Describe in brief the causes and impact of Glacier melting.
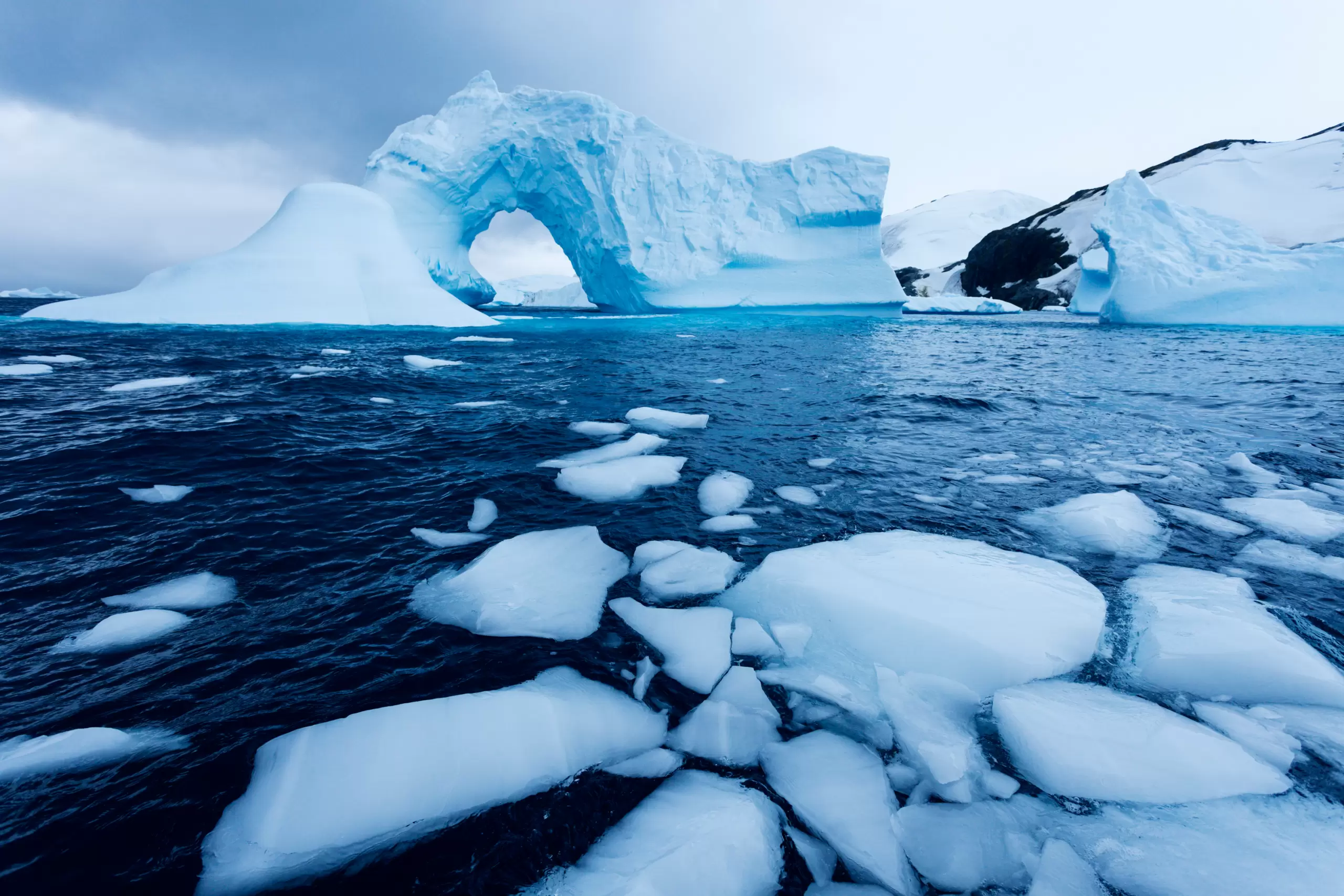
The melting of the glaciers, a phenomenon that intensified in the 20th century, is leaving our planet iceless. Human activity is the main perpetrator in the emission of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses which disturb the heat balance causing the threat of global warming. The sea level and global stability depend on how these great masses of ice i.e. glaciers evolve.
Causes of glacial melting:
The rising temperature of the Earth has, without doubt, been responsible for melting glaciers throughout history. Today, the speed with which climate change is progressing might render them extinct in record time.
- CO2 emissions: The atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses (GHGs) produced by industry, transport, deforestation and burning fossil fuels, amongst other human activities, warm the planet and cause glaciers to melt.
- Ocean warming: Oceans absorb 90% of the Earth’s heat, and ocean currents are a major medium to transfer this heat. However global warming alters the cycle and this fact affects the melting of marine glaciers, which are mostly located near the poles and on the coasts of Alaska.
- Increasing Albedo: The increase in black carbon deposits produced by human activities on the glaciers have increased the albedo which has further enhanced the glacier melting, as suggested by the IPCC’s Vill assessment report.
- Ice breaking ships: During the months of summer, icebreaking ships head to the north into the Arctic Ocean, breaking through the ice at sea, the ships end up leaving trails of open waters. The Arctic sea ice is able to reflect most of the heat thus aiding in keeping the Arctic and the rest of the Northern Hemisphere cool.
Impacts of glacial melting:
- level rise: Glacial melting has contributed to rising sea levels by 2.7 centimeters since 1961. Furthermore, the world’s glaciers contain enough ice to raise sea levels by nearly half a meter.
- Impact on the climate: Glacial thawing at the poles is slowing the oceanic currents, a phenomenon related to altering the global climate and a succession of increasingly extreme weather events throughout the globe.
- Disappearance of speci.: Glacial melting will also cause the extinction of numerous species, as glaciers are the natural habitat of a number of animals, both terrestrial and aquatic. An estimated 22 % of aquatic species are prone to face local extinction according to researchers.
- Reduced source of fresh water: The disappearance of glaciers also means less water for consumption by
the population, a lower hydroelectric energy generation capacity and less water available for irrigation.
Suggestive measures:
- Address the issue of climate change: In order to curtail climate change and save the glaciers, it is indispensable that global CO2 emissions be reduced by 45 % over the next decade, and that they fall to zero after 2050.
- Combine artificial icebergs: Indonesian architect Faris R Kota Hatuhaha won an award for his project Refreeze the Arctic, which consists of collecting water from melted glaciers, desalinating it and refreezing it to create large hexagonal ice blocks.
- Increase their thickness: The University of Arizona proposed a seemingly simple solution of manufacturing more ice. Their proposal consists of collecting ice from below the glacier through pumps driven by wind power to spread it over the upper ice caps, so that it will freeze, thus strengthening the consistency.
Conclusion
Governments must focus on creating enabling environments and empower institutions so that researchers could that valuable information at the regional and global level and try and come to remedial
solution.