Declining Health Spending Risks Achieving SDG Targets
Why in the news?
Health spending in low-income and middle-income countries, including India, has decreased post-pandemic, endangering progress toward Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and public health targets.
Post-Pandemic Health Budget Trends:
- Government health spending in low-income countries (LICs) and lower-middle-income countries (LMICs) has seen a sharp decline after pandemic-related increases.
- A study by the World Bank analysed government health spending from 2019 to 2023 and compared it to pre-pandemic periods (2015-2019), revealing a reversal in the upward trend for health budgets.
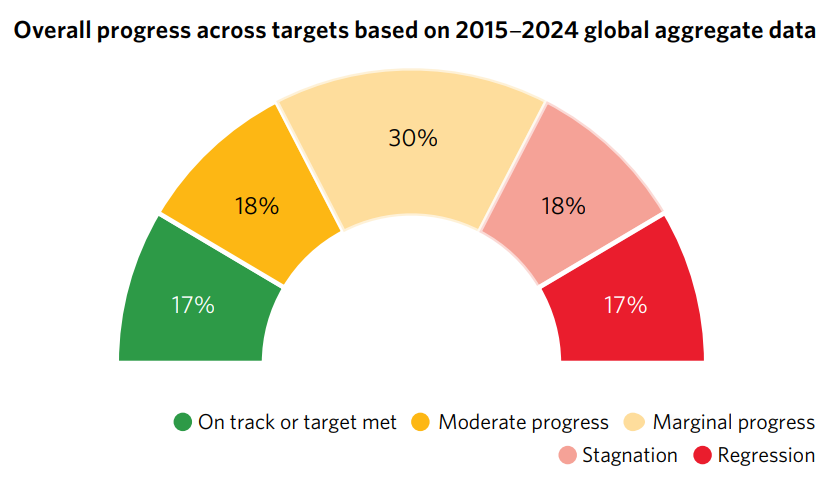
Impact on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- The decline in health spending poses risks to achieving health-related SDG targets.
- As countries approach the SDG deadline, this reduction hampers the momentum needed to address health priorities, particularly for LICs and LMICs where public health funding has become insufficient.
- Projections from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) suggest that budgets in 23 countries, including India, may contract between 2023 and 2029, forcing tough decisions on health spending.
India’s Health Budget Decline:
- India’s health share in the national budget fell below the 2% mark post-pandemic, dropping from around4% in FY18 to about 1.75-1.85% in the years following the pandemic.
- This drop reflects a broader global trend of decreasing health budget allocations amidst rising government expenditure.
- The shift poses challenges for sustaining health infrastructure and services, particularly in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic.
About Sustainable Development:
Sustainable Development: Development that meets current needs without compromising future generations’ ability to meet their needs. It focuses on balancing economic, social, and environmental aspects for long-term global progress.
17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- No Poverty: End all forms of poverty.
- Zero Hunger: Achieve food security and sustainable agriculture.
- Good Health and Well-Being: Promote health for all.
- Quality Education: Ensure inclusive education.
- Gender Equality: Empower women and girls.
- Clean Water and Sanitation: Sustainable water management.
- Affordable and Clean Energy: Provide sustainable energy for all.
- Decent Work and Economic Growth: Promote inclusive economic growth.
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Build resilient infrastructure.
- Reduced Inequality: Address inequality globally.
- Sustainable Cities and Communities: Create safe, resilient
- Responsible Consumption and Production: Promote sustainable production.
- Climate Action: Combat climate change.
- Life Below Water: Protect marine resources.
- Life on Land: Preserve terrestrial ecosystems.
- Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions: Promote justice and effective institutions.
- Partnerships for the Goals: Strengthen global cooperation.
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/aligning-higher-education-with-the-united-nations-sdgs/