CHANGE IN THE VALLEY
Syllabus:
GS 2 :
- Indian Constitution—
Historical Underpinnings, Evolution, Features, Amendments, Significant Provisions .
- Issues and Challenges Pertaining to the Federal Structure.
Why in the News?
- Prime Minister’s recent visit to Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) marked a significant milestone, being his first since the abrogation of Article 370.
- This visit provided an opportunity to assess the region’s situation beyond the lens of terrorism-related incidents, enabling a more balanced examination.
Focus:
- Various dimensions – political, military, social, economic, psychological, and diplomatic – warrant examination to understand the nuanced landscape of J&K.
Psychological Domain:
- Psychological aspects hold paramount importance due to the prolonged external turmoil sponsored by Pakistan.
Source: Bt
- Since 1989, Pakistan has orchestrated a “proxy war” aiming to annex J&K, leading to internal turmoil and external meddling.
- The aftermath of the abrogation of Article 370 witnessed a notable shift in mindset from ‘Kashmir banega Pakistan’ to ‘PoJK banega Hindustan’, reflecting a changing narrative.
- Despite this progress, remnants of a dual mindset persist, underscoring the need for sustained efforts towards normalization.
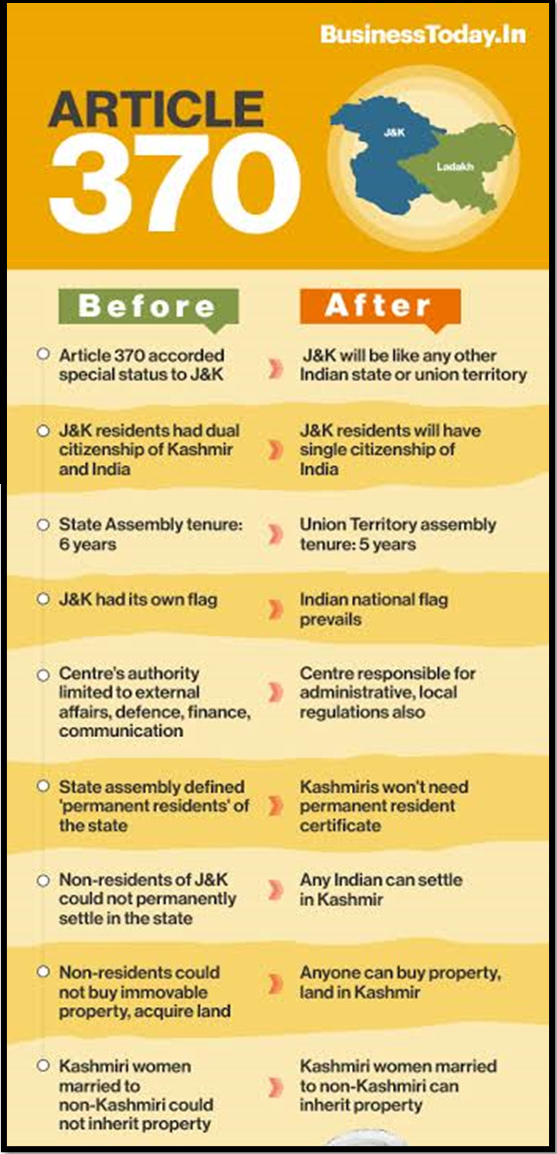
| Understanding Article 370
Special Status to Jammu and Kashmir: · Article 370 granted special status to the disputed region of Jammu and Kashmir in the Indian constitution. · The region was contested by India, Pakistan, and China. Drafting and Inclusion: · Drafted by N Gopalaswami Ayyangar, a member of the Constituent Assembly of India. · Added to the constitution as a ‘temporary provision’ in 1949. Autonomy and Provisions: · Provided Jammu and Kashmir with its own constitution, flag, and autonomy over most matters. · Exceptions included defence, foreign affairs, and communications, which remained under the jurisdiction of the Indian government. Basis: · Based on the terms of the Instrument of Accession signed by the ruler of Jammu and Kashmir, Hari Singh, in 1947. · The accession occurred after an invasion by Pakistan, leading to Jammu and Kashmir joining India. |
Evolution of Strategy:
- The strategic approach towards winning hearts and minds (WHAM) has evolved significantly since 1997.
