CHINA’S MILITARY AMBITIONS
Relevance: GS 2 – India and its neighbourhood – relations; Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Why in the News?
- China’s annual parliamentary meetings provide insights into its future direction.
- Despite economic challenges, a significant observation this year is the ongoing rise in defense expenditure.
- This marks the third consecutive year of substantial increases in China’s defense budget.
- It’s notable that China’s actual military spending surpasses publicly disclosed figures.
Two Sessions Significance
- China’s “two sessions” consisting of the National People’s Congress and the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference are pivotal for assessing the nation’s future trajectory.
- Despite economic challenges, China aims for a 5% growth target in the coming year.
- Notably, amidst economic uncertainties, China plans to increase national defense spending by over 7%.
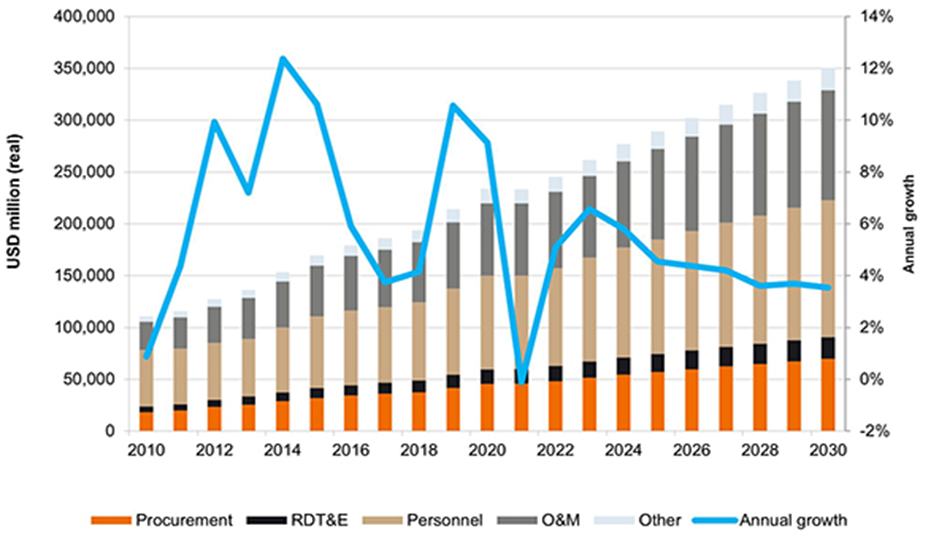
Defence Spending Trends
- This marks the third consecutive year of substantial increases in China’s defense budget.
- China’s actual military expenditure significantly exceeds publicly disclosed figures.
- According to US Senator Dan Sullivan, China’s defense spending is estimated to be close to $700 billion, nearly three times its official statistics.
President Xi’s Military Ambitions
- President Xi Jinping’s vision includes building a world-class military by 2027, coinciding with the centenary of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA).
- Xi’s Strategic Direction
- Xi, as the supreme commander of the armed forces and head of the Central Military Commission, recalibrates defense strategy during the parliamentary sessions.
- He emphasizes the need to enhance PLA capabilities in cyberspace, space, and artificial intelligence (AI), while preparing for potential maritime conflicts.
Corruption in Defence Spending
- Despite significant allocations to the defense establishment, Chinese state media reports reveal widespread mismanagement.
- Glaring shortcomings were identified in Rocket Force units responsible for both conventional and nuclear missiles.
- US intelligence assessments highlight graft within the PLA and its military-industrial complex, leading to compromised defense preparedness, such as missiles being filled with water instead of fuel.
- Combat Capability and Anti-Graft Measures
- Chinese military leaders pledge to address inflated combat capabilities, seen as a reference to corruption within the ranks.
- Efforts to combat graft and improve military efficiency are evident in directives from the top leadership.
- Consequences and Reforms
- The revelation of mismanagement has led to significant repercussions within the military and political spheres.
