ENHANCING ECONOMIC GROWTH AND MANUFACTURING SECTOR
Syllabus:
- GS3 : Changes in Industrial Policy and their Effects on Industrial Growth.
Why in the News?
- The Finance Ministry’s 10-year review highlights India’s economic growth trajectory and forecasts a robust GDP expansion close to 7% in 2024-25.
- The editorial underscores the need for sustained efforts and policy interventions to achieve this growth momentum.
Source: India Today
Economic Growth Outlook:
- The review anticipates India’s GDP to reach $5 trillion in three years and potentially $7 trillion by 2030, positioning it as the world’s third-largest economy.
- It delineates two growth phases: pre-2014 characterized by structural constraints, and post-2014 marked by transformative growth reforms under Prime Minister’s leadership.
Determinants of Economic Growth:
Natural Resources:
The quality and quantity of natural resources significantly impact a country’s economic development trajectory.
Capital Formation:
Essential for economic growth, capital accumulation forms the cornerstone of development efforts.
Foreign Capital:
Early-stage development often relies on foreign assistance, including aid and foreign direct investment (FDI), to fuel growth.
Population Growth:
A growing population can contribute to economic output by expanding the labor force, provided there are opportunities for productive employment.
Education and Health:
Investments in education and healthcare are pivotal for fostering economic development and human capital formation.
Technological Progress:
Advancements in technology and the adoption of innovative production techniques drive substantial increases in per capita output and overall economic growth.
Challenges in Economic Transformation:
- Structural constraints such as tardy decision-making, ill-targeted subsidies, and a large informal sector hampered pre-2014 economic growth.
- Post-2014 reforms have rejuvenated the economy, fostering longer and stronger economic cycles and positioning India as the fastest-growing G-20 nation.
Way forward:
- Despite commendable growth projections, there is a need for a wider private investment revival and broad-based consumption rebound.
- A shift towards an inclusive welfare approach is advocated to expand the middle class and reduce dependency on handouts, fostering meaningful and equitable growth.
- Policy reforms in education, healthcare, and compliance mechanisms, particularly at the sub-national level, are imperative to accelerate growth.
- Addressing flaws in reforms like GST and revisiting blunt policy tools such as import licenses and price controls are essential to enhance market predictability and openness.
Manufacturing Sector Development
Context :
- The government’s efforts, exemplified by the Padma Bhushan conferred on Foxconn’s CEO, underscore its commitment to bolstering the manufacturing sector.
Source: IBEF
Challenges in Manufacturing:
- Inadequate Tech Infrastructure: The Lack of technology – based infrastructure, including communication and transportation, hampers manufacturing competitiveness.
- Limited Access to Credit for MSMEs: Micro, Small, and Medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) struggle with
limited access to credit and face higher working capital costs compared to larger industries.
- Skilled Labour Shortages: The manufacturing sector grapples with a shortage of trained and skilled labor, hindering its growth potential.
- Complex Regulations and Supply Chain Issues: Complex regulations, such as licensing and auditing requirements, pose burdens for businesses, while poor supply chain management leads to inefficiencies and increased costs.
- Competition and Imports: India’s manufacturing sector faces stiff competition from other countries, challenging domestic businesses’ ability to compete globally. Additionally, heavy reliance on foreign imports for various materials adds to the sector’s challenges.
- Infrastructure and Electricity Challenges: Telecom communication facilities are limited mainly to urban areas, and many State Electricity Boards struggle with financial losses and inadequate infrastructure, impacting manufacturing operations.
Initiatives for development of Manufacturing Sector:
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI): Incentive scheme to boost domestic manufacturing by providing financial rewards based on incremental production in specific sectors.
PM Gati Shakti- National Master Plan: Infrastructure project aimed at enhancing multimodal connectivity across the country for efficient transportation of goods and people.
Bharatmala Project: National highway development initiative focused on constructing and upgrading road networks to improve connectivity and logistics efficiency.
Start-up India: Program to promote entrepreneurship and facilitate the growth of startups by providing support, funding, and simplifying regulations.
Make in India 2.0: Renewed initiative to encourage domestic manufacturing and attract foreign investment through policy reforms and infrastructure development.
Atmanirbhar Bharat Campaign: Self-reliance campaign promoting indigenous production, innovation, and economic growth to reduce dependency on imports and boost domestic industries.
Way Forward:
- Innovation Promotion: Supporting research and development in manufacturing, fostering the adoption of new technologies, and processes to drive innovation and productivity.
Result: This could include funding R&D initiatives or implementing policies to facilitate technology adoption.
- Export-Oriented Manufacturing Promotion: Encouraging the growth of export-oriented manufacturing to access new markets and enhance competitiveness.
Result :This could involve supporting businesses in entering new markets or implementing policies incentivizing export-oriented production.
- Infrastructure Investment: Enhancing infrastructure quality and availability, including roads, ports, and power supply, to attract investment and businesses.
Result :This may require constructing new infrastructure or upgrading existing ones.
- Access to Finance Improvement: Facilitating SMEs’ access to credit and financing to support their growth.
Result :This may entail policies encouraging financial institutions to lend to manufacturing SMEs or offering government-backed loan guarantees.
- Regulatory Streamlining: Simplifying regulations to reduce the burden on businesses and attract more investment.
Result : This could involve simplifying licensing processes, permits, or compliance requirements.
- Skill Development Encouragement: Expanding skill development opportunities to address the shortage of skilled labour in manufacturing.
Result :This could include investing in vocational training programs or incentivizing businesses to provide employee training.
The editorial underscores the importance of sustained policy interventions to sustain economic growth momentum and foster inclusive development, emphasizing the need for gender-sensitive approaches in addressing internal female migration and sustained efforts to boost the manufacturing sector’s contribution to GDP.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the factors influencing economic growth in India over the past decade. Evaluate the effectiveness of government policies and initiatives in promoting sustainable economic growth.

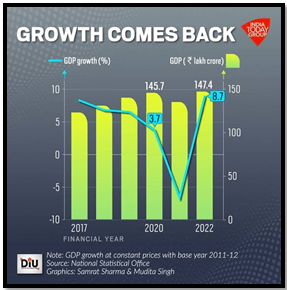 Source: India Today
Source: India Today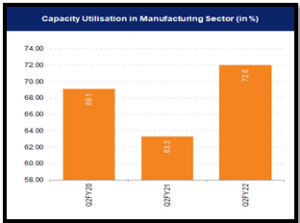 Source: IBEF
Source: IBEF


