DEVELOPMENTS THAT RATTLED CHINA IN A FORTNIGHT
Syllabus:
- GS 2: India and its Neighbourhood- Relations.
Why in the news ?
Recent developments in Sino-Indian relations and India’s strategic achievements spark tensions and objections from China.
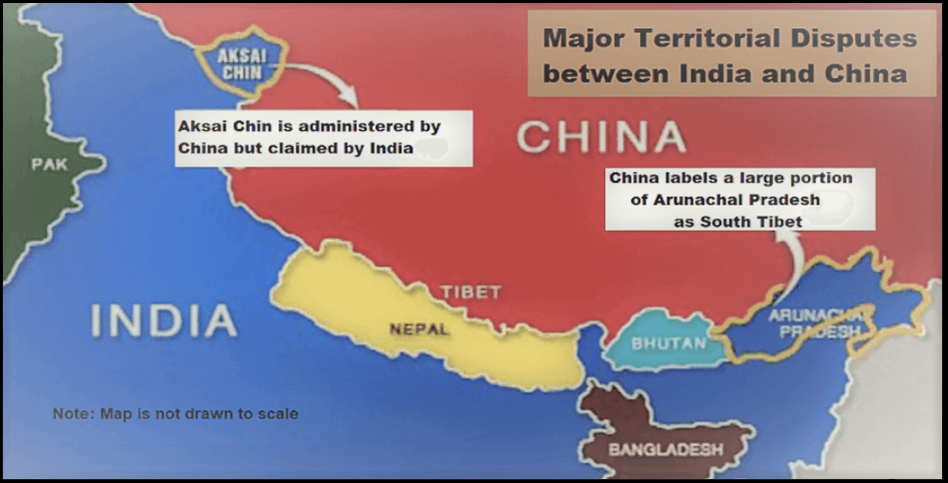
About the Causes of the India-China Conflict:
- Territorial Disputes: The lack of a clearly demarcated border and the
absence of a mutually agreed Line of Actual Control (LAC) have led to frequent tensions and confrontations along the India-China border.
- Historical Conflicts: Past conflicts, such as the 1962 Indo-China war, have left unresolved territorial disputes and deep-seated mistrust between the two countries.
- Strategic Partnerships: India and China’s partnerships with each other’s main adversaries, such as the Soviet Union/Russia and the United States, have hindered efforts to establish strategic cooperation between them.
source: tribuneindia
- Power Imbalance: China’s significant economic and military superiority over India has created a power imbalance, making it challenging for India to assert its interests without risking escalation.
- Infrastructure Development: China’s extensive infrastructure development in Tibet, including military installations and transportation networks, has raised security concerns for India and contributed to a security dilemma.
- Regional Competition:
Competition for influence in South Asia and beyond has led to geopolitical rivalries between India and China, exacerbating tensions along their shared borders.
- Nationalism and Domestic Politics: Nationalistic sentiments and domestic political considerations in both countries often fuel tensions and inhibit diplomatic efforts to resolve disputes peacefully.
- Geopolitical Ambitions: Both India and China harbour ambitions for regional and global influence, leading to competition and occasional clashes as they seek to assert their interests.
- Border Incursions: Incidents of border incursions by both Indian and Chinese troops, often driven by strategic or tactical objectives, have further strained bilateral relations.
- Lack of Dialogue and Trust: A lack of consistent dialogue and trust-building measures between India and China has perpetuated misunderstandings and increased the risk of conflict escalation.
