COMPREHENSIVE REFORMS NEEDED FOR MUNICIPAL ELECTIONS
Syllabus:
- GS 2 : Separation of Power , Local Self Governance.
Why in the News?
- The editorial primarily focuses on highlighting the issues and challenges faced in conducting municipal elections in India.
- It underscores the need for standardized election procedures, enhanced oversight mechanisms, and the adoption of modern voting systems to ensure transparency, fairness, and timely elections.
Source: Edurev
Importance of Municipal Elections:
- Democratic Significance:
- Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections ensure smooth power transitions.
- Municipal elections, crucial for local governance, face persistent challenges.
- Supreme Court’s Observations:
- Chandigarh mayoral election judgement highlights broader reform needs.
- Municipal elections require as much attention as state and national polls.
- Local Governance Impact:
- Efficient municipal elections ensure effective grassroots governance.
- Timely elections promote accountability and community engagement.
- Comparison with State Elections:
- Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections are well-coordinated democratic exercises.
- Municipal elections often face administrative and procedural hurdles.
- Public Participation:
- Local elections provide citizens with a direct voice in governance.
- Empowering municipalities strengthens democratic foundations.
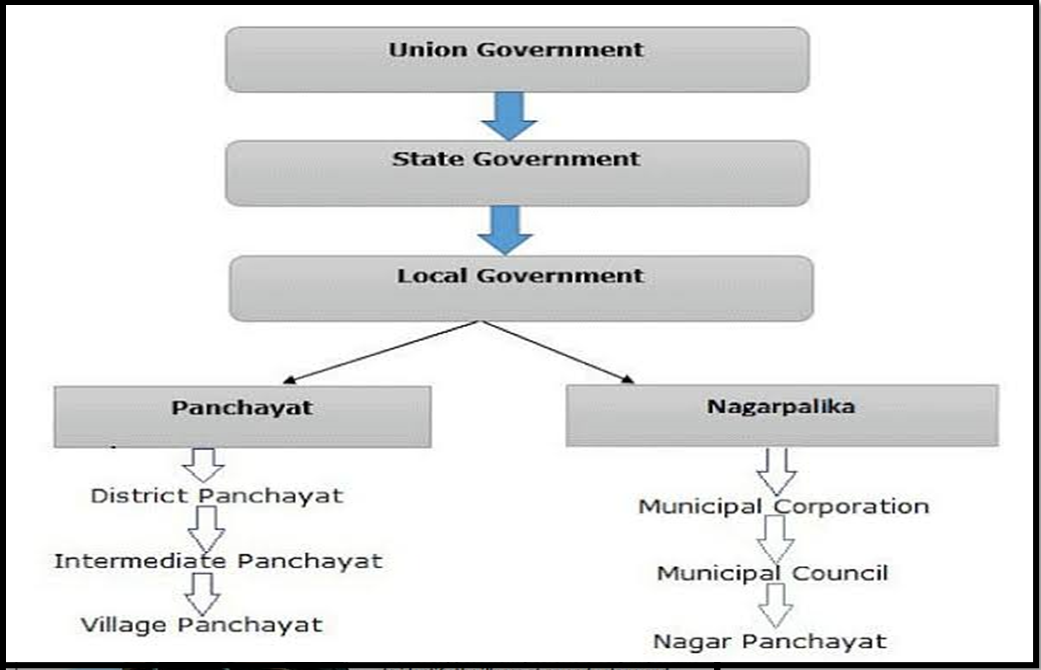
| Evolution of Municipalities in Post-Independence India:
Introduction of 65th Constitutional Amendment Bill (Nagarpalika Bill): · Introduced in Lok Sabha, August 1989. · Aimed to strengthen and revamp municipal bodies. · Not passed by Rajya Sabha during Rajiv Gandhi’s government. Transformation into 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992: · Evolved from the 65th Constitutional Amendment Bill. · Came into force on 1 June 1993. · Occurred during P.V. Narasimha Rao’s prime ministership. Ministries Handling ‘Urban Local Government’: · Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs: States. · Ministry of Defence: Cantonment boards. · Ministry of Home Affairs: Union Territories. Key Objectives of the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act: · Revitalize and strengthen urban governments. · Enhance functionality as “units of local government”. Significance of the Act for Municipalities: · Introduced Part IX A ‘The Municipalities’ – Article 243 P to Article 243 ZG. · Added Twelfth Schedule with 18 functional items under Article 243-W. · Granted constitutional status to municipalities, making it justiciable. · Mandated State governments to adopt the new municipal system as per the Act’s provisions. |
Timeliness And Constitutional Mandate Of Municipal Elections:
- Constitutional Mandate:
- Article 243U of the 74th CAA mandates timely municipal elections.
- Elections should be conducted before the expiration of the urban local government’s term.
- Janaagraha’s Study Findings:
- Over 1,400 municipalities lacked elected councils by September 2021.
- Persistent delays undermine constitutional principles.
- CAG Audit Insights:
- 1,500 municipalities lacked elected councils from 2015-2021.
- Timely elections are essential for maintaining governance continuity.
- Major City Delays:
- Chennai Corporation had a six-year gap between elections.
