ELIMINATING DISEASES, ONE REGION AT A TIME
Syllabus:
- GS 2 : Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health.
Why in the News?
- Recent report by The Carter Centre indicates near eradication of guinea worm disease, showcasing effectiveness of disease elimination.
- Disease elimination serves as precursor to eradication, aligning with global initiatives like SDGs targeting end of infectious diseases by 2030.
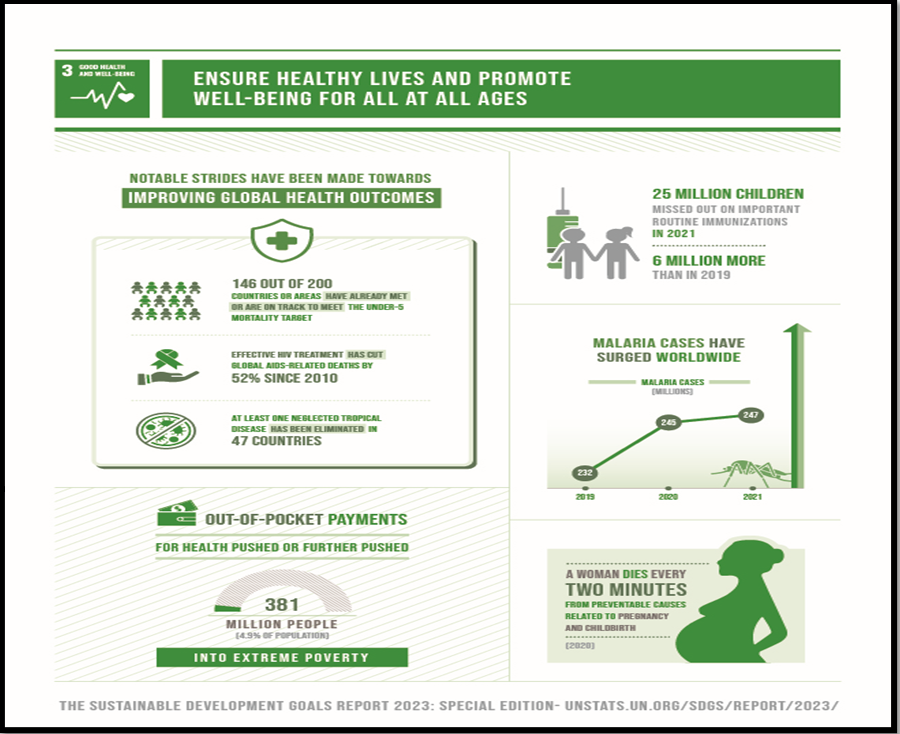
Source: Sdgs.un
Global Health:
- Progress Report :The Carter Center’s recent report highlights significant progress in disease elimination efforts globally.
- Preceding Eradication: Disease elimination precedes eradication and has garnered attention in light of the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Guinea Worm’s Decline : Guinea worm disease’s near eradication underscores the importance of disease elimination strategies.
- Global Health Focus : The focus on disease elimination aligns with global efforts to combat infectious diseases and improve public health.
- Collaborative Success: The success of disease elimination initiatives reflects the dedication and collaboration of various stakeholders in the healthcare sector.
- Public health initiatives : Public health initiatives have contributed to improved health outcomes and socioeconomic development worldwide.
Understanding Disease Elimination:
- Transmission Targets :Disease elimination strategies focus on achieving zero transmission within defined regions, strengthening healthcare systems, and mobilizing resources effectively.
- Energizing Systems: Enhancing primary healthcare infrastructure and disease surveillance are integral to successful elimination efforts.
- Strategic Planning : Strategic planning involves allocating resources efficiently, fostering political commitment, and promoting international cooperation.
- Planning Rigorously : Rigorous planning ensures sustainable funding mechanisms, technological advancements, and capacity building for long-term success.
- International Collaboration : International collaboration facilitates knowledge sharing, innovation, and best practices in disease elimination strategies.
- Socio Economic Impact : Successful disease elimination efforts contribute to improved health outcomes and socioeconomic development in affected regions.
Strategic Approach to Disease Elimination:
- Prioritizing Impact :Prioritizing diseases with high population impact and low prevalence ensures efficient resource allocation and maximum impact.
- Surveillance Systems : Comprehensive surveillance systems monitor disease incidence, guide intervention strategies, and assess progress towards elimination goals.
- Control Measures : Initial disease control measures aim to reduce prevalence to manageable levels, facilitating the transition to elimination strategies.
