Daily News Analysis.
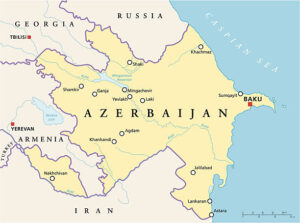
Talks have opened on future of Nagorno-Karabakh as Azerbaijan claims full control of region.
News: The “reintegration” of Nagorno-Karabakh into Azerbaijan will be the main topic of discussion during the discussions between regional leaders and the Baku government on Thursday, according to officials and the Azerbaijan State News Agency.
Issues:
- One of the most prominent and longstanding issues for Azerbaijan has been the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict.
- This conflict, which began in the late 1980s and escalated into a full-scale war in the early 1990s, revolves around the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region and seven adjacent districts.
- The conflict resulted in significant loss of life and displacement of people, with Armenia gaining control over Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding areas.
- Azerbaijan’s role in this issue has primarily been that of the aggrieved party seeking to regain control over its territory.
Azerbaijan’s role in the energy sector has made it an important player in regional and global energy geopolitics, as well as contributing to its economic development.
About Azerbaijan
- Azerbaijan’s geographical location has made it a key player in regional geopolitics. It shares borders with Russia, Iran, Georgia, Armenia, and Turkey, and its relationships with these neighboring countries have had a significant impact on its foreign policy.
- Azerbaijan has sought to balance its relationships with Russia, which has historical ties to the region, and with the West, particularly the United States and the European Union.
- It has also pursued closer ties with Turkey, which shares cultural and historical connections. Navigating these relationships while maintaining sovereignty and pursuing its interests has been a critical challenge and role for Azerbaijan.
Paryushana Parv
News: Paryushana Parv, often simply referred to as Paryushan, is one of the most significant and spiritually important festivals in Jainism.
- This annual observance typically lasts for eight to ten days and is a period of intense introspection, reflection, and spiritual renewal for Jain practitioners.
- During Paryushan, Jains focus on various spiritual practices, including fasting, meditation, prayer, and acts of compassion.
- The primary objective is to attain a deeper level of self-purification, strengthen one’s faith, and seek forgiveness for any harm caused to other living beings intentionally or unintentionally.
- It is a time for Jains to intensify their commitment to non-violence (ahimsa), truth (satya), non-possessiveness (aparigraha), and other Jain principles.
- The culmination of Paryushan is often marked by the Samvatsari Pratikraman, a special ritual of seeking forgiveness and reconciling with others.
- Jains ask for and grant forgiveness to one another, symbolizing the importance of letting go of grudges and promoting harmony and forgiveness in their lives.
- Paryushan Parv is not only a time of personal spiritual growth but also a period when Jains strengthen their sense of community and unity, coming together to observe and celebrate their faith.
- It is a time of reflection, forgiveness, and renewal of one’s commitment to Jain principles.
In Wrestling, India’s Antim Panghal wins bronze medal at World Championships in Serbia.
News: In the women’s 53 kg division, young Indian wrestler Antim Panghal won a bronze medal yesterday at the ongoing World Championships in Belgrade, Serbia.
- He also got India’s quota for the 2024 Summer Olympics in Paris. In the bronze medal match, 19-year-old Antim defeated two-time European Champion Emma Jonna Denise Malmgren, 16–6.
- This is the first medal that India has won in the current competition. Antim has won one gold, five silver, and seventeen bronze medals in the World Championships, making it India’s 23rd medal winner overall.
- In the first round, Antim Panghal defeated USA’s Dominique Olivia Parrish, the 2022 world champion, 3-2.
- After defeating Roksana Marta Zasina of Poland in the round of 16, the Indian grappler defeated Natalia Malysheva of Russia 9–6 in the quarterfinals. In contrast, Antim lost to Belarus’ Vanesa Kaladzinskaya in the women’s 53kg freestyle semifinals of the 2023 World Championships by a score of 5–4.
SHREYAS National Fellowship Scheme benefits more than 21,000 SC students for Higher Education
News: The “SHREYAS” umbrella programme is made up of four sub-schemes for the central sector: “National Fellowship for SCs,” “Free Coaching Scheme for SCs and OBCs,” “Top Class Education for SCs,” and “National Overseas Scheme for SCs.” State-by-state data is not kept up to date for any of these sub-programmes because they are all central sector schemes.
The following is a summary of the SHREYAS sub-schemes, including the allotted budget, information on expenses, and the number of beneficiaries for the last nine years, or from 2014 to 2015:
- Free Mentoring Programme for OBCs and SCs.
- In order to enable economically disadvantaged Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) candidates to appear in competitive and entrance examinations for appropriate jobs in the Public/Private Sector as well as for admission in reputable technical and professional higher education institutions, the Scheme aims to provide high-quality coaching.
- Under the scheme, a family’s annual total income is limited at 8 lakhs. There are 3500 spots available annually.
- In each category, 30% of the spots are set aside for female students, with the SC:OBC student ratio being 70:30.
- Should a sufficient number of candidates in the SC category not be available, the Ministry may choose to lower this percentage. Less than 50% of SC pupils, however, will never be allowed.
- 19,995 recipients have benefited from the discharge of 109.77 crore rupees between 2014–15 and 2022–2023 in total.
Statue of Oneness
News: On September 21, 2023, the Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh will dedicate a large statue of Saint Adi Shankaracharya in Omkareshwar.
- “Ekatmata Ki Pratima” (Statue of Oneness) is the name of the 108-foot-tall statue honoring the prominent and renowned person in Hinduism from the eighth century.
- The imposing building is located in Omkareshwar, in the Khandwa district, atop the Mandhata hill, near the banks of the Narmada river.
- One of Lord Shiva’s twelve Jyotirlingas is located in the temple town of Omkareshwar, which is currently being developed as a global center for the Advaita Vedanta school of thought.
- After making the long journey from Kerala, Adi Shankaracharya met and studied under his Guru Govind Bhagwadapad for four years in Omkareshwar.
Advait Vedanta
|