“DIVERSIFYING PHARMA SUPPLY CHAINS: ADDRESSING CHINA’S DOMINANCE”
Syllabus:
- GS-1- Pharmaceutical industry and overdependence on China ,Strategic significance
Focus :
- The article highlights the need for diversifying pharmaceutical supply chains to reduce dependence on China, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. It explores the current reliance on China for medical supplies and discusses the potential partnership between the United States and India to enhance health security.
Source - ET
Pandemic Wake-Up Call
- The pandemic exposed the world’s over-dependence on China for critical medical supplies.
- China’s role in the origin of the coronavirus adds to the urgency of diversification.
- Buzzwords like “de-risking” and “China plus one” emerged to address the national security threat.
- The origin of the coronavirus in China underscored the geopolitical risks of such dependence.
Strategic Importance of APIs
China’s Dominance:
- China provides 40% of the global supply of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- It is also the primary producer of key starting materials (KSMs) and intermediates for APIs.
India’s Dependence:
- India relies on China for 70% of its APIs, including critical antibiotics like penicillin.
- Historically, India produced its own APIs but was undercut by China’s lower prices and higher volumes.
Recognizing the Need for Diversification
- Both the US and India acknowledge the concentration of pharma supply chains in one country.
- The diversification of supply chains is crucial for health security.
- The partnership on critical and emerging technologies can serve as a model for a similar collaboration on health security.
- Efforts to counter China’s dominance included denying it the edge in semiconductors and critical minerals.
- Focus on diversifying health security supply chains, however, has been inconsistent.
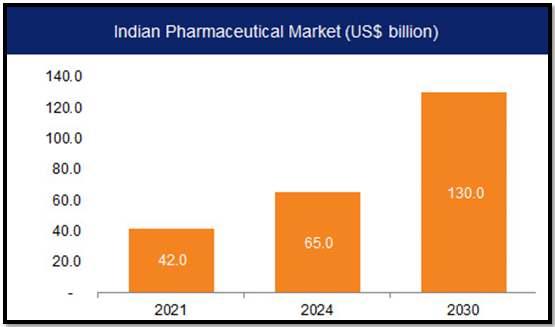
India’s Significance in the Pharma Supply Chain
- India is one of the largest suppliers of generic medicines to the US.
- Indian companies supply a significant percentage of drugs in various therapy areas.
- The US healthcare system saves billions of dollars through India’s generic drug supply.
India’s Efforts to Regain Self-Sufficiency
PLI Schemes:
- India is working to revive domestic production of basic ingredients for 41 products through Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes.
- Small companies face challenges in meeting government requirements.
Improving Standards:
- Indian pharma companies need to improve their standards to meet international norms.
- Addressing shortcomings and cleaning up practices are essential for global competitiveness.
| Schemes to promote India’s Pharmaceutical Industry :
1. Pharmaceuticals Export Promotion Scheme:
2. Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (PTUAS):
3. Jan Aushadhi Scheme:
|
Proposed Solutions
US-India Affordable Medicine Partnership:
- The Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA) proposed a partnership to reduce dependence on China.
- The partnership would focus on 500+ essential medicines listed by WHO.
Capitalizing on Strengths:
- The partnership aims to utilize India’s manufacturing expertise and infrastructure.
- It includes financial incentives, technology sharing, collaborative research, and technology transfers.
Aggregating Demand:
- The strategy involves aggregating US, Indian, and European demand for certain drugs.
- This would help in scaling up production and reducing costs.
US-India Collaboration Challenges
Big Pharma’s Influence:
- In the US, big pharmaceutical companies have been working to discredit Indian companies.
- Encouraging lawsuits and highlighting deficiencies have been tactics used against Indian pharma.
Navigating the Landscape:
- The pharma landscape is complex and requires careful navigation for future collaboration.
- Health security is intertwined with economic and national security.
Conclusion
Future Collaboration:
- Strengthening US-India collaboration in the pharmaceutical sector is crucial for global health security.
- Diversifying supply chains away from China will enhance resilience against future crises.
Actionable Steps:
- Establishing a bilateral framework, improving transparency, and addressing market failures are immediate steps.
- Leveraging each country’s strengths will pave the way for a more secure and diversified pharmaceutical supply chain.
Source:The Economic Times
Associated Article :
https://universalinstitutions.com/india-china-partnership/
Mains Practice Question :
GS-1
“Discuss the significance of diversifying pharmaceutical supply chains to reduce dependence on China. Analyze the potential partnership between the United States and India in enhancing health security and countering China’s monopolistic dominance. “(250 words)