“CHABAHAR PORT: A STRATEGIC HUB”
Syllabus:
- GS-2 : India and its bilateral relations with other countries ,Enhancing trade and security in the region
Focus :
- The focus of the article is on the strategic importance of Chabahar Port for India, tracing its historical context, diplomatic initiatives, and geopolitical challenges.
- It highlights India’s efforts to develop the port as an alternative trade route to Afghanistan, despite obstacles such as US sanctions and competition from China.
Historical Context:
- Before Partition, Chabahar (earlier known as Tiz) was situated in Iran’s Sistan Baluchistan province.
- It was strategically located between the Gulf of Oman and the Strait of Hormuz.
- The town had cultural ties with India, where Panchatantra was once read in Persian.
Early Attempts at Development:
- In 1970, the Shah of Iran envisioned developing Chabahar, considering its strategic location.
- However, ties between independent India and Iran were not close due to geopolitical factors.
- Efforts to develop Chabahar gained momentum in the 1990s and early 2000s.
Diplomatic Initiatives:
- In 1993, Prime Minister Narasimha Rao’s visit to Tehran laid the groundwork for closer ties.
- Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee’s visit in 2001 and President Mohammad Khatami’s visit to Delhi in 2003 sealed the Chabahar deal.
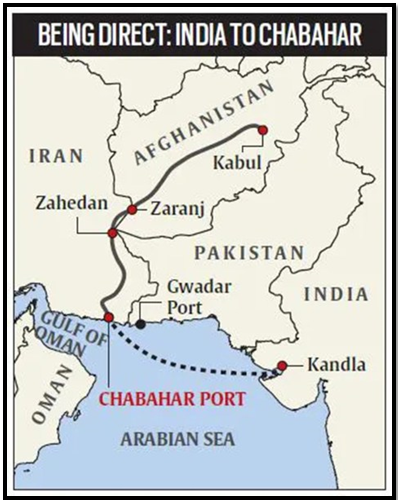
Strategic Importance:
- Chabahar’s location provided India with an alternative trade route to Afghanistan, bypassing Pakistan
- India initiated the construction of Route-606 (Zaranj-Delaram Highway) to facilitate trade with Afghanistan.
- The port became a hub of connectivity, offering immense strategic potential.
Geopolitical Challenges:
- India’s progress in Chabahar was hindered by US sanctions against Iran.
- China’s maritime forays in the Indian Ocean posed competitive challenges.
- Despite obstacles, India continued its engagement with Chabahar, sending its first shipment in 2012.
Source - IE
Evolving Partnerships:
- In 2016, India signed an agreement with Iran to invest $500 million in Chabahar’s development.
- However, US withdrawal from the JCPOA in 2018 led to renewed sanctions against Iran.
- India faced pressure to reduce oil imports from Iran but maintained its commitment to Chabahar.
Recent Developments:
- Despite challenges, Chabahar handled significant cargo traffic, including aid for Afghanistan.
- India recently signed a 10-year contract with Iran to further develop the port, signaling its long-term commitment.
- The project aims to build 32 jetties and process 82 million tonnes of cargo per year by the end of the fourth phase.
Future Prospects:
- The US has raised concerns about sanctions against Indian companies participating in the project.
- However, India’s interest in Chabahar remains steadfast, driven by its strategic importance and long-term goals.
- Despite delays, Chabahar’s development is irreversible, reflecting its enduring geopolitical
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question :
GS-2
“Discuss the strategic significance of Chabahar Port for India and its evolving partnerships with Iran, considering the geopolitical challenges and recent developments.” (250 words)