- Tensions between Jewish immigrants and Palestinian Arabs began to escalate.
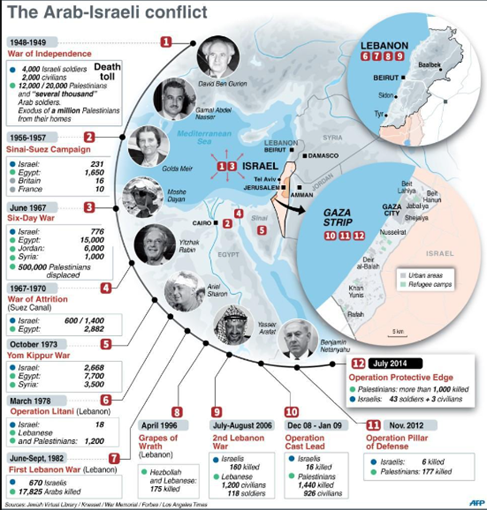
1948 Arab-Israeli War
- The 1948 war, following Israel’s declaration of statehood, led to the first Arab-Israeli conflict.
- Gaza came under Egyptian control, setting the stage for decades of conflict.
1967 Six-Day War
- Israel captured Gaza from Egypt, along with the West Bank and other territories.
- The occupation of Gaza by Israel began.
Intifada
- Intifada is an Arabic word that means “shaking off” or “uprising.”
- It is used to refer to two Palestinian uprisings against Israeli occupation.
- First from 1987 to 1993 and the second from 2000 to 2005.
First Intifada (1987-1993)
- Palestinian resistance to Israeli occupation in Gaza and the West Bank.
- The Oslo Accords in 1993 led to the Palestinian National Authority’s formation,set the stage for limited self-rule in Gaza.
Second Intifada (2000-2005)
- Renewed violence and conflict in Gaza and the West Bank.
- Israel’s unilateral disengagement plan in 2005 led to its withdrawal from Gaza.
Hamas Takes Control (2007)
- In 2007, Hamas, considered a terrorist group by Israel and the West, seized control of Gaza.
- This led to a political and territorial division between Gaza and the West Bank.
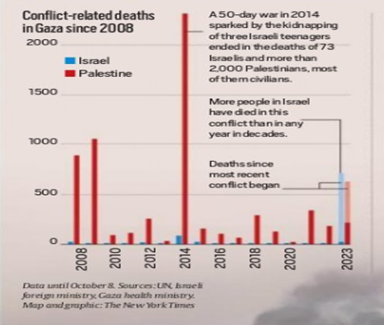
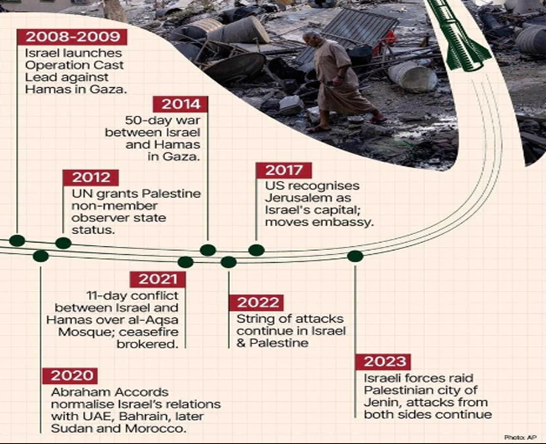
Gaza Wars (2008-2021)
- Multiple conflicts between Israel and Gaza, including Operation Cast Lead (2008-2009), Operation Pillar of Defense (2012), and Operation Protective Edge (2014).
- These conflicts resulted in significant casualties and damage in Gaza.
- Israel imposed a blockade on Gaza, severely restricting the movement of goods and people.
- Gaza faced chronic shortages of essential supplies, contributing to a humanitarian crisis.
Ceasefire was brokered by Egypt
- The most recent ceasefire went into effect on August 5, 2023, following three days of intense fighting between Israel and the Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ).
- The ceasefire was mediated by Egypt and was reportedly agreed to by all parties.
Hamas: Background and Ideology
- Hamas, short for Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiya (Islamic Resistance Movement), was founded in 1987 as an offshoot of the Muslim Brotherhood.
- It embraces Islamist principles, advocating for a significant role of Islam in political life.
