Gantenerumab: New Hope for Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Treatment
Why in the News ?
Gantenerumab, a groundbreaking drug, shows promise in treating Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease by targeting and reducing amyloid plaques in the brain. It offers potential relief by slowing cognitive decline, pending confirmation from ongoing clinical trials.
Gantenerumab: The Promising New Drug
- Mechanism of Action: Gantenerumab works by targeting and reducing amyloid plaque accumulation, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Therapeutic Benefits: By slowing down plaque buildup, the drug aims to delay cognitive decline and improve quality of life for EOAD patients.
- Ongoing Trials: While the drug shows promise, further clinical trials are needed to confirm its long-term efficacy and safety.
A Hopeful Future for Alzheimer’s Treatment
- Significant Advancement: Gantenerumab represents a hopeful advancement in the battle against Alzheimer’s, offering potential relief for patients and families.
- Research Prospects: Ongoing research aims to refine treatments and develop more effective therapies.
- Future Outlook: The breakthrough highlights the importance of targeted therapies in managing neurodegenerative diseases and provides new hope for patients worldwide.
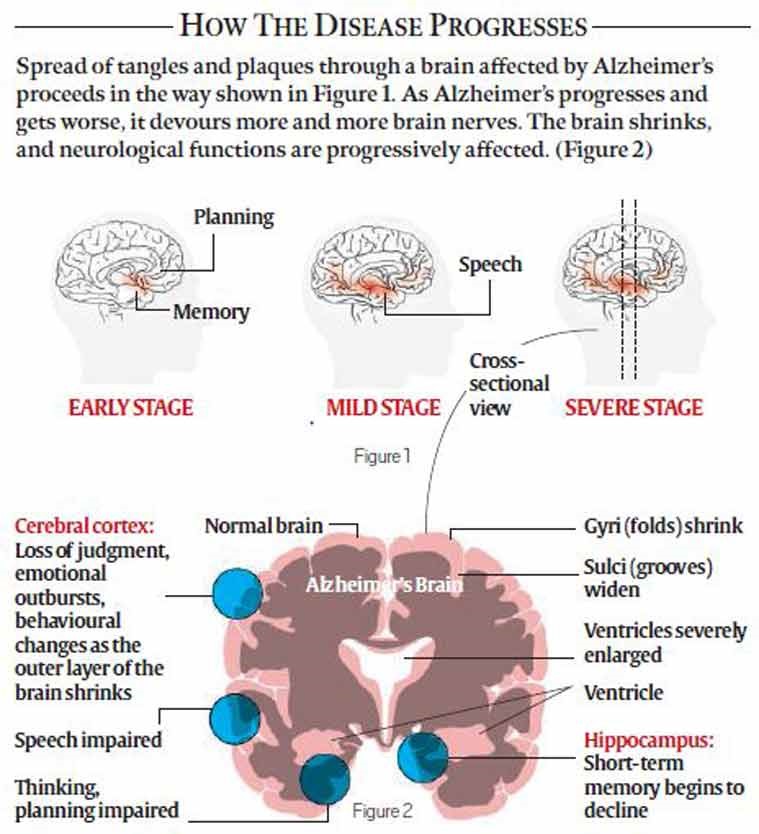
Understanding Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (EOAD):● Definition & Impact: EOAD affects individuals under 65 years old, often during their prime working years. It progresses rapidly, causing significant medical and social challenges. ● Genetic Links: The disease is linked to mutations in the APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 genes. ● Disease Mechanism: EOAD is driven by the accumulation of amyloid beta proteins in the brain, forming sticky plaques that disrupt neuron communication, cause inflammation, and lead to brain cell death. |