- Previously, WHAM lacked a structured approach, with only military involvement; however, over time, a holistic approach involving various government departments has emerged.
- Prime Minister Modi’s emphasis on socio-economic development has instilled hope and countered Pakistan’s narrative, especially amidst economic turmoil.
- Direct rule from Delhi, facilitated by a committed Lieutenant Governor, has strengthened grassroots connections, enhancing governance and outreach.
Youth and Women Empowerment:
- Youth and women empowerment have emerged as vital components of the strategy, effectively addressed through social media engagement and outreach programs.
- Leveraging the Army’s experience, an integrated approach has been adopted, reducing direct involvement while enhancing effectiveness.
- Articulate youth leaders have emerged as patriotic voices, effectively managing aspirations and contributing to the region’s development.
Symbolism and Vision:
- Symbolic references made by the Prime Minister during his visit, including mentions of Mahashivratri, Ramzan, and Kashmir’s lotus emblem, signify integration and inclusivity.
- Emphasis on Kashmir’s participation in the G20 process and the tourism sector underscores India’s vision for international engagement and economic growth.
- Acknowledgment of ongoing challenges amidst progress underscores the importance of a nuanced approach towards addressing complex issues.
Changes After Abrogation of Article 370:
Scheduled Tribe Representation:
- Political reservation granted to the Scheduled Tribe community in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Scheduled Tribe representatives elected in DDC and BDC elections.
3-tier system of democracy
- Establishment of a 3-tier system of grassroot democracy through Panchayati Raj Institutions and Development Councils.
Election Conduct:
- Elections for Panches, Sarpanches, Block Development Councils, and District Development Councils ensure democratic representation.
Dalit Rights and Domicile:
- Thousands of dalits granted their rights and domicile status.
- More than 60,000 West Pak refugees also received rights and domicile.
Recognition of Backward Classes:
- Commission formed to identify socially and economically backward classes.
- Communities like Pahari Padri and Gaddi Brahmin recommended for Scheduled Tribe status.
OBC Recognition:
- OBC community identified for the first time, ensuring constitutional rights.
- Deprived OBC regions in Jammu and Kashmir granted their rights.
Domicile for PoJK Displaced:
- PoJK Displaced community, previously denied domicile status for 70 years, now recognized.
- Over 25,000 domiciles issued to this community.
Women’s Rights:
- Women, regardless of religion, granted freedom and rights even if married outside the state.
Democratic Representation:
- Democracy was established at every level with DDC, BDC, and Gram Sabha elections.
Constitutional Implementation:
- All provisions of the Constitution, including 890 related to public welfare, implemented.
- Acts like the Indian Penal Code, Persons with Disabilities Act, and National Commission for Safai Karamcharis Act now enforced in Jammu and Kashmir.
Continuing Concerns:
- Despite significant strides, challenges persist, particularly in dealing with Pakistan’s commitment to foment separatism and sponsored terrorism.
- Ideological extremism continues to pose threats, both locally and in a global context, necessitating vigilance and proactive measures.
- Caution should be exercised in engaging with Pakistan, avoiding premature talks that may inadvertently elevate its significance on the international stage.
Conclusion:
The Prime Minister’s recent visit to J&K signifies a decisive departure from the past, emphasizing a forward-looking approach focused on integration, development, and stability. Despite achievements, the journey ahead requires concerted efforts towards preserving military structures and concepts while prioritizing holistic development and security. J&K’s rightful place in India’s narrative is contingent upon sustained progress in addressing socio-economic disparities, fostering grassroots connections, and ensuring peace and stability in the region.
Source: Indian Express
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the significant changes witnessed in Jammu and Kashmir post the abrogation of Article 370. Evaluate the impact of these changes on the region’s socio-economic, political, and psychological landscape.