Cloud Seeding
Why in the news?
- IITM Pune demonstrates cloud seeding can produce rainfall.
- The experiment is the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX phase-4).
- The cloud seeding experiment was performed in Solapur City, on the leeward side of the Western Ghats. Resulted in increased rainfall by 18%.
- The relative enhancement of accumulated rainfall was seen over two hours after seeding the clouds.
Cloud Seeding
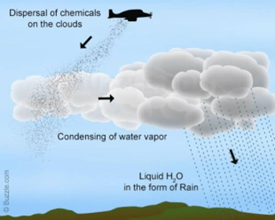
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique used to enhance precipitation in regions facing water scarcity or drought. It involves the introduction of certain substances into clouds to promote rain or snow.
- Pilot Projects in India: India has initiated cloud seeding programs in various states like Karnataka, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana to address water shortages, particularly in rain-shadow areas.
- Technology and Method: Cloud seeding typically employs the dispersal of substances such as silver iodide or calcium chloride into clouds to encourage the formation of ice crystals and subsequent precipitation.
- Aim of Cloud Seeding in India: The primary goal of cloud seeding in India is to increase rainfall and snowfall in regions with deficient water resources, especially during the monsoon season.
- Positive Outcomes: Cloud seeding experiments have shown promising results in some areas. For example, Solapur in Maharashtra witnessed an 18% relative enhancement in rainfall during pilot projects, alleviating water scarcity.
- Challenges and Controversies: Cloud seeding is not without challenges and concerns. Some critics question its effectiveness and potential environmental impacts. The success of cloud seeding largely depends on weather conditions and cloud characteristics.
- Government Initiatives: Various state governments have collaborated with organizations specializing in weather modification to carry out cloud seeding programs, and the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) is involved in monitoring and research.