CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES IN TRANSITION TO ELECTRIC VEHICLES
Why in the news?
- Global EV sales were 14 million in 2023, but adoption rates are lower than needed for climate goals.
- Major EV markets: China, Europe, and the US, account for 95% of sales.
- Countries like Norway and Sweden show high EV adoption, while others lag.
India’s EV Strategy:
- India’s EV sales are growing but are still low compared to global rates.
- Proposed realistic goal: 50% EV adoption by 2040, alongside renewable energy grid transformation.
- GST rates favour EVs (5%) over hybrids and ICE vehicles (28%), but policy needs uniformity to avoid market distortion.
source:slideshare
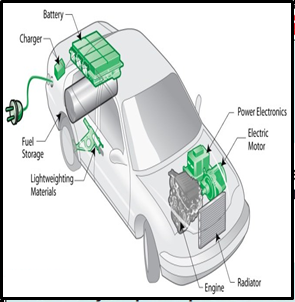
What are Electric Vehicles?
Types:
EV Policies in India:
|