ELEVATED FOOD INFLATION: RBI TO HOLD RATES
Why in the news?
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is expected to keep policy rates unchanged during its meeting from August 6-8 due to elevated food inflation, according to Barclays India and Goldman Sachs Economics Research.
- Economists from both institutions highlighted the persistent upward pressure on food prices as a key reason for the MPC’s cautious approach.
Source: UGI
Economic Insights
- Barclays economists anticipate a 4-2 vote to maintain current policy settings, with no urgency to cut rates despite steady growth, potentially delaying rate cuts beyond December.
- They noted several factors for the MPC to consider, including halted disinflationary trends, fiscal consolidation commitments in the Union Budget, and indications of a potential U.S. Fed rate cut in September.
Future Inflation Risks
- Goldman Sachs economists pointed out that broad-based food inflation has kept headline inflation near 5% for the first half of 2024.
- They warned of upside risks to food inflation due to an uneven monsoon, even though a high base effect may bring headline inflation down towards 4% in Q3.
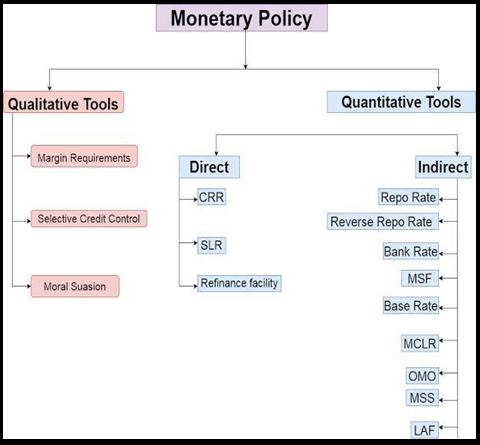
What is the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
Composition:
Associated Article: https://universalinstitutions.com/rbi-and-monetary-policy-in-india/
|