CHARTING A PATH FOR THE POPULATION COMMITTEE
Relevance: GS 1 – Population and associated issues
Why in the News?
- The interim Budget unveiled plans for a “high-powered committee” to address challenges stemming from rapid population growth and demographic shifts.
- The announcement signifies a proactive step towards addressing critical societal concerns.
- Key areas of focus include family planning, maternal and child health, education, employment, and socio-economic development in India.
Mandate and Goals
- The committee’s mandate is to provide recommendations aligned with the objective of ‘Viksit Bharat’ regarding population challenges.
- Its focus includes formulating policies and strategies for managing population growth and addressing related issues such as family planning, maternal and child health, education, employment, and socio-economic development.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: The committee must adopt an interdisciplinary approach, drawing expertise from fields like demography, public health, economics, sociology, and
- Research and Analysis: Rigorous research, data analysis, and monitoring of demographic trends are crucial for identifying emerging issues and evaluating the effectiveness of existing interventions.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Collaboration with various stakeholders, including government agencies, NGOs, civil society groups, academia, and the private sector, is essential for fostering partnerships and enabling collective action.
- Policy Formulation and Implementation: The emphasis should be laid on public awareness and education campaigns to empower individuals and communities with accurate information and resources for responsible family planning practices and improved health outcomes.
- International Collaboration: Facilitating international collaboration and the exchange of best practices in population management should be a focus area for the committee.
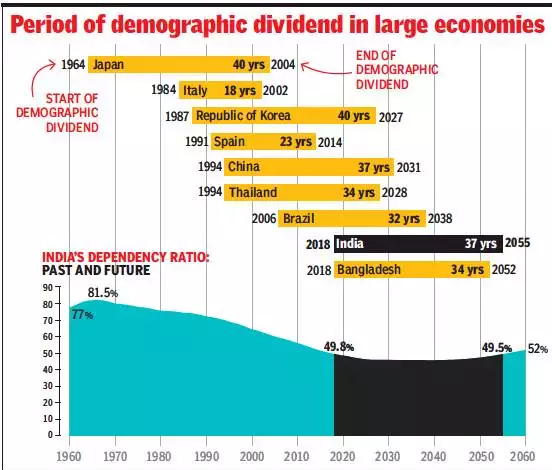
INDIA’S DEMOGRAPHIC LANDSCAPE
Shifts in India’s demographic landscape include women having fewer children, an increase in the working-age population, and steady growth in the elderly population.
- These changes have led to a decrease in the dependency ratio, contributing to economic growth.
Population Projections
- United Nations projections indicate that India’s population is expected to reach 1.46 billion by 2030, representing 17% of the world’s projected population.
- While population growth was rapid until the 1970s, fertility rates have since declined steadily, with the Total Fertility Rate (TFR) expected to reach 1.73 by 2031-35 from 2.5 in 2009-11.
- Demographic Transition: India is undergoing a demographic transition marked by a decreasing proportion of the child population and an increasing proportion of the working-age population.
- Positive trends are observed in life expectancy projections for India, with both female and male life expectancies expected to rise.
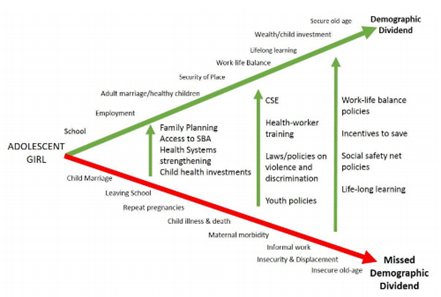
Demographic Dividend
- The demographic dividend, resulting from lower fertility rates and a larger working-age population, offers the potential for accelerated economic growth per capita.
- The rise in the working-age population presents India with an opportunity to capitalize on its demographic advantage for economic growth and development.
- Realizing this potential requires investments in health, education, and skill development.
- Investment in Human Capital
- Maximizing the benefits of a favourable age distribution necessitates investments in human capital development.
- Initiatives include job creation, integration of the informal sector with the formal sector, and empowerment of the female labour force.
