Cybersecurity Responsibility Clarified by Government Amendment
Why in the news?
The Centre’s recent amendment to the Allocation of Business Rules has clarified ministry responsibilities for cybersecurity in India, enhancing coordination and strategic direction under the National Security Council, while addressing the critical skills gap in the field.
About the Recent Amendment:
- The Centre amended the Allocation of Business Rules, 1961, resolving ambiguity regarding the ministry responsible for cybersecurity in India.
- National Cyber Security Coordinator, Lieutenant General MU Nair, emphasised this change during the India Mobile Congress.
New Responsibilities:
- Cybersecurity has now been included in the business rules, assigning specific responsibilities to various ministries.
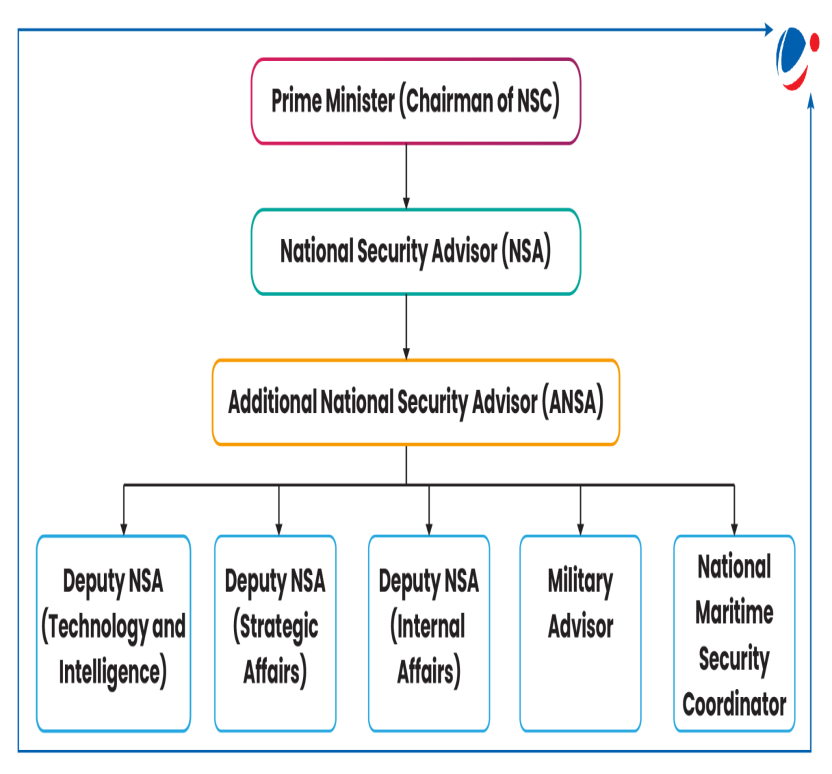
- The National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) will oversee coordination and strategic direction in cybersecurity, enhancing management of national security objectives
Skills Gap in Cybersecurity:
- Addressing Skill Deficiency:
- Nair highlighted a significant skills gap in the cybersecurity field, noting that many computer science graduates lack adequate knowledge in this domain.
- He urged for urgent attention to bridge this gap, given the rising importance of cybersecurity.
About National Security Council’s Role:
- Overview of NSCS:
- The NSCS, headed by the Prime Minister, is the highest decision-making body for national security in India.
- The National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC) functions under the NSCS, with Lieutenant General MU Nair being the third individual in this role.
What is Cyber Security?
- Threat Landscape: India ranks second globally for targeted cyber attacks, with banking and telecom as the most affected sectors; manufacturing, healthcare, and retail also experience significant threats.
- Definition: Cyber Security protects cyberspace and critical information infrastructure from attacks, damage, misuse, and economic espionage.
- Cyber Space: A global domain encompassing interconnected information technology infrastructures, including the Internet and telecommunications networks.
- Critical Information Infrastructure (CII): Defined by the IT Act as resources whose incapacitation or destruction would severely impact national security, economy, public health, or safety.
- Cyber Attack: A malicious attempt by an individual or organisation to breach another’s information system.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times