Contempt of Court
Context: The Supreme Court Monday imposed a fine of Rs 10 lakh on the Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation Limited (MMRCL) for contempt of court. This was in relation to the MMRCL seeking permission from the superintendent of gardens and trees to fell 185 trees in the Aarey forest area for the metro rail project — more than double the figure of 84 that it had mentioned in its application to the top court in 2019.
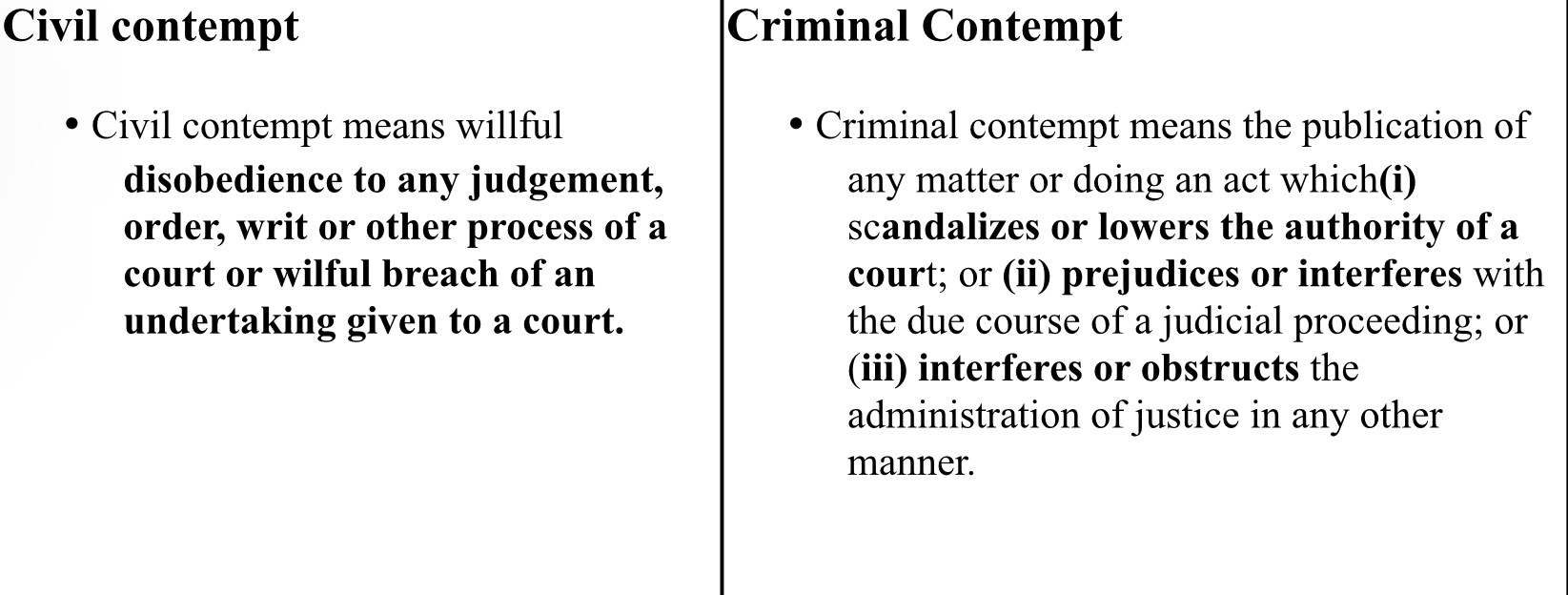
- The Supreme court and High Court have the power to punish for contempt of court, either with simple imprisonment for a term up to six months or with fine up to ₹2,000 or with both.
- In 1991, the Supreme Court ruled that it has power to punish for contempt not only of itself but also of high courts, subordinate courts and tribunals functioning in the entire country.
- Contempt of Courts Act, 1971 empowers the High Courts to punish contempt of its subordinate courts.
- The Attorney-General’s Consent is not required when the Supreme court or High Court itself initiates contempt proceeding.
Some important cases related to contempt of court in India
- Prashant Bhushan Case: In 2020, the Supreme Court found lawyer and activist Prashant Bhushan guilty of contempt of court for his tweets criticizing the judiciary. He was fined Re 1 by the court.
- Arundhati Roy Case: In 2002, author and activist Arundhati Roy was found guilty of contempt of court for her article in a magazine criticizing the Supreme Court’s decision to grant bail to a person accused of attacking the Indian Parliament. She was fined Rs. 2,000 by the court.
- C. Saxena Case: In 1996, the Supreme Court found D.C. Saxena, an environmentalist, guilty of contempt of court for filing a false affidavit in a case related to the pollution of the Ganga river. He was sentenced to one-month imprisonment and fined Rs. 10,000.
- Asok Pande Case: In 1978, Asok Pande, a Member of Parliament, was found guilty of contempt of court for his statements criticizing the judiciary. He was sentenced to three months’ imprisonment.
- N. Duda Case: In 1988, P.N. Duda, a lawyer, was found guilty of contempt of court for shouting at a judge during a court proceeding. He was sentenced to one-month imprisonment.
| Practice Question
What is contempt of Court? Explain it’s constitutional provisions and types? |