- Mumbai and Bengaluru are awaiting elections post their council terms.
- Constitutional Adherence:
- Supreme Court’s emphasis on the inviolability of election timings.
- State governments need to prioritize municipal election timelines.
Delays and Inefficiencies:
- Council Formation Delays:
- In Karnataka, 214 urban local governments faced a 26-month delay post the 2018 elections.
- Chandigarh’s delay was comparatively minimal at 12 days.
- Mayoral and Committee Election Delays:
- Significant delays observed in constituting mayoral and deputy mayoral positions.
- Standing committees faced prolonged election delays in various municipalities.
- Manual Ballot System Challenges:
- Potential for errors and inefficiencies with manual ballot processes.
- Modernizing election methods can streamline the election process.
- Conflict of Interest Concerns:
- Discretion of officials in identifying presiding officers raises conflict of interest issues.
- Ensuring independent presiding officers can enhance election credibility.
- Reform Roadmap Requirement:
- Timely, free, and fair election reforms are crucial.
- Standardizing mayoral terms can alleviate frequent election challenges.
Role of State Election Commissions (SECs):
- Constitutional Mandate Clarity:
- Articles 243K and 243ZA empower SECs for election preparation and conduct.
- SECs enjoy an equivalent status to the Election Commission of India for panchayat and urban local government elections.
- Empowerment Gap:
- Only 11 States empower SECs for ward delimitation.
- SECs need broader empowerment to ensure efficient election management.
- Potential SEC Responsibilities:
- SECs can play a pivotal role in mayoral, deputy mayoral, and standing committee elections.
- Expanding SEC responsibilities can streamline election processes.
- SECs vs. State Governments:
- SECs’ role and empowerment are crucial for transparent elections.
- State governments’ reluctance necessitates enhanced SEC involvement.
- Comparison with Election Commission of India:
- SECs should enjoy similar stature and powers as the Election Commission of India.
- Strengthening SECs can ensure consistent and fair municipal elections.
Potential for Expanded SEC Role:
- Chandigarh Case Implications:
- The Chandigarh incident highlights the need for SEC involvement in mayoral elections.
- Clearer guidelines and policies can prevent election delays and disputes.
- Dual Role of Mayors:
- Municipal mayors handle both legislative and administrative roles.
- Efficient election processes are crucial for mayoral effectiveness and accountability.
- State Governments’ Reluctance:
- Strengthening SECs requires overcoming State governments’ resistance.
- Supreme Court intervention may be necessary to prioritize municipal elections.
- Standardization Needs:
- Inconsistent mayoral terms across cities underscore the need for standardization.
- Five-year mayoral terms can ensure stability and effective governance.
Challenges and Inefficiencies in Election Procedures:
- Arbitrary Election Scheduling:
- Government officials have unchecked authority to set election dates.
- Lack of standardized guidelines leads to inconsistent election timelines.
- Arbitrary election schedules can disrupt local governance and public trust.
- State Government Influence on Election Timing:
- State governments may delay elections for political advantage.
- Political motives can overshadow genuine election needs.
- Delayed elections result in prolonged administrative vacancies.
- Conflict of Interest in Presiding Officer Selection:
- Officials choosing presiding officers may have biases.
- Transparent selection criteria are often lacking.
- Biased officer selection can compromise election integrity.
- Limitations of Manual Voting Processes:
- Manual voting is time-consuming and error-prone.
- Manual counting leads to inconsistencies and delays.
- Outdated methods hinder technological election advancements.
- Transparency Issues in Council Constitution and Key Positions Election:
- Ambiguous election procedures lead to inconsistencies.
- Lack of clear guidelines results in unfair practices.
- Transparency gaps erode public trust in the election process.
Way Forward :
- Standardized Election Guidelines:
- Implement uniform guidelines for scheduling municipal elections.
- Ensure regular and timely elections to uphold democratic principles.
- Enhanced Oversight Mechanism:
- Establish independent bodies to oversee election scheduling.
- Reduce political influence on election timings to ensure fairness.
- Transparent Presiding Officer Selection:
- Introduce clear and transparent criteria for selecting presiding officers.
- Ensure impartiality and fairness in the officer selection process.
- Adoption of Electronic Voting Systems:
- Transition from manual voting to electronic systems for efficiency.
- Implement secure and reliable technology to minimize errors.
- Clear Election Procedures and Regulations:
- Develop comprehensive and transparent election procedures.
- Provide training to officials to ensure adherence to established rules.
- Strengthening State Election Commissions:
- Empower State Election Commissions (SECs) with greater authority.
- Enhance SECs’ role in municipal elections for better oversight.
- Public Awareness and Engagement:
- Conduct public awareness campaigns about the importance of timely elections.
- Encourage citizen participation to foster accountability and transparency.
Conclusion ;
Enhancing municipal election transparency and efficiency is imperative. Collaborative efforts between SECs, state governments, and the judiciary can pave the way for comprehensive reforms.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the challenges and inefficiencies faced in the conduct of municipal elections in India. Examine the implications of delayed elections and the role of State Election Commissions to ensure transparency, fairness, and timely elections.