- Tailored Strategies : Tailored intervention strategies, including vector control, vaccination campaigns, and community engagement, address specific disease challenges.
- Sustainable Support: Sustainable funding mechanisms and political commitment are essential for sustaining disease elimination efforts over the long term.
- Targeted approach : A targeted approach to disease elimination enhances the effectiveness, efficiency, and sustainability of public health interventions.
Regional Focus for Effective Elimination:
- Geographic considerations : Geographic considerations inform regional disease elimination strategies, accounting for variations in disease burden, transmission dynamics, and healthcare infrastructure.
- Efficient Allocation: Efficient resource allocation at the regional level ensures optimal utilization of funds, manpower, and infrastructure for disease control and elimination.
- Collaborative Partnerships : Collaborative partnerships among stakeholders, including governments, healthcare providers, and community organizations, facilitate coordinated efforts and knowledge exchange.
- Community Empowerment: Community empowerment and engagement foster ownership, trust, and resilience, promoting sustainable health outcomes and behavior change.
- Monitoring Frameworks : Monitoring and evaluation frameworks at the regional level enable data-driven decision-making, adaptive management, and accountability in disease elimination programs.
| Initiatives for Disease Prevention and Control
1. National Health Mission (NHM): India’s flagship program to provide accessible and affordable healthcare services, focusing on maternal and child health, immunization, and non-communicable diseases. 2. Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): Health insurance scheme providing coverage for secondary and tertiary healthcare services to over 500 million vulnerable citizens. 3. Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI): Immunization program targeting high-risk populations to accelerate the coverage of routine immunization and achieve full immunization coverage. 4. National AIDS Control Programme (NACP): Initiative to prevent and control the spread of HIV/AIDS through prevention, care, support, and treatment services. 5. Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP): Government initiative to control the spread of tuberculosis through early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of TB cases. 6. National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): Program aimed at preventing and controlling non-communicable diseases through awareness, screening, early diagnosis, and treatment. 7. Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM): A sanitation campaign aimed at eliminating open defecation, promoting hygiene practices, and preventing waterborne diseases. 8. Ayushman Bharat: A health insurance scheme providing coverage for secondary and tertiary healthcare services to over 500 million vulnerable citizens. 9. Pulse Polio Program: Successful immunization initiative to eradicate polio through mass vaccination campaigns and routine immunization drives. 10. National Mental Health Program (NMHP): Aims to provide accessible mental healthcare services, promote awareness, and reduce stigma associated with mental illness. 11. Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY): Incentive-based program encouraging institutional deliveries to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality rates. 12. National Vector Borne Disease Control Program (NVBDCP): Focuses on preventing vector-borne diseases like malaria, dengue, and chikungunya through vector control measures and community awareness. |
Challenges and Considerations:
- Diseases with long incubation periods and high prevalence necessitate localized, phased elimination strategies.
- Sustaining surveillance efforts post-elimination is crucial to prevent pathogen reintroduction.
- Careful planning, informed decision-making, and stakeholder engagement are essential to optimize elimination outcomes.
Ownership and Implementation:
- Local Empowerment: Localized disease elimination initiatives empower communities, promote ownership, and foster resilience against future outbreaks.
- Multisectoral Partnerships: Multisectoral collaboration at the regional level integrates healthcare, education, and community development efforts, promoting holistic approaches to disease elimination.
- Capacity Building: Capacity building initiatives enhance local expertise, technological capabilities, and infrastructure resilience, strengthening the effectiveness and sustainability of elimination efforts.
- National Support: National governments play a crucial role in providing policy support, financial resources, and technical assistance for regional disease elimination initiatives.
- Community Engagement : Community engagement initiatives foster trust, promote behaviour change, and facilitate the adoption of preventive measures, contributing to sustained disease control and elimination.
National Scale-Up and Coordination:
- National and state governments play pivotal roles in providing technical support, resource mobilization, and oversight to regional elimination efforts.
- Union government’s involvement is paramount in addressing cross-state disease spread and controlling potential reintroduction.
Conclusion:
Disease elimination represents a pivotal strategy in the global fight against infectious diseases, paving the way for eventual eradication.
By adopting a regionally focused approach, countries can leverage localized successes to drive national elimination efforts effectively.
Sustained commitment, collaboration, and innovation are essential to overcome challenges and realize the vision of a disease-free world.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
“In the global endeavor to eliminate diseases, regional strategies play a crucial role. Discuss the significance of regional approaches in disease elimination efforts.