CERVICAL CANCER AWARENESS
Focus :
WHO’s Cervical Cancer Elimination Strategy (2022).
- Goals: 90% HPV-vaccinated girls by 2030, 70% women screened (35-45 years), 90% with cervical lesions treated.
- Despite India’s unlikely achievement of 2030 targets, there’s a decline in incidence, possibly due to various factors.
Source : Cleveland clinic
About Cervical Cancer:
- Origin: Develops in a woman’s cervix.
- Global Ranking: 4th most common cancer in women worldwide.
- Indian Ranking: 2nd most common cancer among Indian women.
- India’s Contribution: Highest share of global cervical cancer burden.
- Lancet Study: Almost 1 in 4 global cervical cancer deaths linked to India.
- Cause: 99% of cases linked to high-risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
- Transmission: HPV transmitted through sexual contact.
- Testing : HPV DNA testing is recommended as the primary screening method, offering higher accuracy and fewer quality issues.
| About Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
A common virus transmitted through sexual contact. Linked to cervical cancer . It often shows no symptoms, making regular screenings crucial. HPV vaccines exist to prevent infections and associated cancers. |

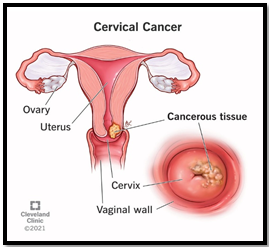 Source : Cleveland clinic
Source : Cleveland clinic

