E-governance – Applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 e-Governance.
- Tags: #egov #digital #governance #egovernance #potential.
What is e-Governance?
e-Governance, short for electronic governance, refers to the use of information and communication technology (ICT) tools and digital platforms to enhance and streamline government operations, improve service delivery to citizens, facilitate communication between government and citizens, and promote transparency and efficiency in the functioning of government institutions.
e-Governance encompasses a wide range of digital technologies and practices aimed at transforming traditional government processes into digital, online, and accessible services.
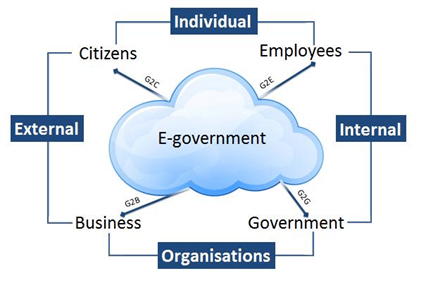
| G2C | G2E | G2B | G2G | |
| Target Audience | Citizens | Government Employees | Businesses and Corporations | Government Entities |
| Purpose | Delivering public services | HR management, payroll, etc. | Regulatory compliance, support | Inter-governmental cooperation |
| Data Sensitivity | Personal and sensitive info | Employee records, payroll data | Business data, financial info | Government data and policies |
| Frequency | Varied, often sporadic | Regular and ongoing | Transaction-based | Ongoing and as needed |
| Channels | Online, in-person, mail | HR systems, internal portals | Online portals, APIs | Data sharing platforms, forums |
| Goals | Citizen satisfaction, access | Employee efficiency, compliance | Business growth, compliance | Government efficiency, policy |
| Examples | Tax filing, license renewal | Payroll management, training | Permit application, procurement | Data sharing, policy coordination |
Governance Applications
E-Governance applications encompass a wide range of digital technologies and practices aimed at transforming traditional government processes into digital, online, and accessible services.
- Online Service Delivery: E-Governance enables citizens to access government services and information online. This includes services related to taxes, permits, licenses, healthcare, education, and more.
- For example, citizens can file their income tax returns online or apply for government licenses through web portals.
- Digital Identity Systems: Many countries have implemented digital identity systems that provide citizens with secure, unique identifiers for accessing government services.
- India’s Aadhaar is a notable example, providing a 12-digit unique identity number based on biometric and demographic data. Citizens can use Aadhaar for identity verification, opening bank accounts, receiving government subsidies, and more
- Government Portals: They provide a single point of access to various services, information, and resources. Citizens can use these portals to apply for government schemes, check the status of applications, and access government publications.
- GSTN is an IT platform for the administration of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Businesses use the GSTN portal for tax filing, return submission, and compliance.
- E-Healthcare: It is transforming healthcare by enabling electronic health records, telemedicine, and online appointment booking. Patients can consult with healthcare providers remotely, access medical records, and receive healthcare information online.
- E-Hospital enables patients to book appointments and access healthcare services online. AIIMS offers online appointment booking and access to medical records.
- E-Education: Educational institutions are using digital platforms for online learning, course registration, and examination management. E-Governance in education also includes providing digital resources and improving communication between students, teachers, and institutions.
- SWAYAM – Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is an e-learning platform that offers free courses and educational resources to students and teachers. Students can access video lectures and study materials on a wide range of subjects through SWAYAM.
- Digital Payments: Governments are promoting digital payments and financial inclusion through e-Governance.
- BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) and UPI (Unified Payments Interface) like applications promote digital payments and financial inclusion. Citizens can use BHIM or UPI apps to make cashless transactions, pay bills, and transfer money.
- India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) is an initiative to transfer government subsidies and benefits directly to beneficiaries’ bank accounts. Under PM-Kisan, farmers receive direct cash transfers to their bank accounts as a part of agricultural subsidies.
- E-Tendering and Procurement: E-Governance simplifies government procurement processes through e-tendering platforms. Vendors can submit bids electronically, making procurement more transparent and efficient.
- Indian Government e-Marketplace – GeM portal is an online platform for government procurement, enabling transparent and efficient e-tendering processes. Government departments and agencies use GeM to procure goods and services, simplifying the procurement process.
- Digital Citizenship: E-Governance encourages citizen engagement through digital platforms. Citizens can provide feedback, file complaints, and participate in surveys and discussions on government policies and initiatives.
- Data Management and Analytics: E-Governance applications include data management tools for government agencies. These tools help in collecting, storing, and analyzing data, enabling better decision-making and policy formulation.
- Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of citizen data is a critical aspect of e-Governance. Robust cybersecurity measures are put in place to protect sensitive information.
