FINTECHS PITCH FOR FOCUS ON DIGITAL PUBLIC INFRA IN BUDGET
Relevance:
- GS 2 – e-Governance applications
- GS 3 – Government Budgeting, FinTech
Why in the news?
- Recently, India has advocated for the global adoption of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to enhance productivity and achieve inclusive and sustainable growth.
- A G20 Task Force’s report, prepared by India, highlights this advocacy.
- The final “Report of India’s G20 Task Force on DPI” was released on Monday.
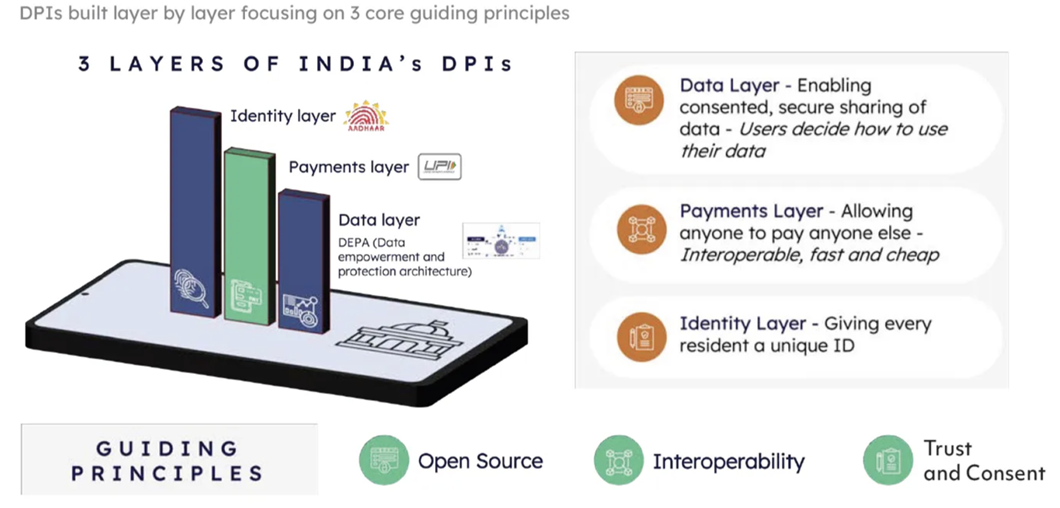
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- DPI refers to the foundational digital infrastructure and platforms created by governments to deliver digital services to citizens.
- It includes a range of technologies and systems aimed at improving the efficiency, accessibility, and inclusivity of public services in the digital age.
- Foundational Elements:
- Digital Identification Systems: Programs like Aadhaar in India that provide a unique digital identity for citizens.
- Payment Infrastructure: Platforms like Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India that facilitate secure and efficient digital payments.
- Data Exchange Solutions: Frameworks that enable secure and standardized exchange of data between different entities.
Fintech Industry’s Union Budget Demands
- GST Exemption and Operational Costs on services offered through BC outlets to reduce tax burdens and operational costs, facilitating easier access to financial services in rural and remote areas.
- Guidelines and Lending Practices: The industry seeks clarity in new guidelines and lending practices, along with measures to support innovation and enhance the digital lending ecosystem, particularly for MSME lending.
- Monetization Opportunities for UPI Payments: A major demand is the phased introduction of fees for UPI payments to create monetization opportunities.
- Balasubramanian, CEO of Financial Software and Systems, suggests charging for digital payments like UPI to allow banks to build robust payment infrastructure and security standards, ensuring fast, simple, and secure payments while protecting consumers from fraud and cybersecurity threats.
- Subsidy on Merchant Discount Rate:
- Rahul Jain, CFO of NTT DATA Payment Services India, calls for a subsidy on the merchant discount rate for UPI transactions through credit cards to make the business model more viable.
- Currently, a 2% merchant discount rate is levied on UPI-linked RuPay credit card transactions, with 1.5% going to the card issuing bank and the remainder shared between the card network and the merchant acquiring bank.
- Licensing Process and Safety Measures: Jain also advocates for simplifying and fast-tracking the licensing process, creating mechanisms to ensure the safety of digital payments, and setting up infrastructure and targeted initiatives to boost the scale and volume of digital transactions.
