Exceptional SRY Gene Cases Redefine Sex Determination
Syllabus:
GS-3:
Biotechnology , Scientific Innovations & Discoveries
Focus:
In 2024, two research teams from Italy and the USA reported exceptional cases of females possessing the SRY gene, typically responsible for male development. These rare findings challenge traditional concepts of sex determination and highlight the genetic complexities behind male and female biological development.
Defining the SRY Gene:
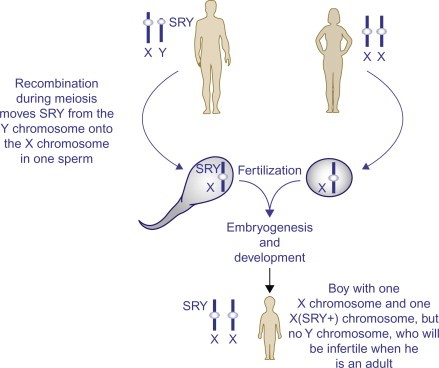
The SRY (Sex-determining Region Y) gene, located on the Y chromosome, plays a critical role in determining male biological development. Its presence triggers male development, while its absence allows the default female pathway to proceed.
- Noteworthy Discoveries in 2024:
Exceptional cases of females possessing the SRY gene were reported twice in 2024—by researchers at the Renato Dulbecco University Hospital in Italy and the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, USA. These instances add to the understanding of sex determination and its anomalies.
Understanding Sex Determination:
Definition:
- Biological mechanism that determines whether an organism develops as male or female.
- In humans, it depends on the sex chromosomes (X and Y) inherited from parents.
Mechanism of Sex Determination in Humans:
- Chromosomal Basis:
- Humans have 46 chromosomes, including one pair of sex chromosomes (XX for females, XY for males).
- Fertilization and Chromosome Inheritance:
- Mother contributes an X chromosome, while father contributes either X or Y.
- XX results in a female, while XY results in a male.
- SRY Gene Activation:
- The SRY gene on the Y chromosome triggers testes formation, initiating male development.
- Hormonal Influence:
- Testosterone from testes promotes male characteristics.
- In the absence of SRY, the development defaults to female reproductive organs.
- Methods of Sex Determination in Species:
- Genetic Methods:
- XY System: Humans and mammals.
- ZW System: Birds and some reptiles.
- Non-Genetic Methods:
- Temperature-Dependent: Reptiles like turtles and crocodiles.
- Sequential Hermaphroditism: Fish change sex based on environmental conditions.
Technological Advancements in Sex Determination:
- Genetic Testing:
- PCR and DNA Sequencing detect Y chromosomes and SRY genes.
- NIPT determines fetal sex from maternal blood.
- Microscopy & Imaging:
- FISH identifies sex chromosomes visually.
- Gene Editing:
- CRISPR modifies sex-determining genes in research.
- AI Applications:
- Analyze genetic data to predict sex and detect sex-linked traits.
How Sex is Determined:
Chromosomal Basis of Sex Determination:
- Humans inherit 23 pairs of chromosomes from their parents, including one pair of sex chromosomes (XX for females and XY for males).
- Eggs always carry an X chromosome, while sperm can carry either an X or a Y.
- Fertilization determines the baby’s sex:
- XX: Female development.
- XY: Male development triggered by the SRY gene.
Role of the SRY Gene:
- The SRY gene initiates male development by promoting testes formation, which produces testosterone and other male-specific traits.
- In its absence (XX embryos), ovaries develop, producing estrogen that leads to female characteristics.
Exceptional Cases of SRY-Positive Females:
Medical Literature Insights:
- Only three instances of females possessing the SRY gene have been documented:
- The first case occurred prior to 2024.
- Two cases in 2024:
- Italian researchers identified a family with SRY-positive females spanning three generations.
- American researchers found SRY-positive females but were unable to conduct postnatal follow-ups.
Unique Characteristics of These Cases:
- Despite having the SRY gene, these females developed typically female characteristics due to “biased X chromosome inactivation” silencing the SRY gene.
- Fertility was preserved in the Italian family’s females, proving the translocation of the SRY gene to an X chromosome could persist across generations without abnormalities.
Mechanisms Behind SRY-Positive Females:
Biased X Chromosome Inactivation:
- In females, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated in each cell.
- In SRY-positive females, the translocation X chromosome carrying the SRY gene is selectively silenced, preventing male development.
- This process ensures essential genes from the unaffected X chromosome remain active, supporting typical female development.
Significance of the SRY Gene:
- The inactivation of the SRY gene underscores its importance as the key trigger for male development.
- Only silenced SRY genes can persist in female genomes without disrupting normal development.
Concerns and Risks:
- Researchers at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital cautioned that low-level SRY expression could lead to sex development disorders later in life, necessitating long-term monitoring.
Implications and Future Research:
Medical Implications:
- Understanding these rare cases provides insights into chromosomal anomalies and their effects on development.
- It highlights the importance of the SRY gene in determining sex while showcasing the complexity of genetic regulation.
Research Directions:
- Long-term follow-up studies are needed to monitor potential health complications in SRY-positive females.
- Investigating similar cases can deepen understanding of chromosomal translocations and their impact on fertility and development.
Broader Understanding of Biology:
- These cases challenge the binary view of sex determination and highlight the genetic intricacies underlying human development.
- They pave the way for advancements in genetic counseling and medical care for individuals with chromosomal abnormalities.
Conclusion:
The discovery of SRY-positive females emphasizes the complexity of human biology and sex determination. While the SRY gene remains a key determinant of maleness, these exceptional cases reveal the intricate interplay of genetics and chromosomal regulation. Further research into such anomalies could unlock deeper understanding and improve medical approaches for affected individuals.
Source: TH
Mains Practice Question (50 Words)
Discuss the significance of the SRY gene in human sex determination. How do recent discoveries of females possessing this gene challenge traditional biological notions? Highlight the implications of such anomalies on genetics research, reproductive health, and long-term medical care.