Female Voter Turnout Surpasses Male in LS Polls
Why in the news?
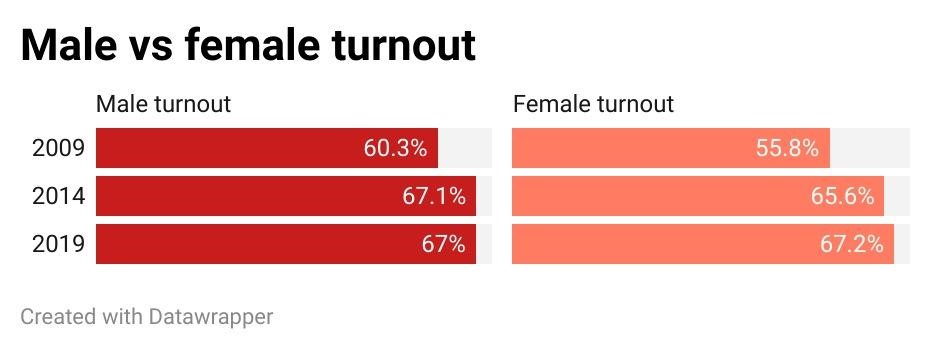
For the 2024 Lok Sabha elections, female voter turnout exceeded male turnout in many states, highlighting trends influenced by gender dynamics, migration patterns, and sociopolitical factors, with Bihar showcasing the most significant gender difference in turnout.
Trends in Female Voter Turnout:
- In the 2024 Lok Sabha elections, female voter turnout exceeded male turnout for the second consecutive time since 2019.
- Female turnout surpassed male turnout in 15 out of 28 major states and union territories.
- States like Bihar, Jharkhand, and Himachal Pradesh had a higher female voter turnout despite having fewer registered female electors than males.
- Conversely, states like Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh saw higher male turnout due to more registered male electors.
Factors Influencing the Anomaly
- Out-migration of male workers may explain lower male turnout in states like Bihar and Jharkhand, where men were unable to vote despite being registered.
- Political motivations or structural factors, such as male workers migrating for employment, contributed to this trend.
- States like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh, with higher female electorates, also witnessed higher female voter turnout.
Insights and Data Analysis
- Granular data from the Election Commission highlights narrowing gender turnout gaps in recent elections.
- Bihar recorded the highest gender difference in turnout among states with low overall turnout.
- States with high turnout, like Arunachal Pradesh and West Bengal, also exhibited higher female participation.
- Migration data revealed that Bihar prominently features as a source state for migrant workers, correlating with lower male voter turnout.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times