Origins in Palestinian Uprising
- Hamas emerged during the Palestinian uprising against Israel’s occupation of Gaza and the West Bank.
- Its formation was a response to perceived injustices and a desire for Palestinian self-determination.
Hamas’s Controversial Status
Terrorist Designations
- Many countries, including the S., the U.K., and Canada, have designated Hamas as a terrorist organization
- Due to its history of attacks on Israel, including rocket salvos and suicide bombings.
- While some nations, like New Zealand, consider only Hamas’s military wing.
- Hamas, however, also provides essential social services in Gaza, such as education and medical care.
Hamas’s Goals and Impact
Freedom-Fighting and Palestinian Liberation
- Hamas presents itself as a freedom-fighting movement aimed at ending the Israeli occupation and reclaiming parts of Israel for Palestinians.
- However, its use of violence has polarized opinions among Palestinians and supporters of a Palestinian state.
Popularity and Recent Polls
- Recent surveys show that Hamas enjoys significant popularity among Palestinians.
- Many perceiving Hamas as a protector of Muslim holy sites in East Jerusalem.
External Support and Backing
Iran’s Role
- Iran provides substantial support to Hamas, including funds, weapons, and training.
- This backing strengthens Hamas’s military capabilities and its ability to pursue its goals.
Turkey’s Involvement
- While Turkey officially claims only political support for Hamas.
- It has faced accusations of funding the group’s terrorism, potentially diverting funds from Turkish government aid programs.
Global Implications of Israel-Hamas Conflict
- Global Security Concerns: The Israel-Hamas conflict in the Gaza Strip raises international security concerns due to the potential for escalation and involvement of regional and global powers.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The conflict exacerbates the humanitarian crisis in Gaza, leading to displacement, casualties, and damage to infrastructure, drawing attention from international aid organizations.
- Diplomatic Efforts: International diplomatic efforts to de-escalate the conflict highlight the world’s interest in stability in the Middle East, involving mediators like Egypt, the United Nations, and the United States.
- Economic Impact: The conflict disrupts trade and economic activities in the region, affecting global markets and energy prices.
India’s Stance on Palestine and Israel
Historical Recognition of Palestine by India
- India recognized the State of Palestine in 1988, establishing diplomatic relations.
- India opened a representative office in Gaza in 1996, later shifted to Ramallah, the de facto capital of Palestine in 2003.
- In October 2003, India voted in favor of a UN General Assembly resolution opposing Israel’s separation wall.
- In 2011, India supported Palestine’s full membership in UNESCO.
- In 2012, India co-sponsored a UN resolution granting Palestine “non-member” observer state status.
- In 2015, India backed the installation of the Palestinian flag at the UN.
Bilateral Ties with Israel
- India established diplomatic relations with Israel in 1992
- India and Israel have developed robust economic, military, and technological cooperation in various sectors, including defense and agriculture.
Balancing Act
- India maintains a delicate balance between its relations with Israel, a strategic partner in defense and technology, and its support for the Palestinian struggle for statehood, reflecting its commitment to a peaceful resolution of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Two state Solution
- Two-state solution was first proposed in 1937 by the Peel Commission, envisioning separate, independent states for Israel and Palestine coexisting harmoniously.
- It proposes borders along pre-1967 lines, land swaps for security, and envisions East Jerusalem as Palestine’s capital and West Jerusalem as Israel’s capital.
- It supports a sovereign and independent Palestine living side by side with Israel in peace and security.
- Supported by – US, India, Saudi Arabia, China
The Gaza Strip’s recent escalation of violence underscores the urgent need for a peaceful resolution. The suffering of civilians, especially in densely populated areas, is a grave concern. International efforts should prioritize a ceasefire, humanitarian aid, and diplomatic negotiations. All parties must engage constructively, adhering to past agreements, and pursue a two-state solution, recognizing the legitimate rights and aspirations of both Israelis and Palestinians. The international community must work collectively to bring stability, security, and prosperity to the region.
Source: BBC news, Indian Express, The Hindu, Deccan Herald, Business standard
Mains Question
The Gaza Strip has been a persistent hotspot of conflict in the Middle East. Discuss the historical background of the Gaza Strip, including its changing political control and the significance of this region in the Israel-Palestine conflict.