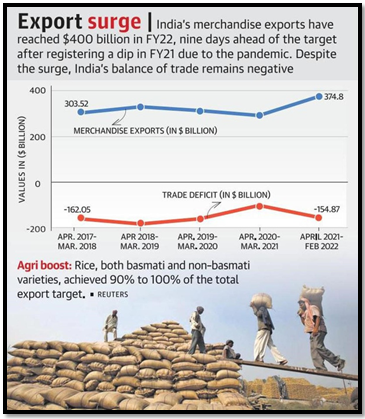
“DYNAMICS OF INDIA’S MERCHANDISE EXPORTS: TRENDS, CHALLENGES, AND PROSPECTS”
Syllabus:
- GS-3– Import , export and related issues and solutions . Role of WTO
Focus:
- The focus of the article is to analyze India’s merchandise export performance amidst global trade dynamics, including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical conflicts. It examines the trends, challenges, and prospects of India’s exports, highlighting sector-wise performance, regional dynamics, and the need to address the decline in labour-intensive sectors for sustained export growth.
Source-TH
Introduction
- Overview of the global merchandise trade scenario since 2022.
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical conflicts on global trade dynamics.
Global Merchandise Trade Trends
- Continuous decline in global merchandise exports as per UNCTAD data.
- Specifics of the 6% decline in global merchandise exports in 2023.
- Sequential improvement observed in the January-March 2024 quarter.
India’s Merchandise Export Performance
- India’s merchandise exports fell by 4.7% in 2023.
- Comparison with developing Asia’s overall decline of 6.8%.
- Total merchandise exports standing at $437.1 billion in 2023-24.
- Monthly data indicating a recovery trend, especially in the second half of 2023.
Factors Affecting India’s Merchandise Exports
- Influence of an uncertain global environment on India’s export performance.
- Impact of lower international commodity prices on India’s export bill.
- Notable contribution of crude oil price decline to the overall export decline.
About WTO:
|
Sector-wise Analysis of India’s Merchandise Exports
- Impact of declining commodity prices on overall merchandise exports.
- Sectors experiencing growth despite the challenging environment.
- Significant growth in electronics goods exports driven by telecom instruments.
- Rise in exports of pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, and agricultural products.
| Agreements under WTO :
1. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT): This agreement focuses on reducing barriers to international trade, such as tariffs and quotas, and promoting fair competition among member countries. 2. Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS): TRIPS establishes minimum standards for the protection of intellectual property rights, including patents, copyrights, and trademarks, to facilitate trade in goods and services. 3. Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS): GATS regulates trade in services among WTO member countries, covering various service sectors such as banking, telecommunications, and transportation. 4. Agreement on Agriculture (AoA): The AoA aims to liberalize agricultural trade and reform domestic agricultural policies to promote fair competition and market access for agricultural products. 5. Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT): TBT addresses technical regulations and standards that may affect trade, ensuring that they are transparent, non-discriminatory, and based on international standards whenever possible. 6. Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS Agreement): The SPS Agreement sets out rules for food safety and animal and plant health measures to protect human, animal, and plant life and health while minimizing disruptions to trade. 7. Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM Agreement): The SCM Agreement regulates the use of subsidies by governments and provides mechanisms for countervailing measures to address unfair trade practices related to subsidies. |
Regional Dynamics of India’s Exports
- Contrasting performance of exports to the US and the Euro region.
- Increasing exports to the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries.
- Noteworthy growth in gems and jewellery exports to the UAE.
Concerns and Priorities
- Decline in labour-intensive sectors’ exports like gems and jewellery, textiles, etc.
- Urgency to address the decline in labour-intensive exports as a priority.
- Drastic reduction in the share of labour-intensive categories in India’s exports.
Future Prospects and Challenges
- Positive outlook due to upward revision of global growth and trade projections.
- Expectations of healthy global growth and trade volume in 2024.
- Potential impact of bilateral free-trade agreements and manufacturing push on India’s exports.
- Caution regarding uneven global growth and geopolitical tensions as potential spoilers.
Source:INDIAN EXPRESS
Mains Practice Question :
GS-3
” Discuss the trends, challenges, and prospects of India’s merchandise exports in the context of the global trade scenario since 2022. What are the key factors influencing India’s export performance, and what measures should be prioritized to address the decline in labour-intensive sectors’ exports?.” (250 words)