- Inclusive Development
- Addressing gender disparities, improving access to education and healthcare, and promoting family planning practices are vital for inclusive and sustainable development.
HEALTH, EDUCATION, EMPLOYMENT CHALLENGES
Ensuring access to quality healthcare and education for all segments of the population is a significant challenge in India’s demographic landscape.
Healthcare
- Public spending on healthcare has remained at around 1% of GDP, highlighting the need for policies prioritizing health promotion and increased funding for health infrastructure.
- Primary Healthcare: Initiatives to strengthen primary healthcare, particularly in rural areas, have shown positive results, including improved child and maternal healthcare and higher life expectancy rates.
- Persisting Challenges: especially concerning nutritional deprivation among children, leading to hunger insecurity and hindering physical and cognitive development.
- Addressing challenges entails coordinating efforts to guarantee access to vital commodities, execute nutrition programs tailored to vulnerable populations, and enhance water availability and sanitation.
Education and Skill Development
Investments in education and skill development are crucial to realize India’s demographic dividend.
- Projected Skills Gap: UNICEF estimates that nearly 47% of Indian youth may lack the necessary education and skills for employment by 2030.
- Impact of COVID-19: The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated challenges, with over 250 million children forced out of school, causing significant setbacks in learning outcomes.
- Mitigating Measures: Increased investment in nutrition and early childhood education is crucial, including the inclusion of pre-primary education in the Right to Education Act.
- Developing adaptable curricula and involving parents, communities, and stakeholders in advocating for early childhood education are crucial steps to enhance outcomes.
- Alignment with Industry Requirements: It is essential to make efforts to narrow the disparity between current skill development initiatives and industry demands to mitigate unemployment and boost productivity.
EVIDENCE-BASED DECISION MAKING
Promoting gender equality and social inclusion is essential for realizing India’s demographic potential and achieving inclusive and sustainable development.
By adopting a holistic approach to population management and prioritizing investments in health, education, employment, and statistical systems, India can address its demographic challenges effectively.
Data Availability
- India faces significant challenges in obtaining current and reliable data on its population, hindering evidence-based policymaking.
- Measures for Improvement: The population committee must prioritize enhancements in data collection methodologies, technology adoption, capacity building, and collaboration with stakeholders.
- Implementing rigorous validation and quality assurance mechanisms is crucial to ensure the reliability and accuracy of population data.
- Independent audits, data validation exercises, and peer review processes can help identify and rectify data errors and inconsistencies.
- The committee should explore the feasibility of incorporating such quality assurance methods within the statistical system to enhance data reliability.
Modernizing Data Infrastructure
- India needs to invest in modernizing its data infrastructure, which includes establishing robust systems for data collection, management, and analysis.
- Upgrade Data Collection Methods and adopting digital technologies for data processing are essential components of modernization efforts.
- Ensure Data Security and Privacy: It is crucial to ensure data security and privacy while modernizing data infrastructure.
Importance of National Censuses and Surveys
- Regular and comprehensive national censuses and surveys are vital for collecting demographic data accurately.
- Priority on Timely Execution: India should prioritize the timely and accurate execution of national censuses and surveys, ensuring coverage of all population segments, including marginalized and hard-to-reach populations.
Promoting Open Data Initiatives
- Promoting open data initiatives and transparency in data sharing is another promising approach to facilitate access to population data for researchers, policymakers, and the public.
- Making population data freely available in standardized formats promotes data reuse, transparency, and accountability.
Collaboration with International Organizations
- Collaborating with international organizations such as the United Nations Population Division, World Bank, and academic institutions can provide access to global best practices, technical expertise, and funding opportunities for population data collection and analysis.
Thus, with strategic planning, effective implementation, and international collaboration, India can navigate its demographic transition to emerge as a global leader in inclusive and sustainable development.
Mains question
Discuss the challenges and strategies for India’s Population Committee in navigating demographic shifts. Evaluate the holistic approaches in navigating such shifts. (250 words)