EVALUATING INDIA’S GROWTH NARRATIVE
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources,
- Growth, Development and Employment.
- Inclusive Growth
Focus:
The article scrutinizes contrasting perspectives on India’s economic recovery post-pandemic, emphasizing data reliability, structural reforms, and policy implications amid debates surrounding growth sustainability and the role of counter-cyclical measures.
Source: Forbes
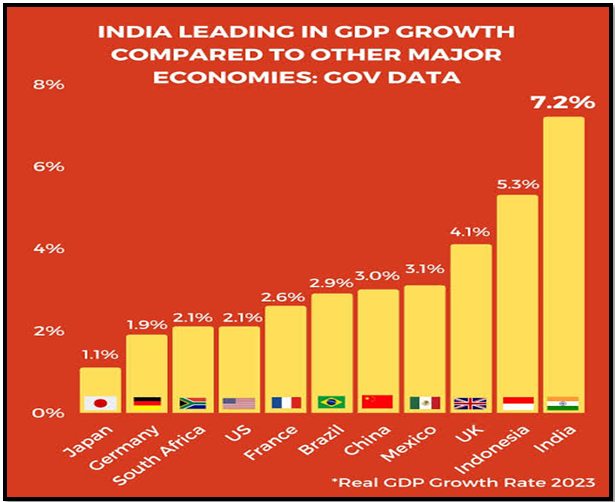
Continued Robust Growth Amid Debates:
- The Perception Divide: Two contrasting views on India’s growth trajectory exist, highlighting fundamental flaws versus the success of recent reforms.
- Evidence of Success: Robust growth rates, contained inflation, and poverty reduction post-pandemic support the argument favouring current policies.
- Disruption Risks: Despite evidence of growth, calls for disruptive policy changes persist, raising questions about the need for such interventions.
- Revision of Growth Figures: Critics initially predicted downward revisions of growth figures, but actual revisions have been upward, challenging their stance.
Debunking Criticisms on Inflation and Growth:
- Misconception on Inflation: Some critics argue that high growth figures are misleading due to negative wholesale price index (WPI) inflation, but fail to acknowledge the potential underestimation of growth during periods of high WPI inflation.
- Double Deflation Fallacy: Critics often raise concerns about the absence of double deflation, overlooking the complexities and limitations associated with this method.
- Interpretation of Quarterly Results: Quarterly growth figures are often misinterpreted due to seasonal and base effects, leading to inaccurate conclusions about the overall growth trend.
- Questioning Data Reliability: Critics cast doubts on data reliability, particularly concerning discrepancies between gross value added (GVA) and expenditure-side measurements, ignoring the robustness of GDP measurement from the production side.
- Selective Data Interpretation: Critics selectively highlight data supporting their preconceived notions while disregarding contradictory evidence, undermining the credibility of their arguments.
- Global Growth Comparison: Comparisons with global growth fail to fully explain India’s growth performance, as appropriate domestic policies play a crucial role in shaping economic outcomes.
Addressing Concerns on Savings and Investment:
- Household Financial Savings: While there’s a decline in household financial savings, physical savings are on the rise, indicating healthier investment patterns.
- Current Account Deficit: Despite concerns about rising current account deficits, improved financial intermediation and domestic investment have helped stabilize the deficit.
- Investment Outlook: Private credit ratios remain low compared to peers, but sustained private investment is evident, driven by improved banking regulations and risk-based pricing.
- Gross Capital Formation: India’s gross capital formation remains significant, primarily driven by sustainable private capital expenditure, ensuring a steady investment cycle.
- Policy Continuity: Policy stability is crucial for sustaining private sector investment, as evidenced by continued private sector projects and investment plans.
| Important Key Terms
Inflation: Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, leading to a decrease in purchasing power over time. It is typically measured as a percentage increase in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) over a specific period. Double Deflation: Double deflation is an economic concept used to adjust for price changes in both output (goods and services produced) and inputs (cost of production factors like labour and capital). It involves deflating both nominal GDP and nominal value-added using appropriate price indices to obtain real measures of output and value-added. Current Account Deficit: The current account deficit (CAD) is a measurement of a country’s trade where the value of goods and services it imports exceeds the value of goods and services it exports. It also includes net income earned from abroad and net transfers. Gross Capital Formation: Gross capital formation (GCF) refers to the total value of new capital investment made within an economy during a specific time period. It includes investments in fixed assets like machinery, equipment, construction, and changes in inventory levels. GCF is a key indicator of economic growth and development. |
Importance of Policy Continuity
- Investor Confidence: Consistent policy frameworks provide certainty to investors, encouraging them to make long-term commitments and deploy capital into the economy.
- Economic Stability: Policy continuity fosters macroeconomic stability by avoiding abrupt changes that could disrupt business operations and consumer behaviour.
- Long-term Planning: Businesses rely on stable policies to make informed investment decisions and undertake strategic planning, which is essential for sustainable growth and development.
- Regulatory Environment: A predictable regulatory environment promotes business confidence, reduces uncertainty, and facilitates smooth operations across sectors.
- Attracting Foreign Investment: Foreign investors seek stable policy environments to mitigate risks and ensure the security of their investments, making policy continuity crucial for attracting foreign capital inflows.
Future Outlook and Implications:
- Data Transparency: Enhancing data transparency and accuracy is imperative for building trust in economic indicators and guiding evidence-based policymaking for future growth strategies.
- Policy Adaptation: Assessing the need for policy adaptations based on evolving economic trends and global developments to ensure resilience and competitiveness in the long run.
- Structural Reforms: Identifying areas for structural reforms to address underlying challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities for sustained economic expansion.
- Investment Climate: Evaluating the investment climate and identifying measures to further improve the ease of doing business to attract domestic and foreign investments.
- Socio-economic Impact: Understanding the socio-economic implications of India’s growth narrative, including its effects on income distribution, poverty alleviation, and social welfare programs, to promote inclusive development strategies.
Way Forward:
- Policy Stability: Emphasize the importance of maintaining policy stability to bolster investor confidence and sustain economic momentum.
- Data Integrity: Strengthen data collection mechanisms and enhance transparency to ensure accurate economic assessments and informed decision-making.
- Structural Reforms: Prioritize structural reforms aimed at addressing underlying challenges and unlocking new avenues for growth and development.
- Investment Promotion: Implement measures to improve the investment climate, streamline regulations, and attract both domestic and foreign investments.
- Sustainable Growth: Focus on fostering sustainable growth by promoting prudent fiscal management, efficient resource allocation, and long-term planning.
- Inclusive Development: Adopt inclusive development strategies that prioritize poverty alleviation, social welfare programs, and equitable distribution of economic benefits.
- Adaptive Policies: Remain vigilant to evolving economic trends and global developments, adapting policies accordingly to ensure resilience and competitiveness in the face of uncertainties.
Conclusion:
India’s growth narrative is marked by robust economic indicators and sustained policy reforms, debunking misconceptions and highlighting the need for policy continuity to support private sector investment and economic resilience.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the factors contributing to India’s economic recovery post-pandemic and the implications for future policy formulations. Evaluate the role of data integrity and structural reforms in sustaining economic momentum.
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/economic-growth-and-development/