COURT REVERSES RAPE CONVICTION OVER DNA EVIDENCE
Why in the news?
The Madras High Court overturned a rape conviction due to overreliance on DNA evidence, highlighting its limitations and the need for corroborative evidence in criminal cases.
source:wikimedia
About DNA Profiling and Its Legal Implications:
- Court Case and Judgment:
- Recent Ruling: The Madras High Court overturned a rape conviction, finding that reliance on DNA evidence alone was insufficient.
- Case Details: The conviction was based on a DNA test showing a 99.999999998% probability of paternity, but the victim later admitted to false accusations.
- Court’s Findings: The judges concluded that the prosecution failed to prove the case beyond reasonable doubt.
- DNA Evidence and Its Reliability:
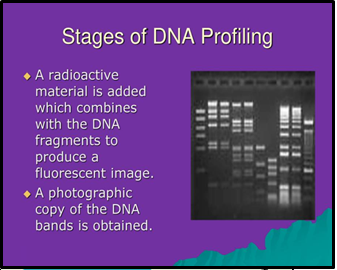
- How DNA Works: DNA, present in all cells, is used in forensic profiling by examining specific genetic markers called Short Tandem Repeats (STRs).
- Limitations: DNA profiling is probabilistic, not infallible, and can be compromised by issues like contamination or procedural errors.
- Forensic Concerns: Issues like sample contamination and procedural flaws can affect the reliability of DNA evidence.
- Legal Perspective on DNA Evidence:
- Probative Value: DNA evidence is not conclusive proof of identity; it indicates likelihood based on statistical analysis.
- Court Precedents: Previous cases highlight that while DNA is valuable for investigations, convictions should not rely solely on DNA without corroborative evidence.
- Future Outlook: Although DNA accuracy is improving, it cannot yet be deemed infallible; hence, absence of DNA evidence should not be used to infer guilt.
About Deoxyribonucleic Acid(DNA):
Types of DNA:
Functions of DNA:
About DNA Profiling Bill:
Institutions:
|