Food Processing Sector’s Job Growth.
Relevance
- GS Paper 3
- Food processing and related industries in India- scope’ and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, and supply chain management.
- Tags: #foodprocessing #MSME #Jobgrowth #currentaffairs #upsc
Why in the News?
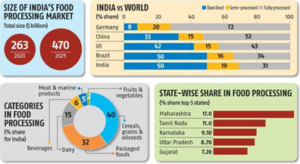
- India’s food processing sector is poised to create 9 million jobs. India’s food processing sector is poised to create 9 million jobs by 2024, with household consumption expected to quadruple by 2030, propelling India to become the world’s fifth-largest consumer of food and food technology.
- Mr. Prabodh Halde, Chairman of the All India Food Processors’ Association (AIFPA) Western Region, made this announcement during the 17th edition of ANUTEC – International FoodTec India. The event was co-located with ANUFOOD India and PackEx India, held in Mumbai.
Foreign Investments Fueling Growth
- The sector’s growth potential, citing the influx of $4.18 billion in foreign direct investments between 2014 and 2020 is highlighted.
- Emphasizes is laid on the significant economic contribution, noting that the food processing sector currently accounts for 13% of India’s exports and 6% of industrial investments.
- The thriving Indian gourmet food sector, with a market size of $1.3 billion, boasts an impressive 20% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR).
Ambitious GDP Contribution Target
- India’s food processing sector has ambitious goals, aiming to double its GDP contribution from 8% to 20% by 2030.
Government Initiatives Driving Growth
- Speaking at the event, Prahlad Singh Patel, Minister of State for the Ministry of Food Processing Industries, Government of India, praised government initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana (PMKSY), Pradhan Mantri Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) scheme, and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- These initiatives have helped the industry meet global quality and safety standards, benefiting the entire food processing value chain.
- The government’s commitment to sector growth is highlighted, citing an allocation of ₹4,600 crore to sustain PMKSY and an additional ₹920 crore recently allocated to further support its development.
MSMEs: A Key Player in the Indian Economy
- These enterprises contribute over 30% of the GDP, nearly 50% of exports, and 45% of industrial output.
| What is Food Processing Sector.
The food processing sector is integral to the transformation of raw ingredients or agricultural produce into edible consumables suitable for human consumption. This sector assumes a critical role in the processing and preservation of perishable materials, ultimately yielding packaged food items with prolonged shelf lives, enhancing their suitability for distribution and consumption. Government Initiatives Promoting Food Processing. · PM Kisan Sampada Yojana: This scheme encourages entrepreneurs to establish food processing units near agricultural areas, supporting cold storage, packaging, warehousing, and preservation facilities. Grants are available, ranging from 35% of eligible project costs in most states to 50% in North-east and Himalayan states. · PM Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme: Aimed at aiding small food processing micro-units, this scheme offers a 35% subsidy on project costs, up to ₹10 lakhs. It benefits businesses involved in activities such as chilli drying, spice packaging, pickle, and papad making. · Operation Greens: Focusing on tomato, potato, and onion crops, this scheme promotes integrated value chain development. Post-harvest processing facilities can receive grants of up to 50% of the project cost, with a maximum limit of ₹50 crores. · National Mission on Food Processing (NMFP): A centrally sponsored scheme decentralizing food processing-related projects through state and district-level missions. This approach enhances state participation, planning, supervision, monitoring, and policy formulation. · Mega Food Parks Scheme: This initiative creates processing hubs that connect farmers, processors, and retailers. It aims to maximize value addition, reduce wastage, increase farmer income, and generate rural employment. · Cold Chain Infrastructure Scheme: Promotes the establishment of cold chain facilities to preserve food products from farm gate to consumer, ensuring freshness and quality. · 100% FDI Approval (Automatic Route): The government allows 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) approval under the automatic route, encouraging foreign investment and technology infusion in the food processing sector. · Special Food Processing Fund with NABARD: A ₹2000 crore fund, in partnership with the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), offers affordable credit for Mega Food Parks, Agro-Processing Clusters, and individual manufacturing units.
|
Sources: MOFPI, The Hindu
Mains Question
Despite experiencing consistent growth, the food processing industry in India continues to hold substantial untapped potential. Please explore and elaborate on this observation with respect to role of MSME. 250words.