- Senior technocrats within the military-industrial complex have been removed from their positions.
- Top military figures have lost their seats in legislative and deliberative bodies, indicating a substantial shake-up within the leadership.
Party Leadership and Accountability
- The Communist Party of China’s top leadership has witnessed changes, with the disappearance of former defense minister Li Shangfu and former foreign minister Qin Gang from public view.
- There’s a heightened narrative on financial misconduct in China, prompting warnings from the PLA’s official newspaper regarding corruption among soldiers and officers.
- Government Response and Initiatives
- President Xi Jinping has ordered rigorous scrutiny of top bureaucrats’ activities, emphasizing accountability and transparency.
- The Central Military Commission (CMC) has intervened, urging arms-acquisition and research units within the PLA to prioritize quality control to meet Xi’s objective of defense modernization.
Implications for External Power Projection
- Increased defense spending and warnings of naval contestation by China coincide with frequent activities of Chinese research vessels in the Indian Ocean and assertive territorial claims along various borders.
- The purge within the PLA and defense-industrial establishment, though initially viewed with Schadenfreude, reflects Xi’s commitment to rooting out corruption, potentially enhancing China’s long-term strategic capabilities.
Focus on Cyber and AI Capabilities
- Xi’s emphasis on improving PLA’s capabilities in cyberspace and AI signifies a shift in China’s strategic approach.
- The establishment of the Strategic Support Force (SSF) underscores China’s modernization efforts, enabling it to project military power beyond its borders through cyber, electronic, and psychological operations.
Comprehensive National Strength
- Chinese strategists advocate for building comprehensive national strength to prepare for protracted warfare, emphasizing non-military factors like science and technology.
- They anticipate military threats supplemented by non-military elements such as cyber attacks and economic coercion, necessitating awareness among Indian policy-makers.
Cyber Espionage and Data Manipulation
- Recent revelations of leaked documents from hacking groups with ties to the Chinese establishment highlight systematic efforts to gather data through cyber infiltrations.
- China’s utilization of data as a strategic asset is exemplified by targeted hacking campaigns aimed at collecting sensitive information from various countries, including India.
- Analysts warn that China’s data harvesting activities could provide strategic advantages in potential conflicts, such as accessing information on key infrastructure in Taiwan.
Challenges for India
- Geopolitical and Security Challenges:
- India faces heightened tensions and potential military confrontations along its borders, particularly with China.
- The assertive stance of China in territorial disputes, such as along the Indian border and in the South China Sea, poses significant challenges to India’s security and territorial integrity.
- Cybersecurity Threats:
- The rise of China’s Strategic Support Force (SSF) and its emphasis on cyber capabilities present India with increased cybersecurity threats.
- India must be vigilant against cyber espionage, data theft, and potential cyber attacks from state-sponsored actors.
- Strategic Competition:
- China’s efforts to enhance its strategic capabilities, including in areas such as artificial intelligence and advanced weaponry, intensify strategic competition in the region.
- India must adapt its defense and security strategies to effectively counter China’s growing military prowess and technological advancements.
- Diplomatic Challenges:
- India must navigate complex diplomatic relations with China while safeguarding its national interests.
- Balancing economic ties with China against security concerns and asserting its stance on territorial disputes requires adept diplomacy and strategic decision-making.
- Economic and Technological Competition:
- China’s advancements in technology and its growing influence in global markets pose economic and technological challenges for India.
- India needs to invest in innovation, research, and development to remain competitive and mitigate dependence on Chinese technology and investment.
- Internal Stability and Unity:
- To effectively address external challenges, India must prioritize internal stability and unity.
- Ensuring social cohesion, addressing internal conflicts, and promoting inclusive development are essential for India to strengthen its position vis-à-vis external adversaries.
Source: https://www.financialexpress.com/opinion/chinas-military-ambitions/3424533/
Mains question
Discuss the strategic implications of China’s increased defense spending and territorial assertiveness on India’s security and diplomatic posture. (250 words)