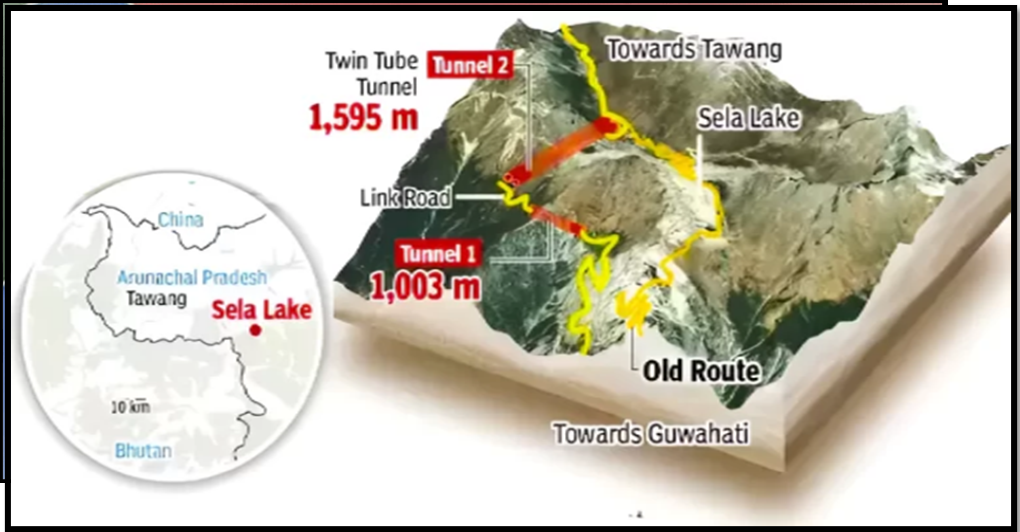
| Understanding SELA Tunnel :
● Location: West Kameng District, Arunachal Pradesh. ● Purpose: Provides all-weather connectivity to Tawang. ● Components: Includes Tunnel 1 (980m long single tube) and Tunnel 2 (1555m long twin tube). ● Altitude: Constructed above 13,000 feet, one of the highest tunnels. ● Additional Roads: Seven-kilometre approach road from BCT Road and 1.3-kilometer link road connecting Tunnel 1 to Tunnel 2. ● Foundation Stone: Laid by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2019. Benefits: ● Faster Transport Route: Provides a faster and strategically important transport route for India. ● ll-Weather Connectivity: Ensures all-weather connectivity to Tawang via Sela Pass on the Northeast region road. ● Boosts Armed Forces’ Preparedness: Enhances the preparedness of the Armed Forces with improved infrastructure. ● Improved Travel: Enhances ease of travel for residents of Tawang. About the Border Roads Organisation (BRO): ● Formation: Established in 1960 by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru to secure borders and develop infrastructure in remote north and northeast areas. ● Administrative Control: Operates under the Ministry of Defence in 2015. ● Motto: “Shramena Sarvam Sadhyam” (everything is achievable through hard work). |
About Developments in Sino-Indian Relations:
- Sela Tunnel Inauguration:
- Prime Minister Modi inaugurated the Sela Tunnel, costing ₹825 crore, at 3,000 metres
- China objected due to Arunachal Pradesh’s territorial claim and India’s assertion of sovereignty.
- Strategic Significance:
- The tunnel enhances rapid troop deployment to Arunachal Pradesh, boosting India’s strategic confidence.
- It acts as a force multiplier for India’s military in border regions, including Kameng.
- Military Implications:
- Provides a psychological boost to India’s military commanders.
- Facilitates all-weather troop induction, crucial for maintaining border security.
- Technological Advancements:
- Agni-5 Missile Test:
- India tested the Agni-5 missile with Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle (MIRV) technology.
- MIRVs enhance India’s nuclear deterrence capability by targeting multiple locations.
- Strategic Implications:
- India’s technological advancements worry China, affecting its perceived strategic advantage.
- China aims to maintain dominance, viewing India’s progress as a threat to its regional hegemony.
Importance of Arunachal Pradesh from Indian/Chinese perspective:
Strategic Significance:
- Arunachal Pradesh, formerly known as NEFA, is the largest state in Northeast India.
- It shares international borders with Tibet, Bhutan, and Myanmar, making it strategically significant.
- Acts as a protective shield for the northeast region of India.
Territorial Dispute:
- China claims Arunachal Pradesh as part of southern Tibet, leading to a territorial dispute.
- China’s primary interest lies in Tawang district, situated in the north-western region of Arunachal Pradesh, bordering Bhutan and
China’s Response and Concerns:
- Hostility and Provocations:
- China resorts to various measures to keep India on the defensive, including military manoeuvres.
- Recent provocations include maritime encroachments and aggressive posturing along the
- Grey Zone Relations:
- Keeping Sino-Indian relations ambiguous hinders mutual progress.
- China’s reluctance to acknowledge India’s rise impedes bilateral cooperation.
Way Forward/Future Prospects:
- India’s Growth Potential:
- India possesses the potential to emerge as a significant global player.
- Technological achievements and demographic advantages position India for rapid growth.
- Opportunities for Collaboration:
- India’s progress can benefit both nations through collaboration and cooperation.
- Addressing misperceptions and building trust is crucial for fostering constructive relations.
Conclusion:
Both nations must recognize each other’s aspirations and potential. Maintaining a cooperative relationship is essential for regional stability and global prosperity. Resolving misunderstandings and promoting dialogue can pave the way for mutually beneficial collaboration. Embracing India’s rise as a middle power offers opportunities for shared growth and prosperity.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the strategic significance of the Sela Tunnel , along with the implications of India’s technological advancements, particularly the Agni-5 missile test.