- Rahul Jain, CFO of NTT DATA Payment Services India, calls for a subsidy on the merchant discount rate for UPI transactions through credit cards to make the business model more viable.
Current Scenario of Digital Public Infrastructure in India
- Digital Transactions: India boasts the highest number of digital transactions, surpassing the combined figures of the US, China, and Europe.
- Digital Economy: The digital economy in India is booming and projected to reach $1 trillion by 2025.
- Internet User Base: Over 759 million Indians are actively connected to the internet, with a significant portion residing in rural areas.
- Aadhaar Programme: The ambitious Aadhaar program, a digital ID system, has enrolled nearly 1.3 billion citizens, facilitating efficient delivery of welfare services, financial transactions, and access to government schemes.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): UPI is witnessing exponential growth, expected to reach a billion transactions daily by 2026.
- Broadband Connectivity: Broadband connectivity has significantly increased, reaching over 93% of Indian villages.
- Commitment to Digital Empowerment: These milestones reflect India’s unwavering commitment to building a digitally empowered and inclusive society.
Government Steps in Advancing Digital Public Infrastructure
- Foundational Programs:
- National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN): Establishes a foundational network for digital connectivity.
- Digital India: Aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
- National Broadband Mission: Focuses on enhancing broadband connectivity across the country.
- National Data Centre Policy: Develops a policy framework for data storage and management.
- Key Projects and Initiatives:
- Bharat Net Project: Ambitious plan to connect villages with high-speed internet.
- Wi-Fi Hotspots: Establishment of Wi-Fi hotspots in public spaces.
- Production Linked Incentive Schemes: Encourages domestic production of telecom equipment.
- Transformational Programs:
- Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) Trinity: Results in millions of new bank accounts and streamlined direct benefit transfers, reducing leakages and ensuring targeted welfare delivery.
- Ayushman Bharat Mission: Transforms the healthcare sector by providing health insurance and services.
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): Enhances logistics sector efficiency.
- Innovative Solutions:
- DigiLockers and Authentication Frameworks: Provide secure storage and access to vital documents.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): Empowers small businesses by offering a global marketplace.
- Digital Platforms:
- National e-Governance Plan (NeGP): Offers a one-stop platform for services such as birth certificates and land records.
Way Forward for India’s Digital Public Infrastructure
- Expand Coverage:
- Continue expanding high-speed internet connectivity to underserved rural and remote areas.
- Accelerate the Bharat Net Project to ensure comprehensive coverage across all villages.
- Enhance Digital Literacy:
- Implement nationwide digital literacy programs to educate citizens on utilizing digital services effectively.
- Focus on training programs for marginalized communities to bridge the digital divide.
- Strengthen Cybersecurity:
- Invest in advanced cybersecurity measures to protect digital infrastructure and user data.
- Develop a national framework for regular security audits and threat assessments.
- Promote Interoperability:
- Ensure seamless integration and interoperability among various digital platforms and services.
- Standardize protocols to facilitate efficient data exchange and service delivery.
- Encourage Innovation:
- Support the development and adoption of emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT to enhance digital services.
- Provide incentives for startups and tech companies working on innovative digital solutions.
- Improve Regulatory Framework:
- Update regulations to address new challenges in digital governance and data privacy.
- Foster transparent and adaptive regulatory practices to accommodate evolving technologies.
- Strengthen Public-Private Partnerships:
- Promote collaboration between government, industry, and academia to drive digital infrastructure advancements.
- Leverage expertise and resources from the private sector to enhance service delivery and infrastructure development.
- Focus on Inclusivity:
- Ensure digital services are accessible to all segments of society, including persons with disabilities and elderly populations.
- Address barriers to digital access and affordability through targeted policies and subsidies.
Alternative Articles
https://universalinstitutions.com/india-urged-to-lead-digital-public-infrastructure-in-global-south/
https://universalinstitutions.com/e-governance-digital-public-infrastructure-dpi/
Source: Live Mint
Mains question
Discuss the key achievements and future challenges of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). How can the government address these challenges to ensure inclusive and secure digital growth? (250 words)