Discuss in detail the photochemical smog emphasizing its formation, effects and mitigation. Explain the 1999 Gothenburg Protocol.
Introduction:
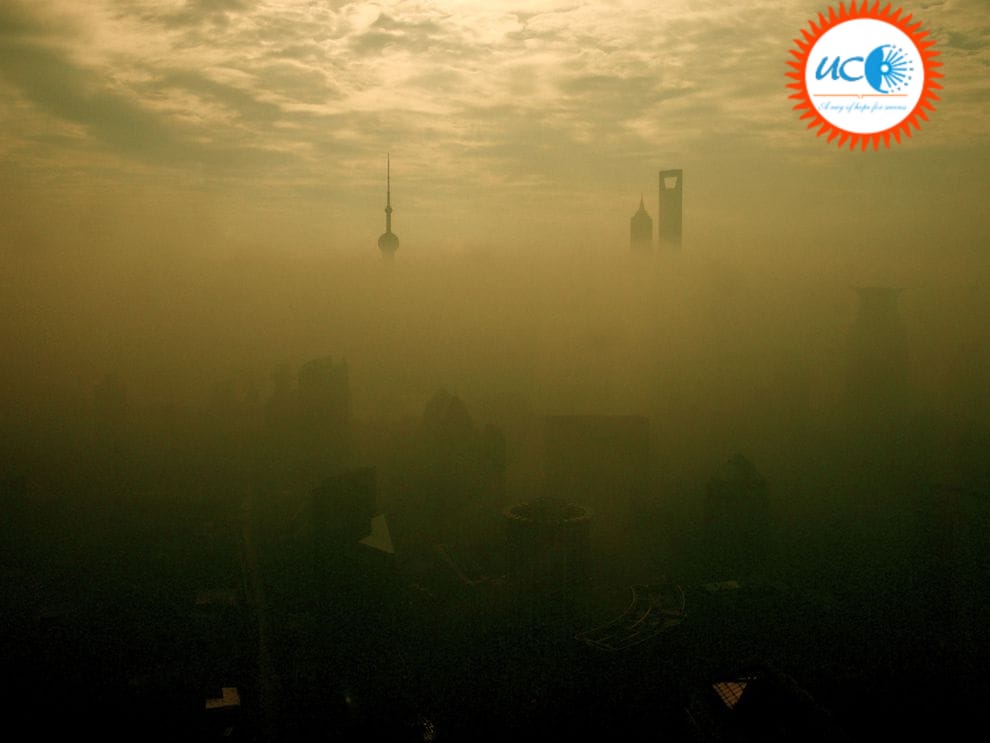
Summer smog, also known as photochemical smog, is a form of smog that develops when UV light from the sun reacts with the nitrogen oxides in the air. A complicated series of chemical processes involving sunlight, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic chemicals that are present in the atmosphere as a result of air pollution lead to the formation of it.
When smog chemicals and hydrocarbons interact, they produce compounds that irritate the eyes. The nitrogen cycle is hampered by the atmospheric radicals because ground-level ozone cannot be removed. Ozone at ground level has the potential to be exceedingly hazardous to people.
1999 Gothenburg Protocol:
- Sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and ammonia emissions ceilings were established by the 1999 Gothenburg Protocol to Abate Acidification, Eutrophication, and Ground-Level Ozone and must be met by 2010.
- The Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution Convention includes the Protocol.
- The Convention is an international agreement to manage and reduce air pollution, particularly long-range transboundary air pollution, in order to protect human health and the environment from air pollution.
Mitigation of Photochemical smog:
The most obvious way to minimize photochemical smog levels is to eliminate the use of fossil fuels by using non-polluting or sustainable sources of electricity, such as nuclear power, hydropower, and wind power.
- Catalytic reduction can be used by both automobiles and industries to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions. Nitrogen oxide emissions could be decreased by using less air during combustion.
- Reducing VOCs by using liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) or compressed natural gas (CNG) instead of gasoline (LPG). promoting and making use of public transportation, including buses.
- The usage of biofuels has drawn interest as a potential way to cut back on unpleasant urban pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
- Vehicles powered by electricity and hydrogen are better for the environment.
- Electricity produced using green, renewable energy sources.
Conclusion Thus Photochemical smog is primarily caused by anthropogenic causes, thus public needs to be aware of it and needs to follow the measures to reduce Photochemical smog.