- DigiLocker is a cloud-based platform that allows citizens to store and access their important documents and certificates digitally.
E-Governance applications vary from one country to another and can encompass a wide range of government functions and services. The ultimate goal is to use technology to make government more responsive, efficient, and citizen-centric while promoting transparency and accountability.
Models of e-Governance
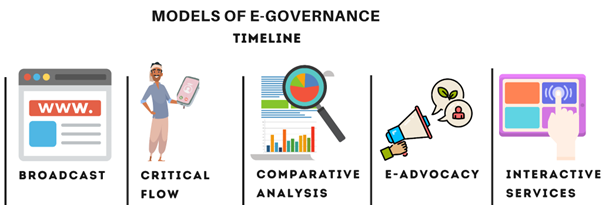
The models involve the use of information and communication technology (ICT) and convergent media to disseminate essential government information to the public domain. Depending on the particular conditions and governance requirements, Professor Arie Halachmi suggested five important models of e-governance –
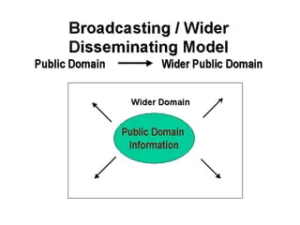
The Broadcasting Model
- This model is effective because an informed citizenry can better assess how government mechanisms function and form well-informed opinions.
- Consequently, citizens become more empowered to exercise their rights and responsibilities. The widespread application of this model addresses “information failure situations” by providing people with relevant governance-related information, enabling them to make informed judgments and influence governance processes.
- For instance, the “MyGov” platform serves as a communication channel for government announcements and citizen engagement.
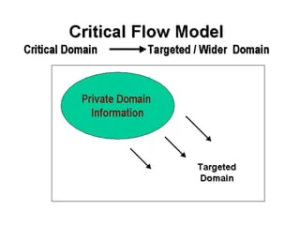
The Critical Flow Model
- This model’s strength lies in the fact that ICT eliminates the constraints of distance and time when information is stored on a digital network. This advantage allows for the immediate transfer of critical information to its intended user group, regardless of their location, or for making it readily accessible to the public at large.
- It streamlines specific functions, such as tax payments or permit applications.
- India’s Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) is an example of the Critical Flow Model. It allows businesses to file tax returns and pay taxes online, simplifying the taxation process.
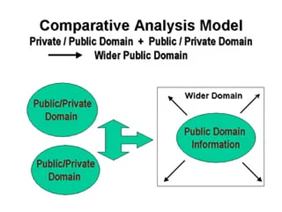
The Comparative Analysis Model
- This model holds immense significance for developing countries as it has the potential to empower people. Essentially, the model continually incorporates the best governance practices and uses them as benchmarks to assess other governance methods. It then utilizes the results to advocate for positive changes or influence public opinion regarding these governance practices.
- This comparison can be made over time to provide insights into past and present situations or to assess the effectiveness of interventions by comparing similar situations.
- The strength of this model lies in the limitless capacity of digital networks to store diverse information and instantly transmit it across geographical and hierarchical boundaries.
- This model enhances transparency and accountability.
- Example: The “Digital India” portal provides comparative data on government services and initiatives across different states and union territories, allowing citizens to assess the progress and performance of various programs.
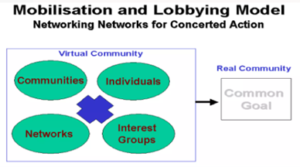
4. The E-Advocacy/Mobilization and Lobbying Model
- This model empowers global civil society by integrating virtual community input into real-world decision-making It facilitates information flow, fostering strong online alliances that complement physical actions.
- Diverse virtual communities are formed, collaborating with real-life groups. This model accumulates ideas, expertise, and resources through virtual networking, enabling collective action beyond geographical or institutional constraints.
- Example: “Change.org” is a platform used by Indian citizens to create and sign online petitions on various social and political issues, influencing policy debates and government actions.
5. The Interactive-Service Model
- This model creates opportunities for direct individual participation in governance processes, enhancing objectivity and transparency in decision-making through the use of ICT.
- Under this model, government services are made directly accessible to citizens in an interactive manner. It achieves this by establishing an Interactive Government-to-Consumer-to-Government (G2C2G) channel across various governance aspects, such as the election of government officials through e-ballots, online resolution of specific grievances, sharing of concerns and expertise, conducting opinion polls on various issues, and more.
- Example: The “Digital Locker” service where citizens can interact with government agencies and access various documents and certificates online, enhancing the ease of obtaining government services.
| Mains Question
Discuss various types of e-governance models. what are the advantages and disadvantages of e-governance models. |