Endless war
Russia, Ukraine and NATO should make a practical assessment of the war
Relevance:
GS 2
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
Why in News:
- A Russian plane carrying Ukrainian prisoners of war crashed in Belgorod, a Russian border town
Source- NBCC NEWS
Recent Developments in the Conflict
- Plane Crash Incident: A Russian plane carrying Ukrainian prisoners of war crashed in Belgorod, a Russian border town. Russia accuses Kyiv of downing the plane, while Ukraine counters with accusations of propaganda.
- Military Dynamics: Ukraine struggles to maintain its frontline defense amid Russia’s incremental advances. After initial setbacks, Russia has regained momentum, capturing key territories.
- Ukrainian Mobilization Plans: Plans to mobilize up to 500,000 soldiers are being considered, facing potential unpopularity.
Political Implications
- Investigation into the Plane Crash: Ukraine’s government, led by Volodymyr Zelensky, commits to investigating the crash. Any confirmation of Ukrainian involvement poses a political challenge for Zelensky.
- War’s Future and Ukraine’s Stance: Despite a stated commitment to recapture all lost territories, Ukraine lacks a practical path to victory. Changing global dynamics, including other international conflicts and potential shifts in U.S. leadership, influence the situation.
Brief History/Timeline of Ukraine-Russia Conflict
Pre-2014: Historical Context
- Centuries of Shared History: Ukraine and Russia share a complex history, with periods of unity and conflict.
- Soviet Era: Ukraine was part of the Soviet Union until its dissolution in 1991.
2014: The Critical Year
- February 2014: Euromaidan Protests lead to the ousting of Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych, known for his pro-Russian stance.
- March 2014: Russia annexes Crimea following a controversial referendum.
- April 2014: Pro-Russian separatists in Eastern Ukraine (Donbas region) declare independence, leading to armed conflict with Ukrainian forces.
2014-2021: Continuing Conflict
- Minsk Agreements (2014 and 2015): Attempts to ceasefire and resolve the conflict in Eastern Ukraine, but they largely remain ineffective.
- Ongoing Skirmishes: Sporadic fighting continues in the Donbas region, with periodic escalations.
2022: Full-Scale Invasion
- February 24, 2022: Russia launches a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, marking a significant escalation in the conflict.
- Global Response: Widespread international condemnation, sanctions against Russia, and support for Ukraine.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The conflict leads to a massive humanitarian crisis with casualties and displacement.
2022-present : Continuing Conflict
- Ongoing Battles: Key battles and sieges in various Ukrainian cities, including Mariupol and Kyiv.
- Territorial Changes: Russia occupies and annexes parts of Eastern and Southern Ukraine, met with international rejection.
- Diplomatic Efforts: Multiple attempts at ceasefire and peace talks, but the conflict continues with varying intensity.
- International Dynamics: Involvement and responses from global powers continue to shape the conflict.
International Context and Support
- Global Attention: Conflicts like Israel’s war on Gaza and potential changes in U.S. administration impact global focus and support for Ukraine.
- S. and NATO Support: Continued support from the U.S. and NATO is crucial for sustaining Ukraine’s resistance.
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization):
· Established in 1949 through the signing of the Washington Treaty, NATO is a security alliance consisting of 30 member countries from North America and Europe. · Finland recently joined NATO as its 31st member. · NATO’s primary objective is to protect the freedom and security of its member nations through both political and military means. · It operates under the principle of collective defense, where independent member states pledge mutual defense in the event of an external attack. · Article 5 of the Washington Treaty forms the cornerstone of the alliance, affirming that an attack on one member is considered an attack on all members, reinforcing the promise of collective defense. · NATO’s headquarters is located in Brussels, Belgium. Functions of NATO: · Political: NATO promotes democratic values and facilitates member consultations and cooperation on defense and security issues, aiming to resolve problems, foster trust, and prevent conflicts. · Military: While committed to diplomatic dispute resolution, NATO possesses the military capabilities to engage in crisis management operations if diplomatic efforts prove unsuccessful. |
Military Tactics and Responses
- Cross-Border Attacks: Ukraine’s use of advanced Western-supplied weapons has led to attacks inside Russia, escalating tensions.
- Suspicions and Misinformation: Both sides harbor deep mistrust and engage in misinformation, increasing the risk of further violence and accidents.
Call for Practical Assessment and Dialogue
- Need for Reassessment: Russia, Ukraine, and NATO should reassess the war’s progress realistically.
- Potential for Negotiations: There is an urgent need to consider dialogue over continuing a seemingly endless conflict that harms all involved parties.
| Geographic Details of Ukraine:
Ukraine, situated in Eastern Europe, boasts Kyiv (Kiev) as its capital, nestled along the Dnieper River in north-central Ukraine. Bordering Nations and Adjacent Bodies of Water:
· To the north, Ukraine shares its border with Belarus, while to the east, it neighbors Russia. · The southern boundary is marked by the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea, with Moldova and Romania as its southwestern neighbors. · In the west, Ukraine is flanked by Hungary, Slovakia, and Poland. · In the far southeastern region, Ukraine is separated from Russia by the Kerch Strait, which links the Sea of Azov to the Black Sea. |
Source
The Hindu
Mains Question
Q “Examine the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine in light of international law and geopolitics. Critically analyze the role of NATO and major global powers in this conflict. Suggest measures that could lead to a peaceful resolution, considering the current geopolitical scenario.”

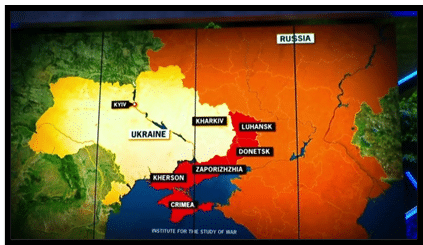 Source- NBCC NEWS
Source- NBCC NEWS Source- Britanica
Source- Britanica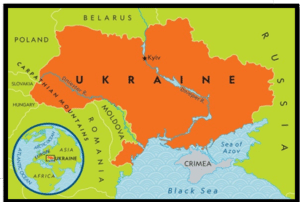 Source:- National Geography
Source:- National Geography

