CRISPR THERAPEUTICS: REVOLUTIONIZING GENETIC MEDICINE
Why in the News ?
- Global Recognition: UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency approved exagamglogene autotemcel for sickle-cell disease and ß-thalassemia.
- Dual Approval: S. FDA also sanctioned it for sickle-cell disease, making it a pioneering CRISPR-based therapeutic approved by two major regulators.
Source: Science in News
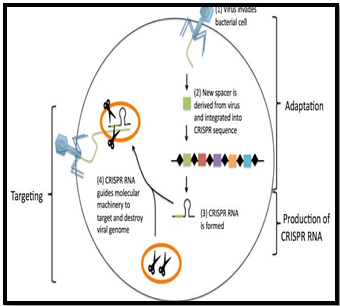
About CRISPR technology:
- Overview: CRISPR, or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, is a gene editing technology inspired by bacteria’s natural defence mechanism against viruses, utilizing the Cas9 protein.
- Genetic Engineering Process: CRISPR involves manipulating genes, either adding new ones or suppressing existing ones, constituting a form of genetic engineering.
- No External Gene Introduction: Unlike some genetic engineering methods, CRISPR doesn’t introduce external genes but works with the organism’s existing genetic material through the CRISPR-Cas9 system.
- CRISPR-Cas9 as ‘Genetic Scissors’: CRISPR-Cas9 is often referred to as ‘Genetic Scissors’ for its precision in cutting and modifying genetic material, making it a powerful tool in genetic manipulation.
CRISPR Evolution:
- Three-Decade Journey: CRISPR discovery resulted from 30 years of academic pursuit, evolving from DNA elements in archaea to a powerful genome-editing tool.
- Molecular Scissors: CRISPR-Cas9 system emerged as a programmable ‘molecular scissor’ in 2012, allowing precise editing of DNA.
Medical Milestones:
- Casgevy Approval: UK and US approvals for Casgevy mark a monumental leap in treating sickle-cell disease at its molecular basis.
- First-Generation Technologies: While ground breaking, these approvals represent first-generation CRISPR technologies.
Advanced Approaches:
- Base Editing: Cutting-edge base-editing refines genome editing at a single nucleotide level.
- Prime Editing: Researchers explore a ‘search-and-replace’ strategy for accurate sequence insertion.
- Epigenetic Modification: CRISPR applications extend to modifying epigenetic effects in a targeted manner.
Future Considerations:
- Safety Challenges: Concerns include off-target CRISPR-Cas9 events, requiring a balance between risks and benefits.
- Technological Scrutiny: Ongoing surveillance will uncover potential side effects as these therapies advance.
Optimistic Outlook:
- Patient Impact: Approvals like Casgevy offer hope for millions with genetic diseases, signalling a promising era in genetic medicine.
- Continuous Advancements: Despite challenges, the future of CRISPR technologies holds tremendous promise for genetic engineering and medical advancements.

 Source: Science in News
Source: Science in News

